by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Back Pain, Chiropractic, Chiropractic Examination, Chronic Back Pain, Chronic Pain, Conditions Treated, Functional Medicine, Health, Herniated Disc, Holistic Medicine, Lower Back Pain, Natural Health, Neck Pain, Neck Pain Treatments, Sciatica, Sciatica Nerve Pain, Spinal Decompression Treatments, Spine Care, Treatments, Wellness
Disc bulge and disc herniation are some of the most common conditions affecting the spine of both young and middle-aged patients. It is estimated that approximately 2.6% of the US population annually visits a clinician to treat spinal disorders. Roughly $ 7.1 billion alone is lost due to the time away from work.
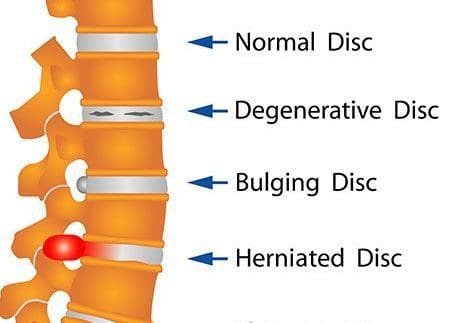
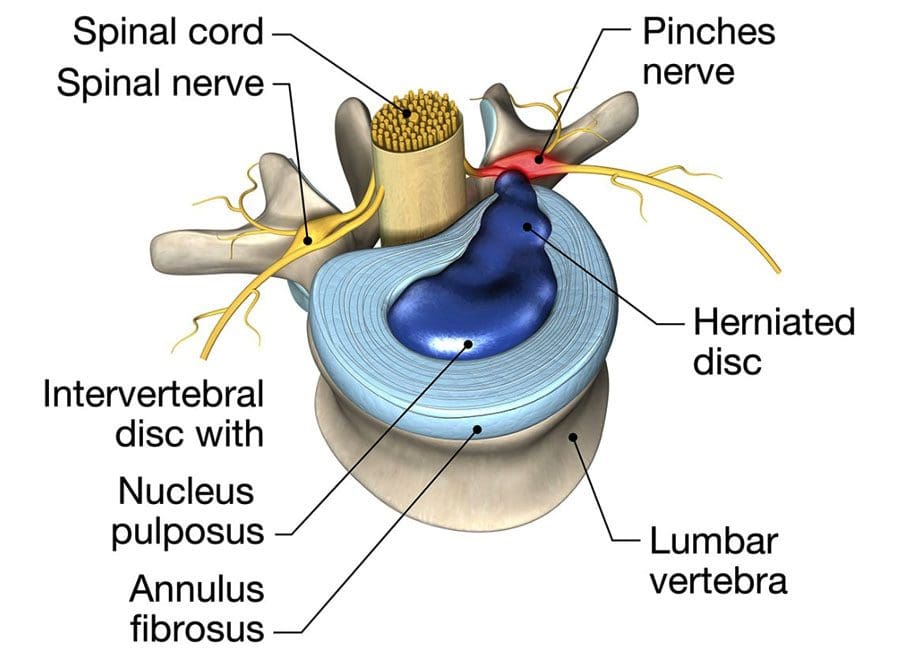
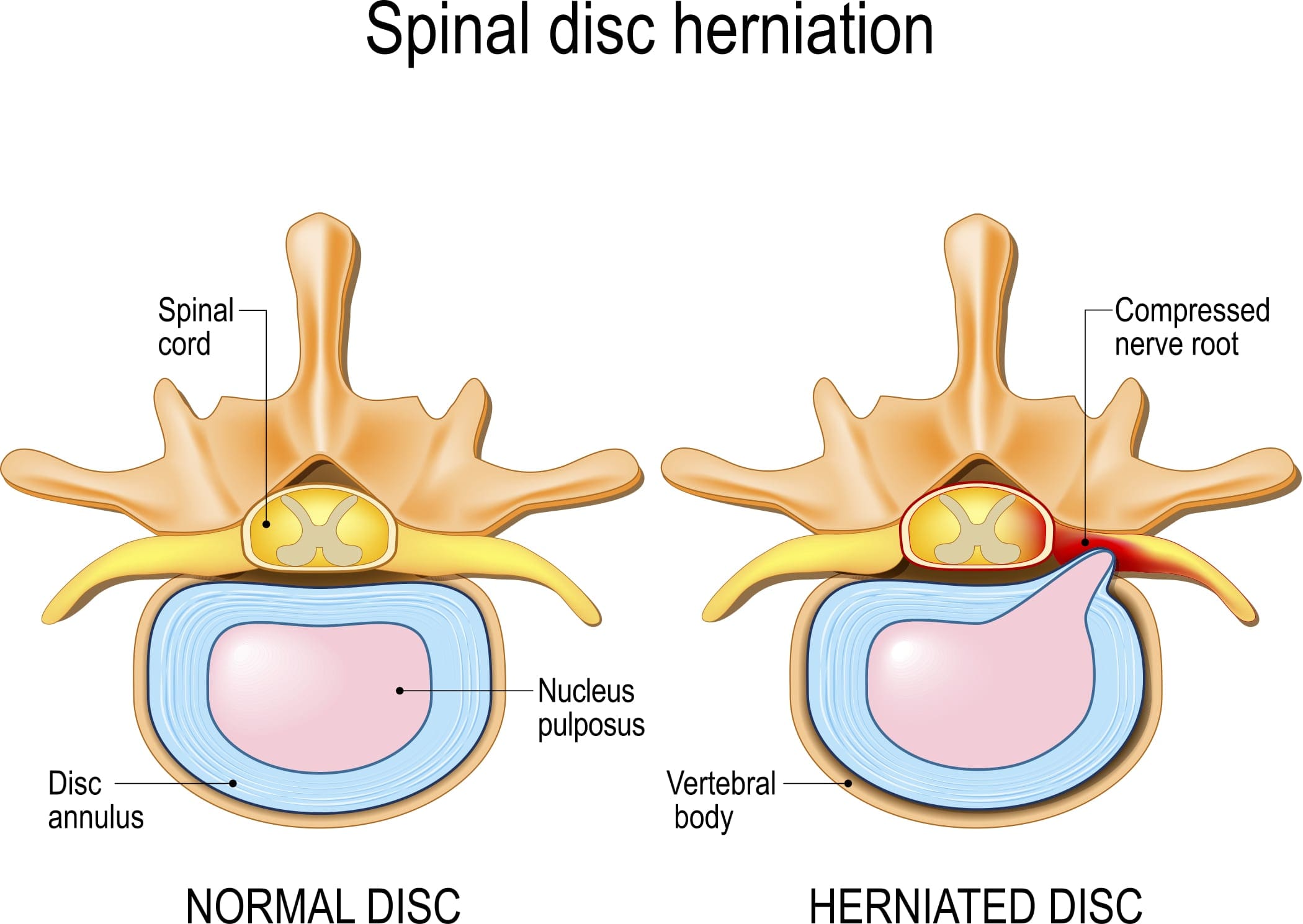
Disc herniation is when the whole or part of the nucleus pulposus is protruded through the torn or weakened outer annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. This is also known as the slipped disc and frequently occurs in the lower back, sometimes also affecting the cervical region. Herniation of the intervertebral disc is defined as a localized displacement of disc material with 25% or less of the disc circumference on an MRI scan, according to the North American Spine Society 2014. The herniation may consist of nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus, apophyseal bone or osteophytes, and the vertebral endplate cartilage in contrast to disc bulge.
There are also mainly two types of disc herniation. Disc protrusion is when a focal or symmetrical extension of the disc comes out of its confines in the intervertebral space. It is situated at the intervertebral disc level, and its outer annular fibers are intact. A disc extrusion is when the intervertebral disc extends above or below the adjacent vertebrae or endplates with a complete annular tear. In this type of disc extrusion, a neck or base is narrower than the dome or the herniation.
