by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Wellness
SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth) is defined as 105 up to 106 organisms of bacteria in the small intestines. It is highly relevant to remember that the abundance of bacteria in the small intestine that has SIBO, are healthy bacteria that live in the gastrointestinal tract. It means that the bacteria in the digestive tract is either missed or dislocated and is in the wrong place in the small intestines. While SIBO still remains a poorly understood disease, it is frequently implicated to be the cause of chronic diarrhea and malabsorption. Individuals who have SIBO can also suffer from many chronic illnesses. This includes unintended weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, and osteoporosis.
SIBO and IBS

Studies have indicated that 84% of individuals that has IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) will have SIBO. SIBO is one of the causes of leaky gut, and leaky gut is one of the triad factors that can lead the body to have an autoimmune disease. Health care professionals that diagnose individuals who have SIBO can link the virus to other health problems that the individual may have. Studies have mentioned that when LPS (lipopolysaccharide) is moving from the large intestines to the small intestines, it can contribute to developing intestinal inflammation. With LPS, it can cause an increase of intestinal tight junction permeability or leaky gut.
So SIBO will release LPS into the gut, causing the leaky gut to the gut system in the body. Another study showed that autoimmune diseases are always a triad of a few different things. To have an autoimmune disease, you have to have the gene to get the disease. Although most people know that if they have a gene, doesn�t mean that they will have an autoimmune disease. Even if they don�t have an autoimmune disease, there�s an environmental trigger that will come on and creates an epigenetic change. This will cause the gene in the human body to be expressed.
So the first two factors of the autoimmune disease, are a genetic factor and an environmental factor, the third and final factor is intestinal permeability. So if the primary two factors that are causing disruption to the intestinal permeability, they will prevent the intestinal permeability to actually heal itself. With all three elements being linked to autoimmune disease and SIBO, it will cause the body to have the leaky gut syndrome and health problems to individuals.
So when doctors are diagnosing the patient that has SIBO, they will do a lactulose breath test. What this test does, is that it will indicate that the patient has IBS bloating, and it is causing them discomfort in their gut. Research stated that the lactulose breath test shows the correlation between the pattern of the bowel movements and the type of excreted gas in the stomach. So for anyone that is positive with IBS and takes the breath test, they will understand the consequences of the factors that are leading to the SIBO disease and causing leaky gut.
How do we get SIBO?
With the understanding of what SIBO is, we can see that SIBO is not the only cause of irritable bowel syndrome, but the big player of the syndrome. So taking a step back, we have to discuss what the MMG (Migrating Motor Complex) is before we go further in explaining the pathogenesis of the SIBO disease. Migrating motor complexes are waves of electrical activity that is sweeping through the intestines in a regular cycle. It often happens when a person is fasting, therefore with MMG, we can look at the acute gastroenteritis in the body.
With acute gastroenteritis, the body has some sort of severe infection like bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or a variety of things that are infectious to the gut; however, they are self-limiting. Healthcare professionals who see patients with these acute infections can see that most of the bacteria can cause gastroenteritis, pile up, and release CTD (cytolethal distending toxin). What CTD does is that it will create a reaction against vinculin; which regulates the ICC (interstitial cells of Cajal) and the ICC then regulates the migrating motor complex.
So when the CTD releases toxins in the gut, it causes a reaction to a molecular mimicry reaction. That reaction causes the body to create antibodies to fight against that toxin but through molecular mimicry. CTD looks exactly like vinculin and cross-reacts with the antibodies, So now those antibodies are attacking vinculin, thus damaging the ICC. Since the MMC clears the intestinal tract, when a person is fasting, and the CTD is damaging the intestines, SIBO is created since the body can not flush out the bacteria.
Studies have shown that there are many ways to get SIBO, it can happen by either food poisoning, abdominal surgery, or low stomach acid. Another thing to mention is that mostly 70% of SIBO is caused by food poisoning. Most people who had to suffer from food poisoning don�t realize that SIBO is already in their gut. So the research states that small bowel motility disorders can be the predispose development of SIBO since the bacteria may not be effectively swept from the bowel into to colon.
Treating SIBO
There are many ways to treat SIBO, healthcare professionals can suggest these treatments to their patients who have SIBO and start restoring their intestinal barrier in the long haul. So here are some of the procedures that can help the body and treat SIBO.
- Pharmaceuticals: If a patient has constipation and is taking rifaximin if the symptoms are not clearing up, adding another medication with rifaximin for 14 days may help in battling SIBO. It will take a bit longer, but it will help clear the SIBO out of the gut.
- Herbal Treatment: With herbal treatments, there are many ways to help treat SIBO naturally. It can be berberine containing herbs, oil of oregano, neem, garlic, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lauricidin, and Antrantil. These herbal treatments can naturally help to fight against SIBO, and studies show that 46% of patients feel a lot better in a short amount of time.
Conclusion
So SIBO is a bacterial disease that can disrupt the gastrointestinal tract and cause the leaky gut to the body. It will cause inflammation and can be in an individual�s body through three factors like genetics, environmental triggers, and food poisoning. It can be treated through pharmaceuticals and herbal treatments prescribed by doctors.� In honor of Governor Abbott’s proclamation, October is Chiropractic Health Month, learn more about this proposal on our website and read what the proposal is all about. The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and nervous health issues as well as functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health protocols to treat injuries or chronic disorders of the musculoskeletal system. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
References:
Bezine, Elisabeth, et al. �The Cytolethal Distending Toxin Effects on Mammalian Cells: a DNA Damage Perspective.� Cells, MDPI, 11 June 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4092857/.
Brown, Kenneth, et al. �Response of Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation Patients Administered a Combined Quebracho/Conker Tree/M. Balsamea Willd Extract.� World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Baishideng Publishing Group Inc, 6 Aug. 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4986399/.
Chedid, Victor, et al. �Herbal Therapy Is Equivalent to Rifaximin for the Treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth.� Global Advances in Health and Medicine, Global Advances in Health and Medicine, May 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4030608/.
Dukowicz, Andrew C, et al. �Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: a Comprehensive Review.� Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Millennium Medical Publishing, Feb. 2007, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3099351/.
Endo, EH, and Dias Filho. �Antibacterial Activity of Berberine against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Planktonic and Biofilm Cells.� Austin Journal of Tropical Medicine & Hygiene, 19 Feb. 2015, austinpublishinggroup.com/tropical-medicine/fulltext/ajtmh-v1-id1005.php.
Fasano, Alessio, and Terez Shea-Donohue. �Mechanisms of Disease: the Role of Intestinal Barrier Function in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Autoimmune Diseases.� Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, 1 Sept. 2005, www.nature.com/articles/ncpgasthep0259.
Ghonmode, Wasudeo Namdeo, et al. �Comparison of the Antibacterial Efficiency of Neem Leaf Extracts, Grape Seed Extracts and 3% Sodium Hypochlorite against E. Feacalis – An in Vitro Study.� Journal of International Oral Health: JIOH, International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry, Dec. 2013, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24453446.
Guo, Shuhong, et al. �Lipopolysaccharide Regulation of Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability Is Mediated by TLR4 Signal Transduction Pathway Activation of FAK and MyD88.� Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), U.S. National Library of Medicine, 15 Nov. 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26466961.
Lin, Henry C. �Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: a Framework for Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome.� JAMA, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 18 Aug. 2004, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15316000.
Preuss, Harry G, et al. �Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Herbal Essential Oils and Monolaurin for Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria.� Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 2005, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16010969.
Sienkiewicz, Monika, et al. �The Antibacterial Activity of Oregano Essential Oil (Origanum Heracleoticum L.) against Clinical Strains of Escherichia Coli and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa.� Medycyna Doswiadczalna i Mikrobiologia, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2012, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23484421.
Soifer, Luis Oscar, et al. �Comparative Clinical Efficacy of a Probiotic vs. an Antibiotic in the Treatment of Patients with Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Chronic Abdominal Functional Distension: a Pilot Study.� Acta Gastroenterologica Latinoamericana, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Dec. 2010, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21381407/.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gastro Intestinal Health, Gut and Intestinal Health, Wellness
The usage of integrated functional medicine is essential when it comes to our bodies overall health. Local practitioners and health coaches, talk with patients on what seems to bother them. Sometimes it is a simple adjustment, but mostly it�s what�s causing them problems on the inside. Some patients have inflammation around their intestinal epithelial barriers, and it can cause a leaky gut.
In the previous article, we talked about what the microbiomes do in our intestines and what is their functions are in the intestinal epithelial barrier. However, today we will discuss what the immunoglobulins antibodies do with proteins and peptides in the intestinal permeability. As well as explaining what the Lectin Zoomer and the Dairy Zoomer does when a patient has a food sensitivity and needs testing in a two-part series about the intestinal permeability and food zoomers.
Immunoglobulins
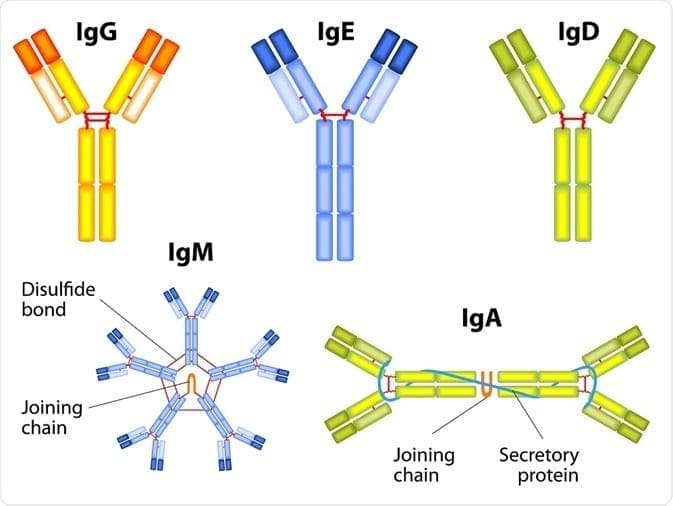
The first thing that we need to know is that immunoglobulins are immune-mediated reactions. So anything that involves the immune system will cause a hypersensitivity reaction to one or more food or foreign proteins, and their presence can be of one or more types of immunoglobulins.