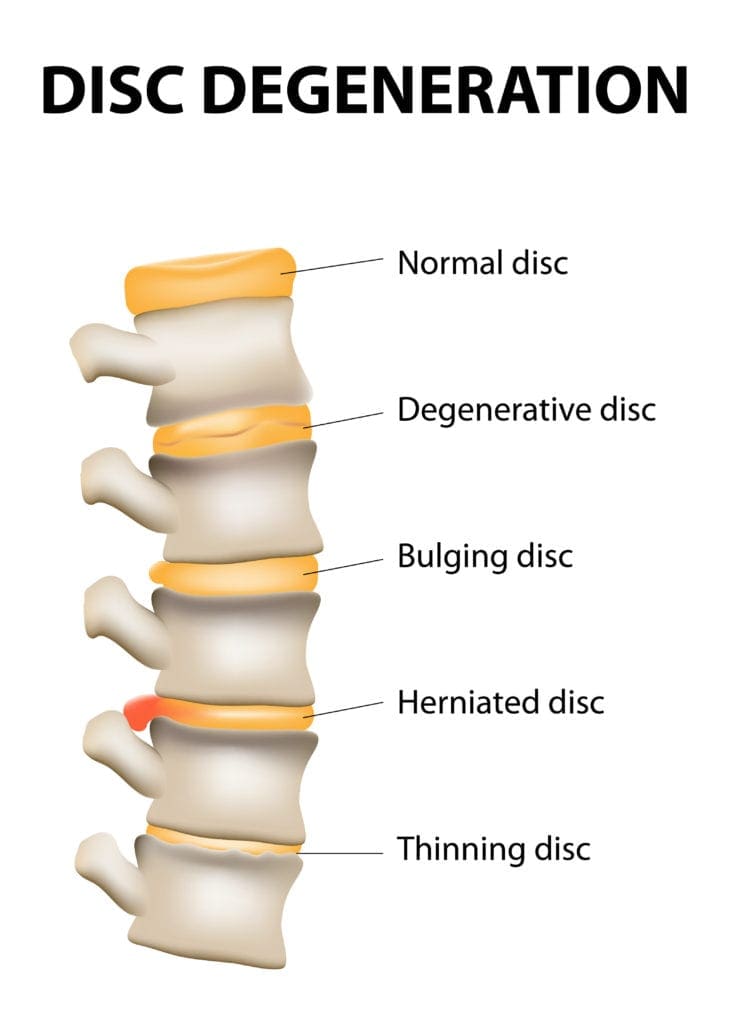
A disc bulge is when the outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus are displaced from the margins of the adjacent vertebral bodies. Here, the displacement is more than 25% of the circumference of the intervertebral disc. It also does not extend below or above the margins of the disc because the annulus fibrosus attachment limits it. It differs from disc herniation because it involves less than 25% of the disc’s circumference. Usually, the disc bulge is a gradual process and is broad. The disc bulge can be divided into two types. In a circumferential bulge, the whole disc circumference is involved. More than 90 degrees of the rim is involved asymmetrically in asymmetrical bulging.
Normal Intervertebral Disc Anatomy
Before going into detail about the definition of disc herniation and disc bulge, we need to look at the standard intervertebral disc. According to spine guidelines in 2014, a standard disc is something that has a classic shape without any evidence of degenerative disc changes. Intervertebral discs are responsible for one-third to one-fourth of the height of the spinal column.
One intervertebral disc is about 7 -10 mm thick and measures 4 cm in anterior-posterior diameter in the lumbar region of the spine. These spinal discs are located between two adjacent vertebral bodies. However, no discs can be found between the atlas and axis and the coccyx. About 23 discs are found in the spine, with six in the cervical spine, 12 in the thoracic spine, and only five in the lumbar spine.
Intervertebral discs are made of fibro cartilages, forming a fibrocartilaginous joint. The outer ring of the intervertebral disc is known as the annulus fibrosus, while the inner gel-like structure in the center is known as the nucleus pulposus. The cartilage endplates sandwich the nucleus pulposus superiorly and inferiorly. The annulus fibrosus comprises concentric collagen fiber sheets arranged in a radial tire-like structure into lamellae. The fibers are attached to the vertebral endplates and oriented at different angles. With their cartilaginous part, the endplates anchor the discs in their proper place.
The nucleus pulposus is composed of water, collagen, and proteoglycans. Proteoglycans attract and retain moisture, giving the nucleus pulposus a hydrated gel-like consistency. Interestingly, throughout the day, the amount of water found in the nucleus pulposus varies according to the person’s level of activity. This feature in the intervertebral disc serves as a cushion or a spinal shock-absorbing system to protect the adjacent vertebra, spinal nerves, spinal cord, brain, and other structures against various forces. Although the individual movement of the intervertebral discs is limited, some form of vertebral motion like flexion and extension is still possible due to the features of the intervertebral disc.
Effect of Intervertebral Disc Morphology on Structure and Function
The type of components present in the intervertebral disc and how it is arranged determine the morphology of the intervertebral disc. This is important in how effectively the disc does its function. As the disc is the most important element which bears the load and allows movement in the otherwise rigid spine, the constituents it is made up of have a significant bearing.
The complexity of the lamellae increases with advancing age as a result of the synthetic response of the intervertebral disc cells to the variations in the mechanical load. These changes in lamellae with more bifurcations, interdigitation and irregular size and number of lamellar bands will lead to the altered bearing of weight. This in turn establishes a self-perpetuated disruption cycle leading to the destruction of the intervertebral discs. Once this process is started it is irreversible. As there is an increased number of cells, the amount of nutrition the disc requires is also increasingly changing the normal concentration gradient of both metabolites and nutrients. Due to this increased demand, the cells may also die increasingly by necrosis or apoptosis.
Human intervertebral discs are avascular and hence the nutrients are diffused from the nearby blood vessels in the margin of the disc. The main nutrients; oxygen and glucose reach the cells in the disc through diffusion according to the gradient determined by the rate of transport to the cells through the tissues and the rate of demand. Cells also increasingly produce lactic acid as a metabolic end product. This is also removed via the capillaries and venules back to the circulation.
Since diffusion depends on the distance, the cells lying far from the blood capillaries can have a reduced concentration of nutrients because of the reduced supply. With disease processes, the normally avascular intervertebral disc can become vascular and innervated in degeneration and in disease processes. Although this may increase the oxygen and nutrient supply to the cells in the disc, this can also give rise to many other types of cells that are normally not found in the disc with the introduction of cytokines and growth factors.
The morphology of the intervertebral disc in different parts of the spine also varies although many clinicians base the clinical theories based on the assumption that both cervical and lumbar intervertebral discs have the same structure. The height of the disc was the minimum in the T4-5 level of the thoracic column probably due to the fact that thoracic intervertebral discs are less wedge-shaped than those of cervical and lumbar spinal regions.
From the cranial to caudal direction, the cross-sectional area of the spine increased. Therefore, by the L5-S1 level, the nucleus pulposus was occupying a higher proportion of the intervertebral disc area. The cervical discs have an elliptical shape on cross-section while the thoracic discs had a more circular shape. The lumbar discs also have an elliptical shape though it is more flattened or re-entrant posteriorly.
What is a Disc Bulge?
The bulging disc is when the disc simply bulges outside the intervertebral disc space it normally occupies without the rupture of the outer annulus fibrosus. The bulging area is quite large when compared to a herniated disc. Moreover, in a herniated disc, the annulus fibrosus ruptures or cracks. Although disc bulging is more common than disc herniation, it causes little or no pain to the patient. In contrast, the herniated disc causes a lot of pain.
Causes for Disc Bulging
A bulging disc can be due to several causes. It can occur due to normal age-related changes such as those seen in degenerative disc disease. The aging process can lead to structural and biochemical changes in the intervertebral discs and lead to reduced water content in the nucleus pulposus. These changes can make the patient vulnerable to disc bulges with only minor trauma. Some unhealthy lifestyle habits such as a sedentary lifestyle and smoking can potentiate this process and give rise to more severe changes with the weakening of the disc.
General wear and tear due to repeated microtrauma can also weaken the disc and give rise to disc bulging. This is because when the discs are strained, the normal distribution of weight loading changes. Accumulated micro-trauma over a long period of time can occur in bad posture. Bad posture when sitting, standing, sleeping, and working can increase the pressure in the intervertebral discs.
When a person maintains a forward bending posture, it can lead to overstretching and eventually weakness of the posterior part of the annulus fibrosus. Over time, the intervertebral disc can bulge posteriorly. In occupations that require frequent and repetitive lifting, standing, driving, or bending, the bulging disc may be an occupational hazard. Improper lifting up of items, and improper carrying of heavy objects can also increase the pressure on the spine and lead to disc bulges eventually.
The bulging intervertebral discs usually occur over a long period of time. However, the discs can bulge due to acute trauma too. The unexpected sudden mechanical load can damage the disc resulting in micro-tears. After an accident, the disc can become weakened causing long-term microdamage ultimately leading to bulging of the disc. There may also be a genetic component to the disc bulging. The individual may have a reduced density of elastin in the annulus fibrosus with increased susceptibility to disc diseases. Other environmental facts may also play a part in this disease process.
Symptoms of Disc Bulging
As mentioned previously, bulging discs do not cause pain and even if they do the severity is mild. In the cervical region, the disease will cause pain running down the neck, deep pain in the shoulder region, pain radiating along the upper arm, and forearm up to the fingers.
This may give rise to a diagnostic dilemma as to whether the patient is suffering from a myocardial infarction as the site of referred pain and the radiation is similar. Tingling feeling on the neck may also occur due to the bulging disc.
In the thoracic region, there may be pain in the upper back that radiates to the chest or the upper abdominal region. This may also suggest upper gastrointestinal, lung, or cardiac pathology and hence need to be careful when analyzing these symptoms.
The bulging discs of the lumbar region may present as lower back pain and tingling feeling in the lower back region of the spine. This is the most common site for disc bulges since this area holds the weight of the upper body. The pain or the discomfort can spread through the gluteal area, thighs, and to the feet. There may also be muscle weakness, numbness or tingling sensation. When the disc presses on the spinal cord, the reflexes of both legs can increase leading to spasticity.
Some patients may even have paralysis from the waist down. When the bulging disc compresses on the cauda equine, the bladder and bowel functions can also change. The bulging disc can press on the sciatic nerve leading to sciatica where the pain radiates in one leg from the back down to the feet.
The pain from the bulging disc can get worse during some activities as the bulge can then compress on some of the nerves. Depending on what nerve is affected, the clinical features can also vary.
Diagnosis of Disc Bulging
The diagnosis may not be apparent from clinical history due to similar presentations in more serious problems. But the chronic nature of the disease may give some clues. Complete history and a physical examination need to be done to rule out myocardial infarction, gastritis, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, and chronic lung pathology.
MRI of Disc Bulge
Investigations are necessary for the diagnosis. X-ray spine is performed to look for gross pathology although it may not show the bulging disc directly. There may be indirect findings of disk degeneration such as osteophytes in the endplates, gas in the disc due to the vacuum phenomenon, and the loss of height of the intervertebral disc. In the case of moderate bulges, it may sometimes appear as non-focal intervertebral disc material that is protruded beyond the borders of the vertebra which is broad-based, circumferential, and symmetrical.
Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI can exquisitely define the anatomy of the intervertebral discs especially the nucleus pulposus and its relationships. The early findings seen on MRI in disc bulging include the loss of normal concavity of the posterior disc. The bulges can be seen as broad-based, circumferential, and symmetrical areas. In moderate bulging, the disc material will protrude beyond the borders of the vertebrae in a non-focal manner. Ct myelogram may also give detailed disc anatomy and may be useful in the diagnosis.
Treatment of Disc Bulging
The treatment for the bulging disc can be conservative, but sometimes surgery is required.
Conservative Treatment
When the disc bulging is asymptomatic, the patient does not need any treatment since it does not pose an increased risk. However, if the patient is symptomatic, the management can be directed at relieving the symptoms. The pain is usually resolved with time. Till then, potent pain killers such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen should be prescribed. In unresolved pain, steroid injections can also be given to the affected area and if it still does not work, the lumbar sympathetic block can be tried in most severe cases.
The patient can also be given the option of choosing alternative therapies such as professional massage, physical therapy, ice packs, and heating pads which may alleviate symptoms. Maintaining correct posture, tapes, or braces to support the spine are used with the aid of a physiotherapist. This may fasten the recovery process by avoiding further damage and keeping the damaged or torn fibers in the intervertebral disc without leakage of the fluid portion of the disc. This helps maintain the normal structure of the annulus and may increase the recovery rate. Usually, the painful symptoms which present initially get resolved over time and lead to no pain. However, if the symptoms get worse steadily, the patient may need surgery
If the symptoms are resolved, physiotherapy can be used to strengthen the muscles of the back with the use of exercises. Gradual exercises can be used for the return of function and for preventing recurrences.
Surgical Treatment
When conservative therapy does not work with a few months of treatment, surgical treatment can be considered. Most would prefer minimally invasive surgery which uses advanced technology to correct the intervertebral disc without having to grossly dissect the back. These procedures such as microdiscectomy have a lower recovery period and reduced risk of scar formation, major blood loss, and trauma to adjacent structures when compared to open surgery.
Previously, laminectomy and discectomy have been a mainstay of treatment. However, due to the invasiveness of the procedure and due to increased damage to the nerves these procedures are currently abandoned by many clinicians for disc bulging.
Disc bulging in the thoracic spine is being treated surgically with costotransversectomy where a section of the transverse process is resected to allow access to the intervertebral disc. The spinal cord and spinal nerves are decompressed by using thoracic decompression by removing a part of the vertebral body and making a small opening. The patient may also need a spinal fusion later on if the removed spinal body was significant.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery can also be used where only a small incision is made and the surgeon can perform the surgery with the assistance of the camera. If the surgical procedure involved removing a large portion of the spinal bone and disc material, it may lead to spinal instability. This may need bone grafting to replace the lost portion with plates and screws to hold them in place.
What is a Disc Herniation?
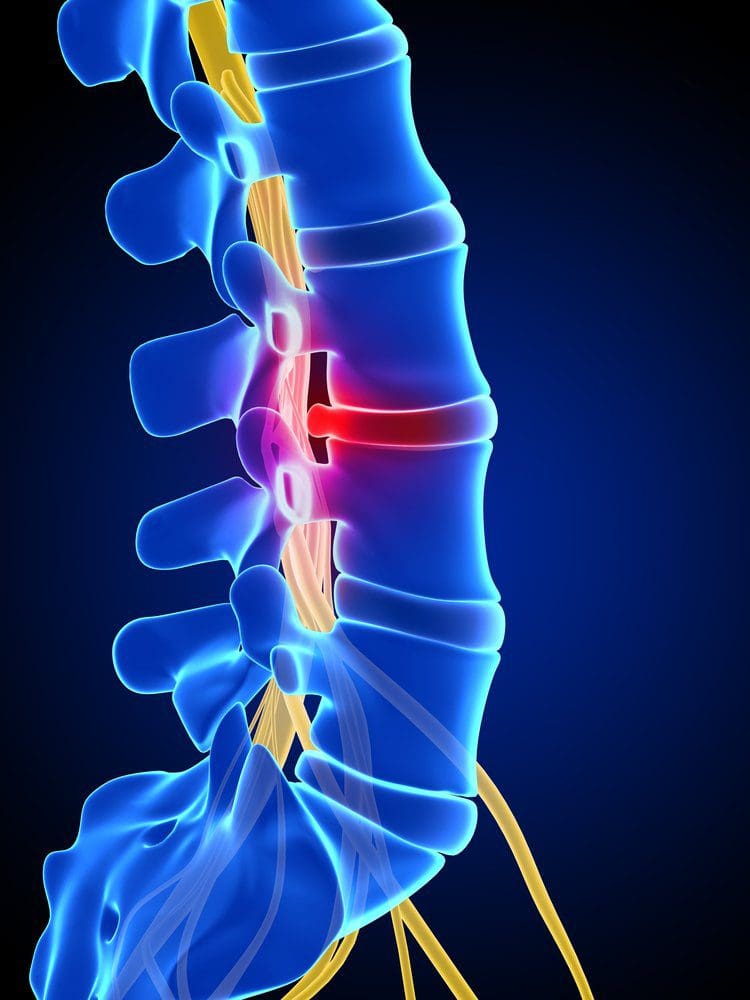
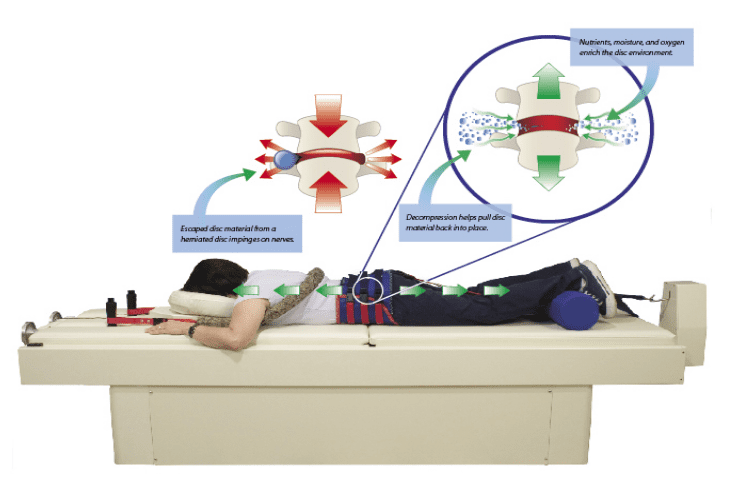
As mentioned in the first section of this article, disc herniation occurs when there is disc material displaces beyond the limits of the intervertebral disc focally. The disc space consists of endplates of the vertebral bodies superiorly and inferiorly while the outer edges of the vertebral apophyses consist of the peripheral margin. The osteophytes are not considered a disc margin. There may be irritation or compression of the nerve roots and dural sac due to the volume of the herniated material leading to pain. When this occurs in the lumbar region, this is classically known as sciatica. This condition has been mentioned since ancient times although a connection between disc herniation and sciatica was made only in the 20th century. Disc herniation is one of the commonest diagnoses seen in the spine due to degenerative changes and is the commonest cause of spinal surgery.