There are 3 terms of hypersensitivities that can be involved with immunoglobulins:
- Allergies are the ones that are most common and are associated with anaphylaxis. Patients can have a very severe and acute immediate reaction to specific allergens like food or environmental like pollen or a bee sting.
- Non-allergies, sensitivity reactions involved either chemical mediators or antibody reactions.
- Food intolerances are non-immune-mediated reactions, and a good example is Lactose Intolerance or a bile salt deficiency. These can make somebody who has a food intolerance, can�t digest fat.
These three terms are often mistaken and used interchangeably clinically, but they are entirely different since they are not interchangeable. Especially when it comes to sensitivities and intolerances because those two commonly get used in place of each other, but they are totally different.
If you are testing your patient�s immunoglobulins, remember that antibodies are particular to each type of foreign substances and can be in three types of hypersensitivity. Antibodies will only bind an react to the specific proteins of the foreign material but not to the substance�s extract. The most common ones are type 3, where it involves IgG, IgA, and IgM. This type can tell us what cells and mechanisms are involved.
Type 3 Hypersensitivity Mechanisms
Here are the types of mechanisms that are involved with Type 3 immunoglobulins.
- Antigens are a foreign protein that is present and is recognized as a threat or non-self.
- Antibodies will bind to the antigen to neutralize or keep it from linking to anywhere else in the body. This is where the immune complex is formed.
- Immune complexes insert themselves into the small blood vessel, joints, tissues, and glomeruli, causing symptoms to the body.
- They are far more capable of interacting with complement proteins to form medium-sized complexes; which has an excess amount of antigens that are high pathogenic.
- However, once the immune complex is in the tissue, it can induce an inflammatory response and cause damage to the body. This damage is the result of the action of cleaved complement anaphylatoxins, which can mediate a mast cell degranulation.
- With the recruitment of inflammatory cells in the tissue, it can lead to tissue damage through phagocytosis.
IgA and IgG
In a previous article, we mentioned the mechanics of the intestinal permeability. However, we going to discuss what IgA antibodies and IgG antibodies do to the gut and to the entire body.
IgA Antibodies
IgA antibodies are found in the body where there is a mucosal lining around the areas like the nose, breathing passages, digestive tract, ears, eyes, and vaginal region. These surfaces are exposed to the outside of the environment either by air, food, or other foreign substances regularly.
IgA antibodies actually protect the body surfaces that are exposed to outside foreign substances, and these antibodies can be found in saliva, tears, and blood.
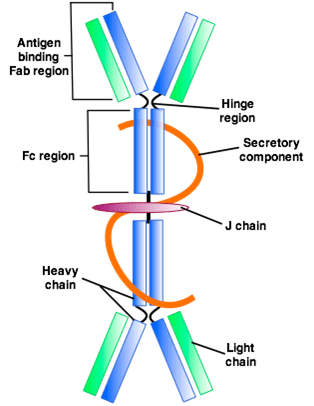
In the gut, however, it can bind to the mucosal layer on the top of the intestinal epithelial cells to form a barrier to neutralizing threats before they reach the cell. And that is very important, especially since IgA is like an insurance policy for your gut.
IgA antibodies are considered as non-inflammatory. Which means that they don�t stimulate inflammatory processes in the body like IgG does. They do, however, create a mucosal response to a foreign antigen, and it is usually microbial (ex., bacteria, yeast, viruses, parasites) or microbial toxins. They can also generate a response to pollutants, toxins, and recognized undigested food as a foreign protein.
In the intestinal lumen, IgA can be indicative of an immune response stimulated by T-b cell interaction. So a healing intervention, if a patient has an abundance of IgA antibodies may need to target TH1 and TH2 balance so it can regulate T-reg production.
IgG Antibodies
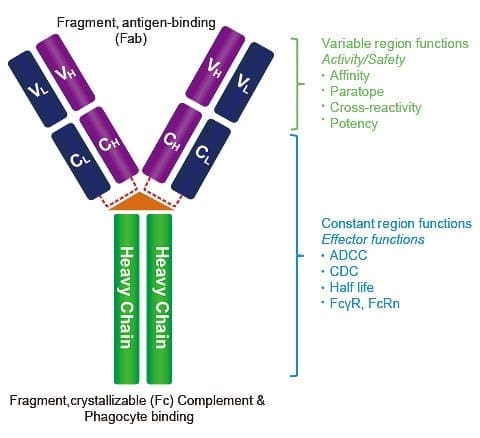
IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. They happen to be the smallest but the most common of all antibodies as they make-ups about 75% to 80% of antibodies found throughout the entire body. These antibodies are essential as they fight against bacterial and viral infections, and they are the only type that can cross the placenta.
They do indicate exposure to a specific antigen, but they don�t always necessarily indicate active inflammation; however, they can contribute to it in a dose-independent.
Why measure IgA and IgG?
So why do we measure IgA and IgG? Surprisingly some people don�t produce as much or any IgA antibodies, and therefore, local practitioners would not know if their patients have formed a reactivity to an antigen if they don�t check their IgG levels.
Surprisingly, some IgG antibodies are not an indicator of actual inflammation or disease process. Some IgG antibodies are formed in response to a protein as sort of a tracker in the body but do not elicit a reaction. However, IgA antibody is coupled with IgG to indicate a bit stronger immune response to an antigen in some cases.
IgA and IgG in the Protein Level
IgA and IgG testing in the protein level is what the food sensitivity tests are looking at. They look for the whole protein, which is the extract level. All food sensitivity test looks for residues of carbohydrate and lipid-based particles. It�s not pure protein but that what the test does, it seems for the reactive compound. Some of the strengths are that the test gives an acute measure of IgG and IgA to a specific protein. It can also be suitable for associating Type 3 reactions involving IgG and IgA complexes, and if the IgG is pathogenic, then it will be beneficial.
Some of the weaknesses are that IgG can be a protective antibody, and it may be a good thing. It means that the immune system is handling it and there�s nothing necessarily wrong about that. IgG and IgA antibodies represent whole proteins being presented to the immune system can it also be an indicator that a patient may have a lack of sufficient digestive capacity when many food sensitivities are being detected.
IgG and IgA in the Peptide Level
When IgG and IgA are being tested at the peptide level, this is where the food zoomer test focuses on. This is because there is a high level of antibodies specificity, cross-reactivity is minimized if not completely eliminated. The concept of foods that are cross-react, for example, gluten, might cross-react to other foods that are similarly shaped in their molecular structure, then you should eliminate the gluten out of your diet as well as the foods that are in contact with them.
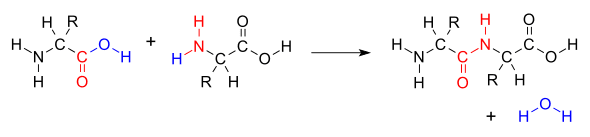
However, if the antibodies to gluten are being picked up at the peptide level, then it won�t look at those foods that are being cross-reactive to gluten. The antibodies will only bind to the individual peptides than the whole protein. This will be a more accurate assessment of whether or not that the patient is sensitive to the foods their body is reacting to.
What is Loss of Oral Tolerance?
Loss of oral tolerance is a term used to describe the phenomenon of someone developing a sensitivity, whether it is accompanied by symptoms or not, and it�s usually a commonly consumed or semi-regularly consumed food. When that happens, there is a production of inflammatory cytokines and antibodies that will respond to the continued exposure to the food.
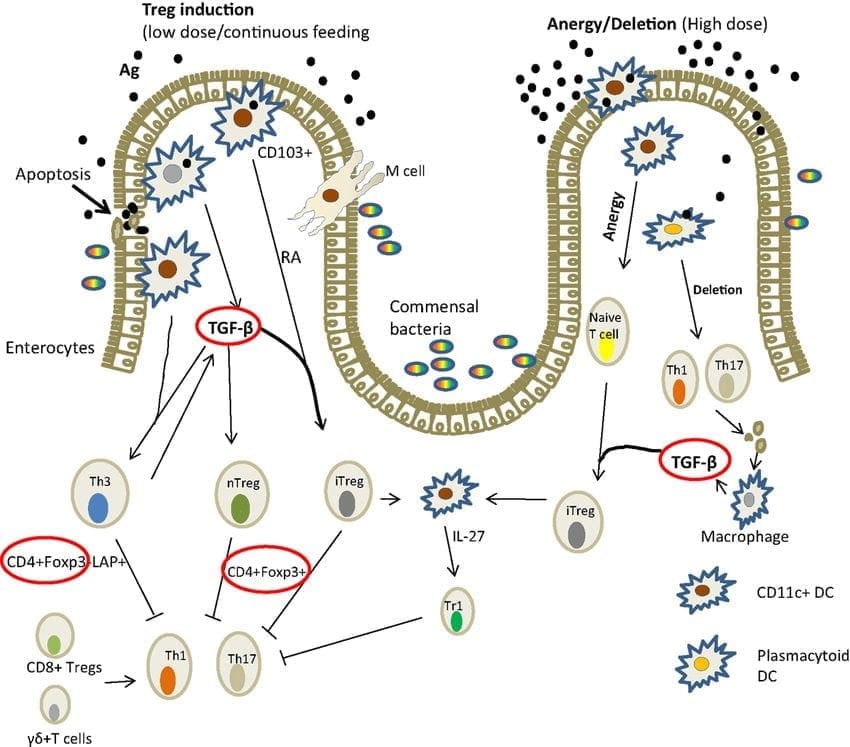
For the inflammatory responses to be eliminated, patients have to remove the offending food for about 3 to 4 weeks if IgA antibodies are present or 3 to 6 months if the IgG antibodies are present as well. This is the only way for the antibodies to disappear, and the intestinal permeability can heal. But the disappearance of antibodies does not guarantee that oral tolerance has been established. If you are retesting a patient and if the antibodies are gone, that indicates that the patient has done an excellent job in eliminating that food from their diet. However, the only way to know is to reintroduce the food and retest after a few months, just to make sure that no antibodies are being produced after the intestinal barrier has been fully healed.
Conclusion
All in all, that is what the intestinal permeability does when we have IgA and IgG antibodies and what do they do when there is food sensitivity in the body.� However, it is crucial that our patients understand that we here at Injury Medical Clinic, take the time to study what causes inflammation in our patients and using integrated functional medicine to make sure that their intestines are being healed naturally. In the next article, we will discuss the difference between peptides and proteins, and about the Lectin and Dairy Zoomer.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Chiropractic, Functional Medicine, Nerve Injury, Wellness
When we look at our patients, we try to figure out what is causing their ailments from living their best lives. Some practitioners would prescribe medications to alleviate pain. While other practitioners will start trying to figure out what is causing the patient to have these ailments. Here at Injury Medical Clinic, we talk to our patients about the importance of functional medicine and how it can benefit them. In this article, we will be discussing Connective Tissue Disorder and how it is linked to wheat-related disorders.
What is Connective Tissue Disorder?
CTD (Connective Tissue Disorder) is an autoimmune disorder that can affect the connective tissues such as the collagen and elastin in our skins. This disease is highly inflammatory and can occur alongside with other autoimmune diseases, and it is common if families have a history of Connective Tissue Disorder.
About 3% of the population has a connective tissue disorder, and it is most likely to occur in women than men. In fact, women who are diagnosed with connective tissue disorder have a ration of 10:1, compared to men.
CTD includes (but is not limited to) the following conditions:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE is a widespread and chronic autoimmune condition, for unknown reasons, can cause the immune system to attack the body�s own tissue and organs, including joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, brain, blood, and skin.
- Sjogren�s Syndrome: This autoimmune disease causes white blood cells to attack moisture-producing glands, such as the tear ducts and salivary glands. This can make it very difficult for the body to produce tears and saliva.
- Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma): This condition causes the skin and connective tissue to harden and tighten.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): RA is a chronic inflammatory condition and an autoimmune disorder that can generally affect the lining of the joints, but mostly in the hands and feet. Rheumatoid arthritis causes painful swelling that can eventually lead to deformity and erosion in the joints and bones.
- Polymyositis: This is a persistent inflammatory muscle disease that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles, which can affect your body movement.
- Dermatomyositis: This is an uncommon inflammatory disease that is marked by muscle weakness and can cause a distinctive skin rash.
These conditions can group together and can be very hard to diagnose because of the research and many tests that the patient is taking. Surprisingly, the average patient suffers from symptoms for 3.6 years before meeting diagnostic criteria. And the systems alone are difficult to classify, and often mimic or overlap other conditions. Some of the symptoms include hair loss, muscle pain, numbness or tingling, inflammation, low-grade fever, weakness and fatigue, joint pain, sensitive skin, and rashes.
Increased Need For Advanced Testing and Early Diagnosis