Classifications of Disc Herniation
There are many classifications regarding intervertebral disc herniation. In focal disc herniation, there is a localized displacement of the disc material in the horizontal or axial plane. In this type, only less than 25% of the circumference of the disc is involved. In broad-based disc herniation, about 25 – 50 % of the disc circumference is herniated. The disc bulge is when 50 – 100 % of the disc material is extended beyond the normal confines of the intervertebral space. This is not considered a form of disc herniation. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc deformities associated with severe cases of scoliosis and spondylolisthesis are not classified as a herniation but rather adaptive changes of the contour of the disc due to the adjacent deformity.
Depending on the contour of the displaced material, the herniated discs can be further classified as protrusions and extrusions. In disc protrusion, the distance measured in any plane involving the edges of the disc material beyond intervertebral disc space (the highest measure is taken) is lower than the distance measured in the same plane between the edges of the base.
Imaging can show the disc displacement as a protrusion on the horizontal section and as an extrusion on the sagittal section due to the fact that the posterior longitudinal ligament contains the disc material that is displaced posteriorly. Then the herniation should be considered an extrusion. Sometimes the intervertebral disc herniation can occur in the craniocaudal or vertical direction through a defect in the vertebral body endplates. This type of herniation is known as intravertebral herniation.
The disc protrusion can also be divided into two focal protrusion and broad-based protrusion. In focal protrusion, the herniation is less than 25% of the circumference of the disc whereas, in broad-based protrusion, the herniated disc consists of 25 – 50 % of the circumference of the disc.
In disc extrusion, it is diagnosed if any of the two following criteria are satisfied. The first one is; that the distance measured between the edges of the disc material that is beyond the intervertebral disc space is greater than the distance measured in the same plane between the edges of the base. The second one is; that the material in the intervertebral disc space and material beyond the intervertebral disc space is having a lack continuity.
This can be further characterized as sequestrated which is a subtype of the extruded disc. It is called disc migration when disk material is pushed away from the site of extrusion without considering whether there is continuity of disc or not. This term is useful in interpreting imaging modalities as it is often difficult to show continuity in imaging.
The intervertebral disc herniation can be further classified as contained discs and discs that are unconfined. The term contained disc is used to refer to the integrity of the peripheral annulus fibrosus which is covering the intervertebral disc herniation. When fluid is injected into the intervertebral disc, the fluid does not leak into the vertebral canal in herniations that are contained.
Sometimes there are displaced disc fragments that are characterized as free. However, there should be no continuity between disc material and the fragment and the original intervertebral disc for it to be called a free fragment or a sequestered one. In a migrated disc and in a migrated fragment, there is an extrusion of disc material through the opening in the annulus fibrosus with a displacement of the disc material away from the annulus.
Even though some fragments that are migrated can be sequestered the term migrated means just to the position and it is not referred to the continuity of the disc. The displaced intervertebral disc material can be further described with regard to the posterior longitudinal ligament as submembranous, subcapsular, subligamentous, extra ligamentous, transligamentous, subcapsular, and perforated.
The spinal canal can also get affected by an intervertebral disc herniation. This compromise of the canal can also be classified as mild, moderate, and severe depending on the area that is compromised. If the canal at that section is compromised only less than one third, it is called mild whereas if it is only compromised less than two-thirds and more than one third it is considered moderate. In a severe compromise, more than two-thirds of the spinal canal is affected. For the foraminal involvement, this same grading system can be applied.
The displaced material can be named according to the position that they are in the axial plane from the center to the right lateral region. They are termed as central, right central, right subarticular, right foraminal, and right extraforaminal. The displaced intervertebral disc material’s composition can be further classified as gaseous, liquefied, desiccated, scarred, calcified, ossified, bony, nuclear, and cartilaginous.
Before going into detail on how to diagnose and treat intervertebral disc herniation, let us differentiate how cervical disc herniation differs from lumbar herniation since they are the most common regions to undergo herniation.
Cervical Disc Herniation vs. Thoracic Disc Herniation vs Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation is the most commonest type of herniation found in the spine which is approximately 90% of the total. However, cervical disc herniation can also occur in about one-tenth of patients. This difference is mainly due to the fact that the lumbar spine has more pressure due to the increased load. Moreover, it has comparatively large intervertebral disc material. The most common sites of intervertebral disc herniation in the lumbar region are L 5 – 6, in the Cervical region between C7, and in the thoracic region T12.
Cervical disc herniation can occur relatively commonly because the cervical spine acts as a pivoting point for the head and it is a vulnerable area for trauma and therefore prone to damage in the disc. Thoracic disc herniation occurs more infrequently than any of the two. This is due to the fact that thoracic vertebrae are attached to the ribs and the thoracic cage which limits the range of movement in the thoracic spine when compared to the cervical and lumbar spinal discs. However, thoracic intervertebral disc herniation can still occur.
Cervical disc herniation gives rise to neck pain, shoulder pain, pain radiating from the neck to the arm, tingling, etc. Lumbar disc herniation can similarly cause lower back pain as well as pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness seen in the lower limbs. Thoracic disc herniation can give rise to pain in the upper back radiating to the torso.
Epidemiology
Although disc herniation can occur in all age groups, it predominantly occurs between the fourth and fifth decade of life with the mean age of 37 years. There have been reports that estimate the prevalence of intervertebral disc herniation to be 2 – 3 % of the general population. It is more commonly seen in men over 35 years with a prevalence of 4.8% and while in women this figure is around 2.5%. Due to its high prevalence, it is considered a worldwide problem as it is also associated with significant disability.
Risk Factors
In most instances, a herniated disc occurs due to the natural aging process in the intervertebral disc. Due to the disc degeneration, the amount of water that was previously seen in the intervertebral disc gets dried out leading to the shrinking of the disc with the narrowing of the intervertebral space. These changes are markedly seen in degenerative disc disease. In addition to these gradual changes due to normal wear and tear, other factors may also contribute to increasing the risk of intervertebral disc herniation.
Being overweight can increase the load on the spine and increase the risk of herniation. A sedentary life can also increase the risk and therefore an active lifestyle is recommended in preventing this condition. Improper posture with prolonged standing, sitting, and especially driving can put a strain on the intervertebral discs due to the additional vibration from the vehicle engine leading to microtrauma and cracks in the disc. The occupations which require constant bending, twisting, pulling and lifting can put a strain on the back. Improper weight lifting techniques are one of the major reasons.
When back muscles are used in lifting heavy objects instead of lifting with the legs and twisting while lifting can make the lumbar discs more vulnerable to herniation. Therefore patients should always be advised to lift weights with their legs and not the back. Smoking has been thought to increase disc herniation by reducing the blood supply to the intervertebral disc leading to degenerative changes of the disc.
Although the above factors are frequently assumed to be the causes for disc herniation, some studies have shown that the difference in risk is very small when this particular population was compared with the control groups of the normal population.
There have been several types of research done on genetic predisposition and intervertebral disc herniation. Some of the genes that are implicated in this disease include vitamin D receptor (VDR) which is a gene that codes for the polypeptides of important collagen called collagen IX (COL9A2).
Another gene called the human aggrecan gene (AGC) is also implicated as it codes for proteoglycans which is the most important structural protein found in the cartilage. It supports the biochemical and mechanical function of the cartilage tissue and hence when this gene is defective, it can predispose an individual to intervertebral disc herniation.
Apart from these, there are many other genes that are being researched due to the association between disc herniation such as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) cartilage intermediate layer protein, thrombospondin (THBS2), collagen 11A1, carbohydrate sulfotransferase, and asporin (ASPN). They may also be regarded as potential gene markers for lumbar disc disease.
Pathogenesis of Sciatica and Disc Herniation
The sciatic pain originated from the extruded nucleus pulposus inducing various phenomena. It can directly compress the nerve roots leading to ischemia or without it, mechanically stimulate the nerve endings of the outer portion of the fibrous ring and release inflammatory substances suggesting its multifactorial origin. When the disc herniation causes mechanical compression of the nerve roots, the nerve membrane is sensitized to pain and other stimuli due to ischemia. It has been shown that in sensitized and compromised nerve roots, the threshold for neuronal sensitization is around half of that of a normal and non-compromised nerve root.
The inflammatory cell infiltration is different in extruded discs and non-extruded discs. Usually, in non-extruded discs, the inflammation is less. The extruded disc herniation causes the posterior longitudinal ligament to rupture which exposes the herniated part to the vascular bed of the epidural space. It is believed that inflammatory cells are originating from these blood vessels situated in the outermost part of the intervertebral disc.
These cells may help secrete substances that cause inflammation and irritation of the nerve roots causing sciatic pain. Therefore, extruded herniations are more likely to cause pain and clinical impairment than those that are contained. In contained herniations, the mechanical effect is predominant while in the unconfined or the extruded discs the inflammatory effect is predominant.
Clinical Disc Herniation and What to Look for in the History
The symptoms of the disc herniation can vary a great deal depending on the location of the pain, the type of herniation, and the individual. Therefore, history should focus on the analysis of the main complaint among the many other symptoms.
The chief complaint can be neck pain in cervical disc herniation and there can be referred pain in the arms, shoulders, neck, head, face, and even the lower back region. However, it is most commonly referred to as the interscapular region. The radiation of pain can occur according to the level at the herniation is taking place. When the nerve roots of the cervical region are affected and compressed, there can be sensory, and motor changes with changes in the reflexes.
The pain that occurs due to nerve root compression is called radicular pain and it can be described as deep, aching, burning, dull, achy, and electric depending on whether there is mainly motor dysfunction or sensory dysfunction. In the upper limb, the radicular pain can follow a dermatomal or myotomal pattern. Radiculopathy usually does not accompany neck pain. There can be unilateral as well as bilateral symptoms. These symptoms can be aggravated by activities that increase the pressure inside the intervertebral discs such as the Valsalva maneuver and lifting.
Driving can also exacerbate pain due to disc herniation due to stress because of vibration. Some studies have shown that shock loading and stress from vibration can cause a mechanical force to exacerbate small herniations but flexed posture had no influence. Similarly, activities that decrease intradiscal pressure can reduce the symptoms such as lying down.
The main complaint in lumbar disc herniation is lower back pain. Other associated symptoms can be a pain in the thigh, buttocks, and anogenital region which can radiate to the foot and toe. The main nerve affected in this region is the sciatic nerve causing sciatica and its associated symptoms such as intense pain in the buttocks, leg pain, muscle weakness, numbness, impairment of sensation, hot and burning or tingling sensation in the legs, dysfunction of gait, impairment of reflexes, edema, dysesthesia or paresthesia in the lower limbs. However, sciatica can be caused by causes other than herniation such as tumors, infection, or instability which need to be ruled out before arriving at a diagnosis.
The herniated disc can also compress on the femoral nerve and can give rise to symptoms such as numbness, tingling sensation in one or both legs, and a burning sensation in the legs and hips. Usually, the nerve roots that are affected in herniation in the lumbar region are the ones exiting below the intervertebral disc. It is thought that the level of the nerve root irritation determines the distribution of leg pain. In herniations at the third and fourth lumbar vertebral levels, the pain may radiate to the anterior thigh or the groin. In radiculopathy at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra, the pain may occur in the lateral and anterior thigh region. In herniations at the level of the first sacrum, the pain may occur in the bottom of the foot and the calf. There can also be numbness and tingling sensation occurring in the same area of distribution. The weakness in the muscles may not be able to be recognized if the pain is very severe.
When changing positions the patient is often relieved from pain. Maintaining a supine position with the legs raised can improve the pain. Short pain relief can be brought by having short walks while long walks, standing for prolonged periods, and sitting for extended periods of time such as in driving can worsen the pain.
The lateral disc herniation is seen in foraminal and extraforaminal herniations and they have different clinical features to that of medial disc herniation seen in subarticular and central herniations. The lateral intervertebral disc herniations can when compared to medial herniations more directly irritate and mechanically compress the nerve roots that are exiting and the dorsal root ganglions situated inside the narrowed spinal canal.
Therefore, lateral herniation is seen more frequently in older age with more radicular pain and neurological deficits. There is also more radiating leg pain and intervertebral disc herniations in multiple levels in the lateral groups when compared to medial disc herniations.
The herniated disc in the thoracic region may not present with back pain at all. Instead, there are predominant symptoms due to referred pain in the thorax due to irritation of nerves. There can also be predominant pain in the body that travels to the legs, tingling sensation and numbness in one or both legs, muscle weakness, and spasticity of one or both legs due to exaggerated reflexes.
The clinician should look out for atypical presentations as there could be other differential diagnoses. The onset of symptoms should be inquired about to determine whether the disease is acute, sub-acute, or chronic in onset. Past medical history has to be inquired about in detail to exclude red flag symptoms such as pain that occurs at night without activity which can be seen in pelvic vein compression, and non-mechanical pain which may be seen in tumors or infections.
If there is a progressive neurological deficit, with bowel and bladder involvement is there, it is considered a neurological emergency and urgently investigated because cauda equine syndrome may occur which if untreated, can lead to permanent neurological deficit.
Getting a detailed history is important including the occupation of the patient as some activities in the job may be exacerbating the patient’s symptoms. The patient should be assessed regarding which activities he can and cannot do.
Differential Diagnosis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Mechanical pain
- Myofascial pain leading to sensory disturbances and local or referred pain
- Hematoma
- Cyst leading to occasional motor deficits and sensory disturbances
- Spondylosis or spondylolisthesis
- Discitis or osteomyelitis
- Malignancy, neurinoma or mass lesion causing atrophy of thigh muscles, glutei
- Spinal stenosis is seen mainly in the lumbar region with mild low back pain, motor deficits, and pain in one or both legs.
- An epidural abscess can cause symptoms similar to radicular pain involving spinal disc herniation
- Aortic aneurysm which can cause low back pain and leg pain due to compression can also rupture and lead to hemorrhagic shock.
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma in advanced stages can lead to space-occupying lesions in the spinal column leading to symptoms like that of intervertebral disc herniation
- Tumors
- Pelvic endometriosis
- Facet hypertrophy
- Lumbar nerve root schwannoma
- Herpes zoster infection results in inflammation along with the sciatic or lumbosacral nerve roots
Examination in Disc Herniation
Complete physical examination is necessary to diagnose intervertebral disc herniation and exclude other important differential diagnoses. The range of motion has to be tested but may have a poor correlation with disc herniation as it is mainly reduced in elderly patients with a degenerative disease and due to disease of the joints.
A complete neurological examination is often necessary. This should test muscle weakness and sensory weakness. In order to detect muscle weakness in small toe muscles, the patient can be asked to walk on tiptoe. The strength of muscle can also be tested by comparing the strength to that of the clinician. There may be dermatomal sensory loss suggesting the respective nerve root involvement. The reflexes may be exaggerated or sometimes maybe even absent.
There are many neurologic examination maneuvers described in relation to intervertebral disc herniation such as the Braggart sign, flip the sign, Lasegue rebound sign, Lasegue differential sign, Mendel Bechterew sign, Deyerle sign both legs or Milgram test, and well leg or Fajersztajin test. However, all these are based on testing the sciatic nerve root tension by using the same principles in the straight leg raising test. These tests are used for specific situations to detect subtle differences.
Nearly almost all of them depend on the pain radiating down the leg and if it occurs above the knee it is assumed to be due to a neuronal compressive lesion and if the pain goes below the knee, it is considered to be due to the compression of the sciatic nerve root. For lumbar disc herniation detection, the most sensitive test is considered to be radiating pain occurring down the leg due to provocation.
In the straight leg raising test also called the Lasegue’s sign, the patient stays on his or her back and keeps the legs straight. The clinician then lifts the legs by flexing the hip while keeping the knee straight. The angle at which the patient feels pain going down the leg below the knee is noted. In a normal healthy individual, the patient can flex the hip to 80- 90? without having any pain or difficulty.
However, if the angle is just 30 -70? degrees, it is suggestive of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation at the L4 to S1 nerve root levels. If the angle of hip flexion without pain is less than 30 degrees, it usually indicates some other causes such as tumor of the gluteal region, gluteal abscess, spondylolisthesis, disc extrusion, and protrusion, malingering patient, and acute inflammation of the dura mater. If pain with hip flexion occurs at more than 70 degrees, it may be due to tightness of the muscles such as gluteus maximus and hamstrings, tightness of the capsule of the hip joint, or pathology of sacroiliac or hip joints.
The reverse straight leg raising test or hip extension test can be used to test higher lumbar lesions by stretching the nerve roots of the femoral nerve which is similar to the straight leg raising test. In the cervical spine, in order to detect stenosis of the foramina, the Spurling test is done and is not specific to cervical intervertebral disc herniation or tension of the nerve roots. The Kemp test is the analogous test in the lumbar region to detect foraminal stenosis. Complications due to the disc herniation include careful examination of the hip region, digital rectal examination, and urogenital examination is needed.