Sadly though, patients wait longer when they have these conditions, and it can worsen in the process as it takes years to get diagnosed for CDT. Practitioners can use treatments on their patients, but the medications act as a band-aid to mask the symptoms, but it does not adequately address the root causes of the disease. Sometimes the symptoms can progress faster than the current diagnostic test. So if you want to make sure your patients have any autoimmune diseases, run a diagnostic test on them, so you can detect early stages of the disease and start treating them so it can go away.
ENA and ANA
Extractable nuclear antigen (ENA) is a blood test that looks for antibodies to about 6 or 7 different proteins in the body.
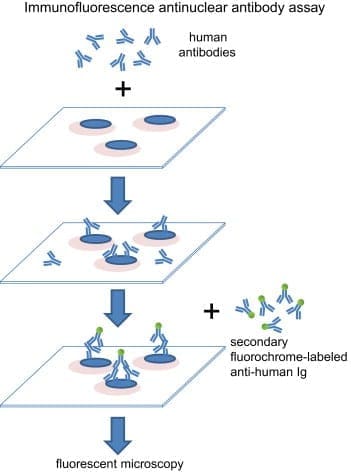
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) is used as an initial test that can help evaluate a person for an autoimmune disorder that can affect many tissues and organs throughout the body. It is most often used when practitioners are diagnosing patients for systemic lupus erythematosus.
Surprisingly ENA can be more predictive than ANA. However, patients were followed for 2 years, and about 20% of those patients developed positive ENA.
Vibrant Wellness Wheat Zoomer
In�a�previous article, we talked about gluten sensitivity and introduced the wheat zoomer. What the Vibrant Wheat Zoomer does is that it actually runs a test on your microbiomes to determine if you have a wheat sensitivity or a gluten sensitivity. It can actually detect IgG and IgA antibodies as well as detecting if your body has the celiac disease and intestinal permeability.� It pairs well with the Vibrant Gut Zoomer, and here at Injury Medical, we use the Wheat Zoomer on our patients to inform them about what is causing them to have gut inflammation or even leaky gut.
Celiac Disease and Wheat Allergens
Celiac Disease and Wheat Allergens is an autoimmune disorder in genetically susceptible individuals, and it affects about 1% of the population. In a previous article, we mentioned the hidden problems that gluten does to the body. And surprisingly, any wheat-related disorders can exist on a spectrum, this includes wheat allergy, gluten sensitivity, and wheat sensitivity.
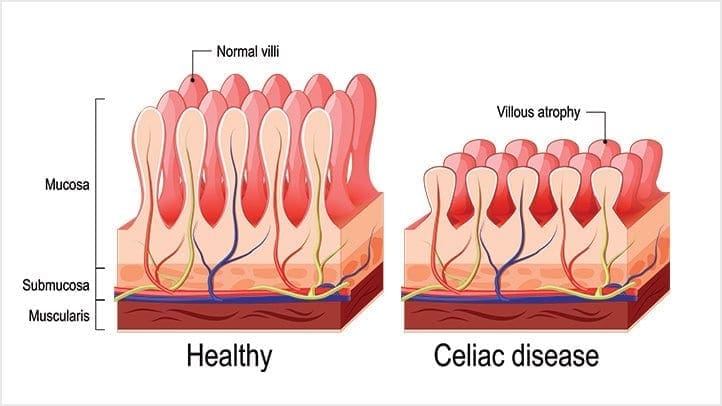
When a person, has the celiac disease, having any traces of wheat can actually upset their intestinal permeability and causing them to have a leaky gut.
The Connection to CTD and Celiac Disease
But how do connective tissue disorder and celiac disease are connected? Well, surprisingly, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and celiac disease (CD) share multiple aspects in epidemiology and clinical manifestations. Both disorders have been proven to be influenced by comparable environmental factors and a recent incidental surge of associated antibodies. Even though they have different depositions, both of them are mediated by endogenous enzymes that target different tissues and organs.
Conclusion
However through functional medicine; local chiropractors and health coaches here at Injury Medical Clinic, strive to understand what do our patients need to make their bodies feel better. If we can use functional medicine to prevent leaky gut at the early stages and help our patients with any ailments that they may have, then we can gently push them into the right direction of exercising throughout the week (even if it is about thirty minutes) and eating nutritious, whole, organic foods; as well as, preventing their ailments coming back then their bodies can finally heal.
by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Wellness
In the last article, we talked about what the polyphenols do in the microbiome and in the previous section, we discussed about the microbiome functions in our bodies. However, today we will be concluding the three-part series of the microbiome functions in our bodies as well as presenting on the top 5 environmental toxins that can disrupt the gut microbiome, finding ways to de-stress ourselves, and learning about the different foods that can help detoxify our bodies so we can live a healthier life.
Top 5 Environmental Toxins Disrupting the Gut Microbiome
Triclosan
This is a synthetic antibacterial chemical found in personal care products such as soap, mouthwash, toothpaste, hand sanitizer, and deodorant. It is easily absorbed through the skin and gastrointestinal tract and rapidly alters the microbial composition of the digestive tract if it is ingested. However, this rapid restructuring of the gut microbiome impairs the immune system-regulating activities of gut microbes.
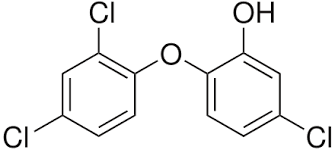
We use this chemical mostly in our daily skincare and hygiene routine so that way we won�t be sick. We tend to use this chemical compound to make us smell, look, and feel good frequently, especially in the cold and flu seasons where we use them the most so we won�t get sick. In fact, the frequent use of antibacterial products has been associated with an increased risk of food sensitivities, seasonal allergies, and asthma.
Pesticides