Investigation of Disc Herniation
For the diagnosis of intervertebral disc herniation, diagnostic tests such as Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Computed tomography (CT), myelography, and plain radiography can be used either alone or in combination with other imaging modalities. Objective detection of disc herniation is important because only after such a finding the surgical intervention is even considered. Serum biochemical tests such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, Alkaline phosphatize value, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), urine analysis for Bence Jones protein, serum glucose level, and serum protein electrophoresis may also be needed in specific circumstances guided by history.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is considered the best imaging modality in patients with history and physical examination findings suggestive of lumbar disc herniation associated with radiculopathy according to North American Spinal Society guidelines in 2014. The anatomy of the herniated nucleus pulposus and its associated relationships with soft tissue in the adjacent areas can be delineated exquisitely by MRI in cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral areas. Beyond the confines of the annulus, the herniated nucleus can be seen as a focal, asymmetric disc material protrusion on MRI.
On sagittal T2 weighted images, the posterior annulus is usually seen as a high signal intensity area due to radial annular tear associated with the herniation of the disc although the herniated nucleus is itself hypointense. The relationship between the herniated nucleus and degenerated facets with the nerve roots which are exiting through the neural foramina are well-demarcated on sagittal images of MRI. Free fragments of the intervertebral disc can also be distinguished from MRI images.
There may be associated signs of intervertebral disc herniation on MRI such as radial tears on the annulus fibrosus which is also a sign of degenerative disc disease. There may be other telling signs such as loss of disc height, bulging annulus, and changes in the endplates. Atypical signs may also be seen with MRI such as abnormal disc locations, and lesions located completely outside the intervertebral disc space.
MRI can detect abnormalities in the intervertebral discs superiorly to other modalities although its bone imaging is a little less inferior. However, there are limitations with MRI in patients with metal implant devices such as pacemakers because the electromagnetic field can lead to abnormal functioning of the pacemakers. In patients with claustrophobia, it may become a problem to go to the narrow canal to be scanned by the MRI machine. Although some units contain open MRI, it has less magnetic power and hence delineates less superior quality imaging.
This is also a problem in children and anxious patients undergoing MRI because good image quality depends on the patient staying still. They may require sedation. The contrast used in MRI which is gadolinium can induce nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients who had pre-existing renal disease. MRI is also generally avoided in pregnancy especially during the first 12 weeks although it has not been clinically proven to be hazardous to the fetus. MRI is not very useful when a tumor contains calcium and in distinguishing edema fluid from tumor tissue.
Computed Tomography (CT)
CT scanning is also considered another good method to assess spinal disc herniation when MRI is not available. It is also recommended as a first-line investigation in unstable patients with severe bleeding. CT scanning is superior to myelography although when the two are combined, it is superior both of them. CT scans can show calcification more clearly and sometimes even gas in images. In order to achieve a superior imaging quality, the imaging should be focused on the site of pathology and thin sections taken to better determine the extent of the herniation.
However, a CT scan is difficult to be used in patients who have already undergone laminectomy surgical procedures because the presence of scar tissue and fibrosis causes the identification of the structures difficult although bony changes and deformity in nerve sheath are helpful in making a diagnosis.
The herniated intervertebral discs in the cervical disc can be identified by studying the uncinate process. It is usually projected posteriorly and laterally to the intervertebral discs and superiorly to the vertebral bodies. The uncinate process undergoes sclerosis, and hypertrophy when there is an abnormal relationship between the uncinate process and adjacent structures as seen in degenerative disc disease, intervertebral disc space narrowing, and general wear and tear.
Myelopathy can occur when the spinal canal is affected due to disc disease. Similarly, when neural foramina are involved, radiculopathy occurs. Even small herniated discs and protrusions can cause impingement of the dural sac because the cervical epidural space is narrowed naturally. The intervertebral discs have attenuation a little bit greater than the sac characterized in the CT scan.
In the thoracic region, a CT scan can diagnose an intervertebral disc herniation with ease due to the fact that there is an increased amount of calcium found in the thoracic discs. Lateral to the dural sac, the herniated disc material can be seen on CT as a clearly defined mass that is surrounded by epidural fat. When there is a lack of epidural fat, the disc appears as a higher attenuated mass compared to the surrounding.
Radiography
Plain radiography is not needed in diagnosing herniation of the intervertebral discs, because plain radiographs cannot detect the disc and therefore are used to exclude other conditions such as tumors, infections, and fractures.
In myelography, there may be deformity or displacement of the extradural contrast-filled thecal sac seen in herniation of the disc. There may also be features in the affected nerve such as edema, elevation, deviation, and amputation of the nerve root seen in the myelography image.
Diskography
In this imaging modality, the contrast medium is injected into the disc in order to assess the disc morphology. If pain occurs following injection that is similar to the discogenic pain, it suggests that that disc is the source of the pain. When a CT scan is also performed immediately after discography, it is helpful to differentiate the anatomy and pathological changes. However, since it is an invasive procedure, it is indicated only in special circumstances when MRI and CT have failed to reveal the etiology of back pain. It has several side effects such as headache, meningitis, damage to the disc, discitis, intrathecal hemorrhage, and increased pain.
Treatment of Herniated Disc
The treatment should be individualized according to the patient-guided through history, physical examination, and diagnostic investigation findings. In most cases, the patient gradually improves without needing further intervention in about 3 – 4 months. Therefore, the patient only needs conservative therapy during this time period. Because of this reason, there are many ineffective therapies that have emerged by attributing the natural resolution of symptoms to that therapy. Therefore, conservative therapy needs to be evidence-based.
Conservative Therapy
Since the herniation of the disc has a benign course, the aim of treatment is to stimulate the recovery of neurological function, reduce pain, and facilitate early return to work and activities of daily living. The most benefits of the conservative treatment are for younger patients with hernias that are sequestered and in patients with mild neurological deficits due to small disc hernias.
Bed rest has long been considered a treatment option in herniation of the disc. However, it has been shown that bed rest has no effect beyond the first 1 or 2 days. The bed rest is regarded as counterproductive after this period of time.
In order to reduce the pain, oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can be used. This can relieve the pain by reducing inflammation associated with the inflamed nerve. Analgesics such as acetaminophen can also be used although they lack the anti-inflammatory effect seen in NSAIDs. The doses and the drugs should be appropriate for the age and severity of the pain in the patient. If pain is not controlled by the current medication, the clinician has to go one step up on the WHO analgesics ladder. However, the long-term use of NSAIDs and analgesics can lead to gastric ulcers, liver, and kidney problems.
In order to reduce the inflammation, other alternative methods such as applying ice in the initial period and then switching to using heat, gels, and rubs may help with the pain as well as muscle spasms. Oral muscle relaxants can also be used in relieving muscle spasms. Some of the drugs include methocarbamol, carisoprodol, and cyclobenzaprine.
However, they act centrally and cause drowsiness and sedation in patients and it does not act directly to reduce muscle spasm. A short course of oral steroids such as prednisolone for a period of 5 days in a tapering regime can be given to reduce the swelling and inflammation in the nerves. It can provide immediate pain relief within a period of 24 hours.
When the pain is not resolved adequately with maximum effective doses, the patient can be considered for giving steroid injections into the epidural space. The major indication for the steroid injection into periradicular space is discal compression causing radicular pain that is resistant to conventional medical treatment. A careful evaluation with CT or MRI scanning is required to carefully exclude extra discal causes for pain. The contraindications for this therapy include patients with diabetes, pregnancy, and gastric ulcers. Epidural puncture is contraindicated in patients with coagulation disorders and therefore the foraminal approach is used carefully if needed.