Surprisingly there are a staggering 1 billion pounds of pesticides used per year in the United States, and 5.6 billion pounds are used worldwide. Most farmers used it to spray down the insects so that way their crops won�t be destroyed. And we used pesticides on our lawns to get rid of weeds and keep the bugs off our gardens.
However, did you know that pesticides can kill beneficial bacteria in our gut? Studies, especially animal studies, indicate that pesticides can destroy the beneficial gut bacteria and can increase the risk of intestinal dysbiosis and cause immune system disorders, among with many other chronic health issues.
Plasticizers
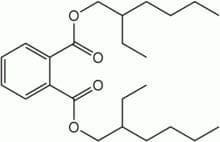
These are chemicals that provide flexibility or rigidity to plastic products. These chemicals are highly prevalent in our environment and have a significant impact on gut bacteria. �Surprisingly the most common plastics are mostly BPA (Bisphenol-A).

Bisphenol-A (BPA) can be found in plastic water bottles, receipts, and the lining of canned foods. They can alter the healthy gut flora and disrupts the body�s hormonal system by mimicking the hormone estrogen. We do use these to put our leftovers in after we consume food. But now and days when we meal prep our food, we do look for containers that are BPA- free. However, while often being marketed as �BPA-free,� the plastic alternatives may be equally, if not more, harmful to our gut microbes.
Bisphenol-S and bisphenol-F demonstrate endocrine-disrupting effects that are comparable to BPA. These adverse effects may extend to the gut microbiome, causing disruption. Phthalates are another class of endocrine-disrupting plasticizers that are used as solvents in personal care products and vinyl plastic, and they also reduce the levels of beneficial gut bacteria.
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals, such as cadmium, lead, and arsenic, can reduce the levels of beneficial bacteria in the gut that protect against intestinal inflammation and may promote inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders. All microbes are responsible for methylating or demethylating metals, and the exposure may exceed the capacity to perform this. Due to industrial pollution, heavy metals are the most common contaminants that are in the soil and drinking water when we grow food and drink from the tap.
Pharmaceutical Drugs
Surprisingly most pharmaceutical drugs can help our bodies fight off infections or alleviate some pains we may be inflicted. But those antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiome and cause an imbalance to our gut bacteria. We here at Injury Medical clinic, actually recommend our patients to alternatives to these drugs if you don�t want to disrupt your gut microbiome.
Functional medicines like whole foods and supplements can actually alleviate the pains that may cause disruption in your body.
Protecting the Microbiome From Environmental Toxins
When you want to live a healthier life and want to protect your body�s microbiome try these alternatives to get rid of these environmental toxins.
- Instead of using conventional cleaning products, which often contain triclosan, try switching to a plant-based brand. Also, try making your own cleaning products at home with natural ingredients.
- Avoid commercial body care products, as these are a significant source of triclosan, phthalates, and parabens. If you have any absorption of these chemicals, try checking out the Environmental Working Group�s Skin Deep Cosmetics Database. This database can help you find natural, healthy body care products that don�t contain microbiome-disrupting chemicals.
- Eat organic produce. Conventionally-grown fruits and vegetables are a significant source of microbiome-disrupting pesticide exposure. Research indicates that consuming organic food can significantly lower your body burden of pesticides, thus protecting your gut microbes. But y9ou are going to eat organic produce, remember to wash it first to get rid of excess pesticides.
- Try reducing your plastic intakes and limit your consumption of canned foods to reduce your exposure to BPA and BPA alternatives. When you are meal prepping, try using glass or stainless-steel water bottles and storage dishes instead of plastic, and opt for fresh food instead of canned.
- Try filtering your drinking and bathing water. Unfortunately, tap water is rife with pesticide residues, heavy metals, plasticizers, and pharmaceutical drug residues and can come off as a milky white if it�s not treated. So try to consider investing in a high-quality water filter that can remove these substances from your drinking water.
- Support your gut microbiome by consuming prebiotics and probiotics. In a previous article, we talked about probiotics in our gut. Probiotics can add beneficial bacteria to your stomach and may even help in the metabolism of toxins that are in your body�s microbiome. Prebiotics, a form of indigestible dietary fiber, that feeds probiotics and helps to support their growth and proliferation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Other Forms of Whole Body Detoxification

There are many ways to try and detoxify our bodies, so here are some examples:
- Sauna therapy
- Yoga, trampoline
- Meditation
- Energy healing/shamanism
- Taking a much-needed vacation
- Learn communication methods to accommodate multiple needs and to deal with stressful situations
Rebuilding the Gut Microbiome
When local health coaches, practitioners, and chiropractors are helping patients, they can provide a comprehensive strategy to help them gain a healthier life. When you want to rebuild your gut microbiome, try to reconstruct the natural digestive function with food/herbals. This will help support the immune system and nutritional status by creating the good bacteria in your liver and flushing out the toxins out of your system. However, try to avoid any foods that can trigger inflammation and can cause leaky gut.
Rebuild Natural Digestive Function
When you are rebuilding your natural digestive function, try finding food and supplements that contain zinc, Vitamin C, and bitter greens that can aid in the production of hydrochloric acid (HCL). However, avoid excessive amounts of fat in your diet so you won�t cause a leaky gut Also take some enzymes if you need them until your digestive is balanced and fully restored.
Support the Immune System and Nutritional Status
When your immune system is being overworked, try using micronutrient testing to identify deficiencies. Most SIBO patients are typically low in B12/iron, zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D.� But all these vitamins and supplements can support the immune system. With SIBO patients, they try to work on cleaning out their liver since it�s one of the major organs that flushes out the toxins in our bodies. If you do have SIBO, try adding more fruits and plant foods that can help �clean out the liver.� Certain fruits can be tolerated and titrated up after treatment over time, but try to reduce meat/animal fats and fats in general; since they are harder to digest and can contribute to imbalanced bile acid secretion. Also, use liver support herbs and supplements such as glutathione and silymarin.
Avoid Foods that Can Provoke Inflammation

In a previous article, we talked about food sensitivity and what to do if you have it. Some testing can be helpful to determine if other foods may need to be eliminated. Here are the most common foods that provoke inflammation in dysbiosis are:
- Gluten
- Dairy
- Eggs
- Soy
- Corn
So if you have a food sensitivity, start by slowly build the natural SCFA�s with small amounts of natural resistant starch (e.g., cooked/cooled potatoes). However, if the patient is being treated with SIBO, introduce it after. Also considering adding other sources of food so it can help grow the good bacteria in your gut. But also keep HCL production active to clean out the stomach and upper part of the small intestine.
This will ensure that the good bacteria will grow over time with your diet and the help of probiotics and fermented food. But if a patient has SIBO take caution so the patient won�t disrupt the treatments they are in and are completed.
If you are taking care of a patient, carefully choose probiotic based on symptoms they have. Some will need a d-lactate free formula, and you can bring up the dosage over time until their treatment is complete. Some CFUs (colony forming units) will vary by product and viability through the GI tract (enteric-coated vs. not), and some probiotics may need to be used long term in some individuals.
Fermentation

Fermented foods are very beneficial to our gut flora as they actually help in the production of good bacteria in our intestinal barriers. Fermented foods and beverages are literally alive with strong pronounced flavor and nutrition. However, not all preserved foods are fermented with live cultures; some may be brined through the use of vinegar and/or salt, and do not impart probiotic benefit.
 �Fermentation is the transformation of food by various bacteria, fungi, and the enzymes they produce. It is important to recognize that fermentation is a natural phenomenon much broader than social, culinary practices; cells in our bodies are capable of fermentation. In other words, humans did not invent fermentation; it would be more accurate to state that fermentation created us.� � Dr. Alex Jimenez�D.C., C.C.S.T.
�Fermentation is the transformation of food by various bacteria, fungi, and the enzymes they produce. It is important to recognize that fermentation is a natural phenomenon much broader than social, culinary practices; cells in our bodies are capable of fermentation. In other words, humans did not invent fermentation; it would be more accurate to state that fermentation created us.� � Dr. Alex Jimenez�D.C., C.C.S.T.
Conclusion
So all in all, those are some of the many ways to actually help our bodies microbiome when we want to live a healthier life. Here at Injury Medical Clinic, local chiropractors and health coaches, actually use functional medicine to patients so that way, they can fix their ailments naturally, without the use of drugs and non-conventional methods. If we can change a person�s lifestyle with functional medicine, we can repair the microbes in our bodies, one at a time naturally, of course.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Wellness
In the last article, we talked about how the microbiomes in our body worked and functioned. As well as learning what each microbe does in our bodies but mostly in our gut. When we are learning more and more about the microbiome, we discover many exciting things that our bodies are capable of as well as being the workers in our intricate immune system. In today�s article, we will be taking a look at what polyphenols does to our microbiomes as well as specific vitamins that are very helpful to our gut and going in-depth more with SCFAs (Short Chain Fatty Acids) and the Tight Junction.
The Role of Polyphenols in Microbiome Balance
Polyphenols, or phenolic compounds, are considered a type of micronutrients, and they are plentiful in plants. They have been well-studied for their role in the prevention of chronic diseases such as CVD, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. They also have antioxidant properties, and there are several hundreds of polyphenols that are found in edible plants that serve a giant purpose of defending our bodies against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens.
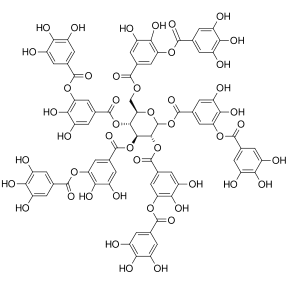
To figure this out, think of it like this: The bacteria in our large intestine releases polyphenols from the plants we eat in our diets. It is then transformed into a diet composition that alters the bacterial ecosystem (through the prebiotic effects and antimicrobial properties) to make our gut happy.
Here are some of the microbes that are in polyphenols:
- Phenolic acids: These are derivatives of benzoic acid and derivatives of cinnamic acid.
- Flavonoids: These microbes contain flavonols (e.g., quercetin), flavones, isoflavones (e.g., phytoestrogens), flavanones, anthocyanidins, and flavanols (e.g., catechins and proanthocyanidins)
- Stilbenes: These microbes are resveratrol
- Lignans: these are minor in the human diet and are linseed oil
Surprisingly some factors affect the polyphenol content of plants, and these include:
- The ripeness at the time of harvest
- The environmental factors (exposure to light, soil nutrients, pesticides)
- processing and storage
When we eat organic fruits and vegetables, they have more polyphenol content that is usually, due to growing under slightly more stressed conditions. Which requires the plant to generate a stronger �defense and healing� response to the environment, and only 5�10% of the total polyphenol intake is absorbed in the small intestine. And 90-95% polyphenols that are linked to fibrous components must be liberated through hydrolysis by bacteria in the large intestine.
Surprisingly some polyphenols do not show up in plasma in humans after ingestion, and a large quantity is metabolized by intestinal bacteria or used to neutralize various pro-oxidizing agents in the intestinal lumen.
Clostridium and Eubacterium (which are both Firmicutes), are the primary metabolizers of polyphenols. Studies theorized that higher polyphenol intake may play a role in shaping the Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes ratio (e.g., inflammatory response potential, obesity, etc.) and can be harmful to our bodies.
However, more recent studies have shown effects of inhibition on Clostridium and Staphylococcus of polyphenols such as grape seed extract, in favor of Lactobacillus and other studies have demonstrated potent inhibition of phenolic compounds thymol (thyme) and carvacrol (oregano) on Escherichia, Clostridia and other pathogens, while simultaneously leaving Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria have been unaffected.
Here are some other examples of some polyphenols:
- Resveratrol increases Clostridia, Lactobacillus, and Bifidobacteria
- Blueberry phenolics increase Bifidobacteria
- Phenolic compounds in tea suppress C difficile and C perfringens
- Catechins (found in high doses in teas and chocolate) act on different bacterial species (E. coli, Bordetella bronchiseptica, Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella pneumonia, Salmonella cholestasis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis) by generating hydrogen peroxide and by altering the permeability of the microbial membrane
- Some studies have shown that polyphenols can interfere with bacterial cell signaling and quorum sensing (environmental sampling)
- Polyphenols can also cause bacterial populations to stop expansion through signaling interference
- Some research indicates certain polyphenols may be able to block the production of bacterial toxins (H. pylori and tea/wine polyphenols)
The Applications for A Diet