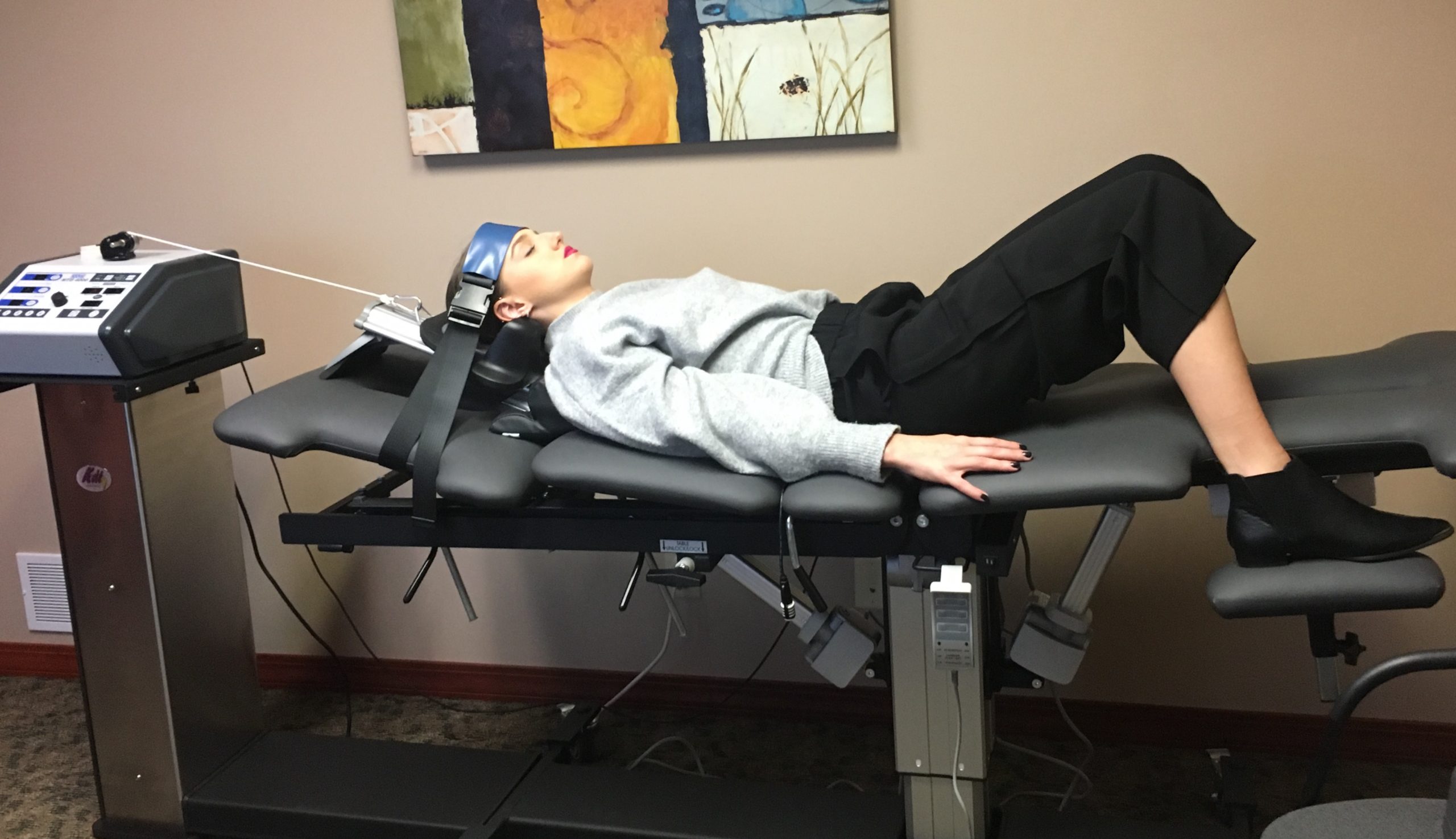
This procedure is performed under the guidance of fluoroscopy and involves injecting steroids and an analgesic into the epidural space adjacent to the affected intervertebral disc to reduce the swelling and inflammation of the nerves directly in an outpatient setting. As much as 50% of the patients experience relief after the injection although it is temporary and they might need repeat injections at 2 weekly intervals to achieve the best results. If this treatment modality becomes successful, up to 3 epidural steroidal injections can be given per year.
Physical therapy can help the patient return to his previous life easily although it does not improve the herniated disc. The physical therapist can instruct the patient on how to maintain the correct posture, walking, and lifting techniques depending on the patient’s ability to work, mobility, and flexibility.
Stretching exercises can improve the flexibility of the spine while strengthening exercises can increase the strength of the back muscles. The activities which can aggravate the condition of the herniated disc are instructed to be avoided. Physical therapy makes the transition from intervertebral disc herniation to an active lifestyle smooth. The exercise regimes can be maintained for life to improve general well-being.
The most effective conservative treatment option that is evidence-based is observation and epidural steroid injection for the relief of pain in the short-term duration. However, if the patients so desire they can use holistic therapies of their choice with acupuncture, acupressure, nutritional supplements, and biofeedback although they are not evidence-based. There is also no evidence to justify the use of trans electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) as a pain relief method.
If there is no improvement in the pain after a few months, surgery can be contemplated and the patient must be selected carefully for the best possible outcome.
Surgical Therapy
The aim of surgical therapy is to decompress the nerve roots and relieve the tension. There are several indications for surgical treatment which are as follows.
Absolute indications include cauda equina syndrome or significant paresis. Other relative indications include motor deficits that are greater than grade 3, sciatica that is not responding to at least six months of conservative treatment, sciatica for more than six weeks, or nerve root pain due to foraminal bone stenosis.
There have been many discussions over the past few years regarding whether to treat herniation of intervertebral disc disease with prolonged conservative treatment or early surgical treatment. Much research has been conducted in this regard and most of them show that the final clinical outcome after 2 years is the same although the recovery is faster with early surgery. Therefore, it is suggested that early surgery may be appropriate as it enables the patient to return to work early and thereby is economically feasible.
Some surgeons may still use traditional discectomy although many are using minimally invasive surgical techniques over recent years. Microdiscectomy is considered to be the halfway between the two ends. There are two surgical approaches that are being used. Minimally invasive surgery and percutaneous procedures are the ones that are being used due to their relative advantage. There is no place for the traditional surgical procedure known as a laminectomy.
However, there are some studies suggesting microdiscectomy is more favorable because of its both short-term and long-term advantages. In the short term, there is a reduced length of operation, reduced bleeding, relief of symptoms, and reduced complication rate. This technique has been effective even after 10 years of follow-up and therefore is the most preferred technique even now. The studies that have been performed to compare the minimally invasive technique and microdiscectomy have resulted in different results. Some have failed to establish a significant difference while one randomized control study was able to determine that microdiscectomy was more favorable.
In microdiscectomy, only a small incision is made aided by an operating microscope and the part of the herniated intervertebral disc fragment which is impinging on the nerve is removed by hemilaminectomy. Some part of the bone is also removed to facilitate access to the nerve root and the intervertebral disc. The duration of the hospital stay is minimal with only an overnight stay and observation because the patient can be discharged with minimal soreness and complete relief of the symptoms.
However, some unstable patients may need more prolonged admission and sometimes they may need fusion and arthroplasty. It is estimated that about 80 – 85 % of the patients who undergo microdiscectomy recover successfully and many of them are able to return to their normal occupation in about 6 weeks.
There is a discussion on whether to remove a large portion of the disc fragment and curetting the disc space or to remove only the herniated fragment with minimal invasion of the intervertebral disc space. Many studies have suggested that the aggressive removal of large chunks of the disc could lead to more pain than when conservative therapy is used with 28% versus 11.5 %. It may lead to degenerative disc disease in the long term. However, with conservative therapy, there is a greater risk of recurrence of around 7 % in herniation of the disc. This may require additional surgery such as arthrodesis and arthroplasty to be performed in the future leading to significant distress and economic burden.
In the minimally invasive surgery, the surgeon usually makes a tiny incision in the back to put the dilators with increasing diameter to enlarge the tunnel until it reaches the vertebra. This technique causes lesser trauma to the muscles than when seen in traditional microdiscectomy. Only a small portion of the disc is removed in order to expose the nerve root and the intervertebral disc. Then the surgeon can remove the herniated disc by the use of an endoscope or a microscope.
These minimally invasive surgical techniques have a higher advantage of lower surgical site infections and shorter hospital stays. The disc is centrally decompressed either chemically or enzymatically with the use of chymopapain, laser, or plasma (ionized gas) ablation and vaporization. It can also be decompressed mechanically by using percutaneous lateral decompression or by aspirating and sucking with a shaver such as a nucleosome. Chemopapin was shown to have adverse effects and was eventually withdrawn. Most of the above techniques have shown to be less effective than a placebo. Directed segmentectomy is the one that has shown some promise in being effective similar to microdiscectomy.
In the cervical spine, the herniated intervertebral discs are treated anteriorly. This is because the herniation occurs anteriorly and the manipulation of the cervical cord is not tolerated by the patient. The disc herniation that is due to foraminal stenosis and that is confined to the foramen are the only instances where a posterior approach is contemplated.
The minimal disc excision is an alternative to the anterior cervical spine approach. However, the intervertebral disc stability after the procedure is dependent on the residual disc. The neck pain can be significantly reduced following the procedure due to the removal of neuronal compression although significant impairment can occur with residual axial neck pain. Another intervention for cervical disc herniation includes anterior cervical interbody fusion. It is more suitable for patients with severe myelopathy with degenerative disc disease.