When it comes to eating a healthy diet, variety does matter. The colors, the types of fibers each organic food has, and whether you are going to do it daily or weekly. When you are trying to be in a healthy lifestyle, it always starts with the food. When you are looking for fresh produce, try to emphasize fresh, organic, and minimally processed versions of polyphenol-rich foods. However, don�t boil produce. Instead, try steaming then, and it is the best, but roasting or light frying is not only better, but it tastes so good.
Vitamins that help our Microbiome
When we are older, we tend to lose specific vitamins that actually helps us and our bodies to be healthier. Here are some of the vitamins that are really good for our gut and can help us prevent leaky gut.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D controls the development of gut-associated lymphoid tissue in our bodies. It is trafficking between gut dendritic cells, and they can differentiation of T-regs and T-reg function in our gut. But the expression of VDR, which influences IL (interleukin) production and tight junction integrity to help our gut.
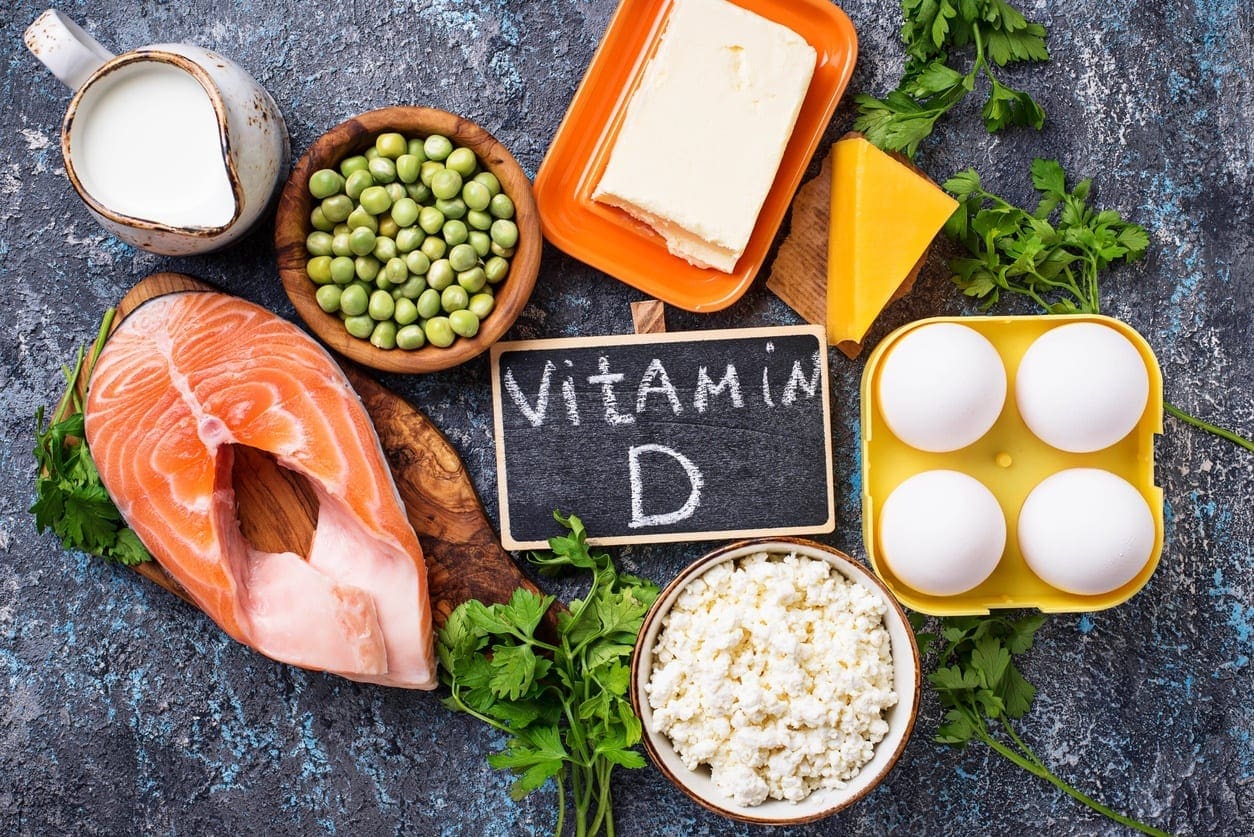

When it comes to our gut, here are some of the effects of Vitamin D on the gut microbiome. The higher the Vitamin D levels are, they will allow commensal bacteria to secrete more AMPs (antimicrobial peptides). When patients take a high dose of Vitamin D, over 5 weeks can lead to a significant reduction in Pseudomonas spp and Shigella/Escherichia spp in upper gut intestines.
Another thing that Vitamin D does is that it can increase T cell differentiation in the colon. A lack of T-regs increased the incidence of asthma, allergies, autoimmune, and autism. But T-regs can prevent the development of aberrant immune responses such as autoimmune and food sensitivities. We here at Injury Medical Clinic, talk about functional medicine to our patients and try to help them recover from their ailments.
Because Vitamin D exposure fluctuates seasonally for many individuals, it has been observed that lower Vitamin D levels in the winter tend to lead to changes in the intestinal microbial balance. This will make our bodies have a decreased level of Bacteroidetes and an increased level of Firmicutes. This is the reason for �winter weight gain� in many individuals as F: B ratio changes.
Vitamin A

This is a retinoic acid that is required by dendritic cells (DCs) to induce T-cells (and B cells) which are the �tracking and regulation system� of the mucosal immune response. Because of this, T-cells must differentiate into T-regs to maintain a �calm and cool� system or immune tolerance to both our environment, symbiotic organisms, and food.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids

We talked about Omega-3s in a previous article as they are one of the many supplements that we can�t produce in our bodies. It can be mostly found in fish, and some plants can contain omega-3s. But it is a vital team player when we are trying to be healthy and can prevent a leaky gut. Not only that but omega-3s are crucial importance to more youthful skin.
SCFAs (Short Chained Fatty Acids)
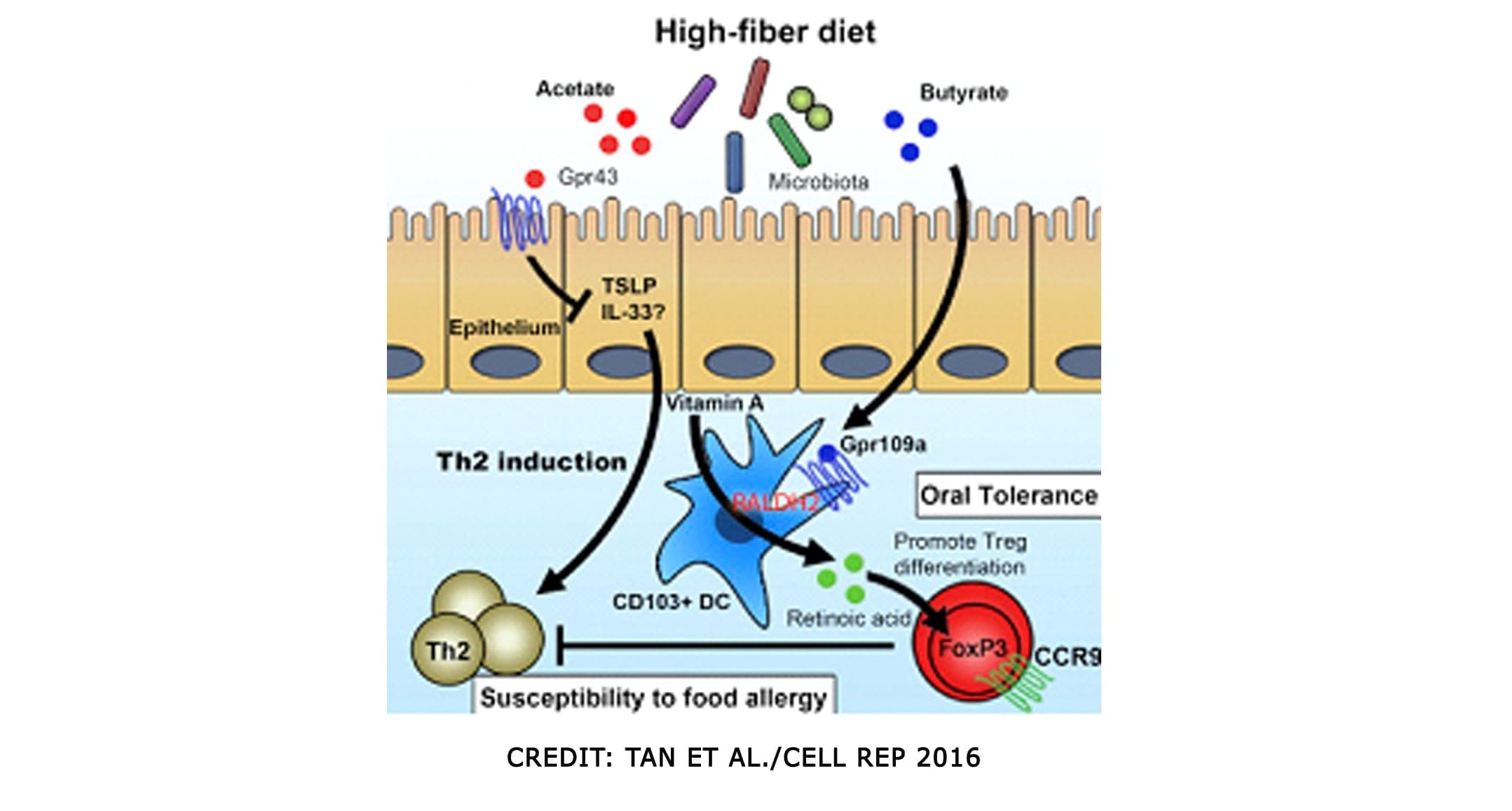
SCFAs (Short Chained Fatty Acids)�are well-studied to demonstrate anti-inflammatory properties in the large intestine. They are the primary source of fuel for cells lining the intestinal epithelium of the large intestine. They contained: �Butyrate, Proprionate, Acetate. In a previous article, we discussed what SCFAs do when we eat fatty food. It can be both good or bad, depending on what kinds of food you consume. SCFAs act on G-protein coupled receptors to induce differentiation of T-cells, but also on those GPRs in DCs. They can both be direct and indirect influences on our gut.
SCFAs can produce bacteria and can directly impact T-reg production. And that SCFAs inhibit the mucosa and competitively inhibit opportunists. Some foods that provide higher resistant starch will typically yield the most short-chain fatty acids upon microbial fermentation
Tight Junction Modulations
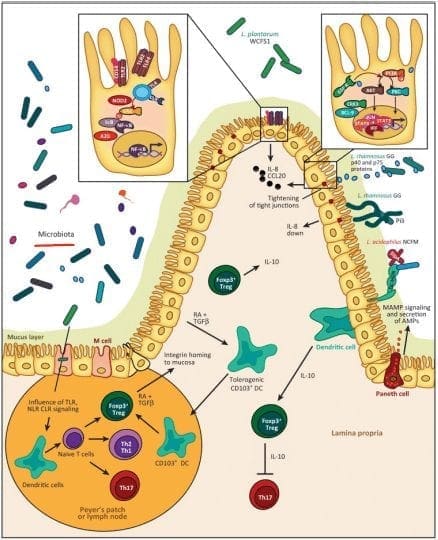
The tight junctions are the gateways between the epithelial cells. In a previous article, we took a look at what the tight junction is. They control the flow of nutrients, macromolecules, and other substances that are usually allowed to pass through without cellular diffusion or absorption.
Conclusion
All in all, we covered a lot of information about what polyphenols does as well as specific vitamins and supplements that can help our bodies prevent a leaky gut. The microbiomes in our collection and the use of functional medicine can be beneficial in helping us not only to a better, healthier life but, a working, functional body for us when we are older. Tomorrow we will end this three-part series with foods and tips to have a healthy microbiome in our gut and our bodies.
by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Wellness
To understand exactly how lipopolysaccharides and gram-negative bugs affect the immune system we must first investigate what lipopolysaccharides are and their role in gram-negative bacteria and the human body as a whole.
LPS (Lipopolysaccharides)
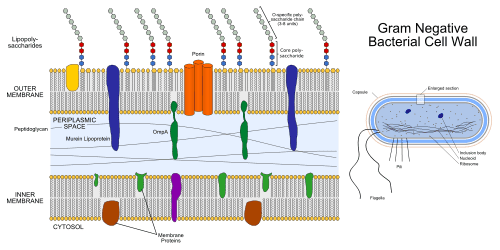
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid (fatty acid) and a polysaccharide composed of the O-antigen, outer core, and the inner core all joined by covalent bonds. �Lipid A in LPS is the hydrophobic component responsible for the major bioactivity of LPS. Hydrophilic polysaccharides consist of long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) linked together by glycosidic linkages. LPS play their role in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria by supporting the structure of the bacteria and shielding the membrane from chemical attack. Gram-negative bacteria are related to foodborne diseases, respiratory infections, plagues, and some sexually transmitted diseases. Some gram-negative bacteria have become so resistant to antibiotic drugs that they are often very difficult to treat and unfortunately vaccines are not available for these types of bacterial infections. Additional enzymes can sometimes alter the structure of the LPS, and though the structure is not required for the bacteria�s survival it is closely related to the virulence of bacteria. For example, the lipid A component of LPS can cause toxic reactions when lysed by immune cells. LPS in humans trigger the immune system to produce cytokines (hormone regulators). Production of cytokines is a common cause of inflammation.
Now that we are able to recognize the relationship between LPS, gram-negative bacteria, and inflammation/infections in the human body, we must understand how to prevent and treat infections related to gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative bacterial infections are caused by contact between infected and non-infected peoples. They are very common in healthcare settings, but by taking simple measures such as hand washing and keeping a strong immune system will help prevent them. How do we keep a strong immune system? Choosing a healthy lifestyle is the first most basic step in this process. Because the immune system is a system, we must understand that there is no direct way to improve its strength. It is strengthened through what we put into our body and how we treat our body. However, it is important to distinguish between building a strong immune system and boosting the number of immune cells in our body. It is potentially harmful to boost the number of immune cells because there are so many different kinds of cells in the immune system that respond to so many different microbes in so many ways. Diet, exercise, reducing stress levels, and some herbs and supplements all contribute to building and supporting a strong immune system.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have learned about lipopolysaccharides and the role they play in gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria are known to be harmful to the human body so we have found ways to prevent the harmful infections it causes. The immune system plays an obviously important role in fighting infections, but it needs to be strong to support our body and fight infections efficiently. This basic knowledge is provided to set the basis for further research on how to support the immune system.
Resources:
www.niaid.nih.gov/research/gram-negative-bacteria
www.scbi.nih.gov/pubmed/20593260
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gram-negative_bacteria
www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/how-to-boost-your-immune-system