Complications of the Surgery
Although the risk of surgery is very low, complications can still occur. Post-operative infection is one of the commonest complications and therefore needs more vigorous infection control procedures in the theatre and in the ward. During the surgery, due to poor surgical technique, nerve damage can occur. A dural leak may occur when an opening in the lining of the nerve root causes leakage of cerebrospinal fluid which is bathing the nerve roots. The lining can be repaired during the surgery. However, headache can occur due to loss of cerebrospinal fluid but it usually improves with time without any residual damage. If blood around the nerve roots clots after the surgery, that blood clot may lead to compression of the nerve root leading to radicular pain which was experienced by the patient previously. Recurrent herniation of the intervertebral disc due to herniation of disc material at the same site is a devastating complication that can occur long term. This can be managed conservatively but surgery may be necessary ultimately.
Outcomes of the Surgery
There has been extensive research done regarding the outcome of lumbar disc herniation surgery. Generally, the results from the microdiscectomy surgery are good. There is more improvement of leg pain than back pain and therefore this surgery is not recommended for those who have only back pain. Many patients improve clinically over the first week but they may improve over the following several months. Typically, the pain disappears in the initial recovery period and it is followed by an improvement in the strength of the leg. Finally, the improvement of the sensation occurs. However, patients may complain of feeling numbness although there is no pain. The normal activities and work can be resumed over a few weeks after the surgery.
Novel Therapies
Although conservative therapy is the most appropriate therapy in treating patients, the current standard of care does not address the underlying pathology of herniation of the intervertebral discs. There are various pathways that are involved in the pathogenesis such as inflammatory, immune-mediated, and proteolytic pathways.
The role of inflammatory mediators is currently under research and it has led to the development of new therapies that are directed at these inflammatory mediators causing damage to the nerve roots. The cytokines such as TNF ? are mainly involved in regulating these processes. The pain sensitivity is mediated by serotonin receptor antagonists and ?2 adrenergic receptor antagonists.
Therefore, pharmacological therapies that target these receptors and mediators may influence the disease process and lead to a reduction in symptoms. Currently, cytokine antagonists against TNF ? and IL 1? have been tested. Neuronal receptor blockers such as sarpogrelate hydrochloride etc have been tested in both animal models and in clinical studies for the treatment of sciatica. Cell cycle modifiers that target the microglia that are thought to initiate the inflammatory cascade have been tested with the neuroprotective antibiotic minocycline.
There is also research on inhibiting the NF- kB or protein kinase pathway recently. In the future, the treatment of herniation of the intervertebral disc will be much more improved thanks to the ongoing research. (Haro, Hirotaka)

Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, RN, CCST
A disc bulge and/or a herniated disc is a health issue that affects the intervertebral discs found in between each vertebra of the spine. Although these can occur as a natural part of degeneration with age, trauma or injury as well as repetitive overuse can also cause a disc bulge or a herniated disc. According to healthcare professionals, a disc bulge and/or a herniated disc is one of the most common health issues affecting the spine. A disc bulge is when the outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus are displaced from the margins of the adjacent vertebral bodies. A herniated disc is when a part of or the whole nucleus pulposus is protruded through the torn or weakened outer annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. Treatment of these health issues focuses on reducing symptoms. Alternative treatment options, such as chiropractic care and/or physical therapy, can help relieve symptoms. Surgery may be utilized in cases of severe symptoms. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References
- Anderson, Paul A. et al. Randomized Controlled Trials Of The Treatment Of Lumbar Disk Herniation: 1983-2007. Journal Of The American Academy Of Orthopaedic Surgeons, vol 16, no. 10, 2008, pp. 566-573. American Academy Of Orthopaedic Surgeons, doi:10.5435/00124635-200810000-00002.
- Fraser I (2009) Statistics on hospital-based care in the United States. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville
- Ricci, Judith A. et al. Back Pain Exacerbations And Lost Productive Time Costs In United States Workers. Spine, vol 31, no. 26, 2006, pp. 3052-3060. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health), doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000249521.61813.aa.
- Fardon, D.F., et al., Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology, and the American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine J, 2014. 14(11): p. 2525-45.
- Costello RF, Beall DP. Nomenclature and standard reporting terminology of intervertebral disk herniation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2007;15 (2): 167-74, v-vi.
- Roberts, S. Disc Morphology In Health And Disease. Biochemical Society Transactions, vol 30, no. 5, 2002, pp. A112.4-A112. Portland Press Ltd., doi:10.1042/bst030a112c.
- Johnson, W. E. B., and S. Roberts. Human Intervertebral Disc Cell Morphology And Cytoskeletal Composition: A Preliminary Study Of Regional Variations In Health And Disease. Journal Of Anatomy, vol 203, no. 6, 2003, pp. 605-612. Wiley-Blackwell, doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00249.x.
- Gruenhagen, Thijs. Nutrient Supply And Intervertebral Disc Metabolism. The Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery (American), vol 88, no. suppl_2, 2006, p. 30. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health), doi:10.2106/jbjs.e.01290.
- Mercer, S.R., and G.A. Jull. Morphology Of The Cervical Intervertebral Disc: Implications For Mckenzies Model Of The Disc Derangement Syndrome. Manual Therapy, vol 1, no. 2, 1996, pp. 76-81. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1054/math.1996.0253.
- KOELLER, W et al. Biomechanical Properties Of Human Intervertebral Discs Subjected To Axial Dynamic Compression. Spine, vol 9, no. 7, 1984, pp. 725-733. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health), doi:10.1097/00007632-198410000-00013.
- Lieberman, Isador H. Disc Bulge Bubble: Spine Economics 101. The Spine Journal, vol 4, no. 6, 2004, pp. 609-613. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2004.09.001.
- Lappalainen, Anu K et al. Intervertebral Disc Disease In Dachshunds Radiographically Screened For Intervertebral Disc Calcifications. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, vol 56, no. 1, 2014, Springer Nature, doi:10.1186/s13028-014-0089-4.
- Moazzaz, Payam et al. 80. Positional MRI: A Valuable Tool In The Assessment Of Cervical Disc Bulge. The Spine Journal, vol 7, no. 5, 2007, p. 39S. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2007.07.097.
- Lumbar Disc Disease: Background, History Of The Procedure, Problem. Emedicine.Medscape.Com, 2017, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/249113-overview.
- Vialle, Luis Roberto et al. LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia 45.1 (2010): 1722. PMC. Web. 1 Oct. 2017.
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus: Background, Anatomy, Pathophysiology. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1263961-overview.
- Vialle, Luis Roberto et al. LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION. Revista Brasileira De Ortopedia (English Edition), vol 45, no. 1, 2010, pp. 17-22. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/s2255-4971(15)30211-1.
- Mullen, Denis et al. Pathophysiology Of Disk-Related Sciatica. I. Evidence Supporting A Chemical Component. Joint Bone Spine, vol 73, no. 2, 2006, pp. 151-158. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2005.03.003.
- Jacobs, Wilco C. H. et al. Surgical Techniques For Sciatica Due To Herniated Disc, A Systematic Review. European Spine Journal, vol 21, no. 11, 2012, pp. 2232-2251. Springer Nature, doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2422-9.
- Rutkowski, B. Combined Practice Of Electrical Stimulation For Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Herniation.Pain, vol 11, 1981, p. S226. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health), doi:10.1016/0304-3959(81)90487-5.
- Weber, Henrik. Spine Update The Natural History Of Disc Herniation And The Influence Of Intervention.Spine, vol 19, no. 19, 1994, pp. 2234-2238. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health), doi:10.1097/00007632-199410000-00022.
- Disk Herniation Imaging: Overview, Radiography, Computed Tomography.Emedicine.Medscape.Com, 2017,
- Carvalho, Lilian Braighi et al. Hrnia De Disco Lombar: Tratamento. Acta Fisitrica, vol 20, no. 2, 2013, pp. 75-82. GN1 Genesis Network, doi:10.5935/0104-7795.20130013.
- Kerr, Dana et al. What Are Long-Term Predictors Of Outcomes For Lumbar Disc Herniation? A Randomized And Observational Study. Clinical Orthopaedics And Related Research, vol 473, no. 6, 2014, pp. 1920-1930. Springer Nature, doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3803-7.
- Buy, Xavier, and Afshin Gangi. Percutaneous Treatment Of Intervertebral Disc Herniation. Seminars In Interventional Radiology, vol 27, no. 02, 2010, pp. 148-159. Thieme Publishing Group, doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253513.
- Haro, Hirotaka. Translational Research Of Herniated Discs: Current Status Of Diagnosis And Treatment. Journal Of Orthopaedic Science, vol 19, no. 4, 2014, pp. 515-520. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1007/s00776-014-0571-x.