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Wellness
In the last three articles, we introduced the wheat zoomer, went in-depth about the intestinal permeability, and the microbes in our gut. We also talked about the hidden problem with gluten as well. Today we will be discussing what to do after your patient comes in for a check-up after completing their gut healing process. For this to work, patients have to be gluten-free for the results to work. After the healing phase, local chiropractors, health coaches, and physicians can introduce gluten back slowly into the patient’s diet.
Checkups
When the patient comes in for a check-up, here are some of the things doctors look for:
- If everything is green, re-introducing gluten may be possible for patients.
- If anything is still yellow or red, patients must continue to avoid gluten and keep the gut healing process until the test results are all green.
After the appointment, patients can retest the wheat zoomer in about 3-9 months. However, there are about 50% of individuals with celiac disease that may also have antibodies to casein and may have to go dairy-free to heal their gut. Although some individuals are gluten sensitive may not be lactose intolerant but can go dairy free if they want to.
Lectins
Surprisingly all plants have lectin, but some of them are not problematic to humans thankfully. Legumes and grains play a role in increasing the diversity of microbes that may be beneficial or harmful to our bodies. Wheat Germ Agglutinin is the only specific lectin to the Wheat Zoomer, but it doesn�t reflect the overall lectin sensitivity but, consider the lectin zoomer to determine any particular lectins that your patient is sensitive to without eliminating unnecessary foods that are beneficial to the gut healing process.
Soy

Many studies show that soy may be a problem due to the saponin since it does have higher lectin count. Here at Injury Medical clinic, we suggest that running the Lectin Zoomer on our patients with intestinal permeability makes sense for them to heal correctly. But animal studies stated that soybean agglutinin has the effect of the increasing release of zonulin away from the TJ (tight junction). And a human study reported that if the soy saponin is poorly absorbed or utilized by the human intestinal epithelial cell will end up metabolizing the intestinal bacteria and cause more harm to human.
Surfactants

Known as sucrose monoester fatty acids is mostly used in cosmetics, food preservatives, food additives. Sucrose esters are used as a surface treatment on some fruits like peaches, pears, cherries, apples, and bananas. It keeps the moisture on the peel or rind controlled. Sucrose mono ester used in cosmetics as an emulsifier.
Bone broth/Collagen

Up to this date, there are minimal studies that have examined the role of bone broth or collagen that it repairs the intestinal barrier. It all depends on the animal and the bone it comes from and the contents that people have put in a bone broth soup.
However, there is a small body of evidence for the use of collagen peptides seem to support the usage in their autoimmune disease treatment protocol. But the results cant be extrapolated whether bone broth would have similar effects. So more studying about bone broth is needed.
Organic Produce

When people say that they are going organic, it is beneficial for people that are willing to change to a healthy lifestyle. Granted that organically produces are locally grown, but still, organic produce or non-organic produce will not have less or safer pesticides. They are different, but all of the crops like fruits and vegetables are grown with pesticides.
Just like all fruits and vegetables, still, wash them thoroughly to reduce the number of pesticides and surfactants exposure and enjoy them to your heart’s content.
Resistant Starches

Resistant starch foods are a form of carbohydrates that can be converted to short fatty acids by SCFA-producing bacteria. With higher SCFA levels, these starches aid immune tolerance, T-cell differentiation, and intestinal barrier homeostasis. Other types of fibers are high value, and variety is essential. Like for example, cooked/cooled rice and potatoes are excellent resistance starch foods.

“Eat like a vegetarian who eats meat.”- Dr. Alex Jimenez�D.C., C.C.S.T.
Polyphenol Foods
Polyphenols, flavonoids and other phenolic compounds will aid to maintained TJ stability through inhibiting phosphorylation of TJ complexes.
Fermented Foods

Fermented food or drinks that contain live probiotic cultures are excellent in promoting a healthy gut. However, it is challenging to study fermented food and beverages due to highly variable stains, composition, nutrient content. But studies found that participants who drink a fermented plant extract drink saw improvements in their body and increased total antioxidants and total phenolic in plasma as well as with reducing total C and LDL-C.
Beneficial bacteria like Bifido and Lactobacillus were increased while E Coli and C perfringens were decreased in the gut. So drinking or eating fermented food can help our gut and help our bile growth to be flushed out.
Granted, we all know that trying to be healthy is very hard. It is true that even though exercising is easy because we can do it over and over again until we are masters at it but, when we overdo the exercises it will cause harm to our bodies and hurting it in the process. �Eating healthy is hard as well because our bodies may have a food allergen or a food sensitivity that will make us disappointed that we can�t enjoy the foods we want to eat. Yes, eliminating diets are very hard and challenging to follow in the long term and have poor compliances when we don�t put in the work. So start by exploring other tests to tailor patients diets to meet their health needs and prolong their recovery period.
Supplements

Supplements are fantastic to aid the valuable nutrients and minerals our bodies can�t produce. Common supplements prescribed include:
- L-glutamine
- Vitamin D3
- Collagen
- Colostrum
- Zinc carnosine
- Ox bile
- Omega-3s
- Turmeric/Quercetin
- Magnesium
Stress Management

Granted that stress is part of our lives and we can manage small amounts of it, and it is beneficial to us, but some people have chronic stress and have to go to a doctor to get it treated. But there is hope as there are ways to manage stress and doing it functionally and naturally.
Conclusion
So all in all, just to recap, if your patient is good to go and their test results are all green, you can introduce gluten back to their diets again in small increments and can be rested in about 3 to 9 months. But if your patient does have a gluten allergen then just let them know that they must continue to be gluten-free. We here at Injury Medical Clinic, always put our patient�s needs first for them to live their best lives with functional natural medicine.






























 �Fermentation is the transformation of food by various bacteria, fungi, and the enzymes they produce. It is important to recognize that fermentation is a natural phenomenon much broader than social, culinary practices; cells in our bodies are capable of fermentation. In other words, humans did not invent fermentation; it would be more accurate to state that fermentation created us.� � Dr. Alex Jimenez�D.C., C.C.S.T.
�Fermentation is the transformation of food by various bacteria, fungi, and the enzymes they produce. It is important to recognize that fermentation is a natural phenomenon much broader than social, culinary practices; cells in our bodies are capable of fermentation. In other words, humans did not invent fermentation; it would be more accurate to state that fermentation created us.� � Dr. Alex Jimenez�D.C., C.C.S.T.






















