Nutritional Guidelines: Best Foods to Eat For Head Injuries
Discover key nutritional guidelines for head injuries. Support your healing process with the right dietary choices today.
Healing the Brain After Injury: How Nutrition Supports Recovery from Traumatic Brain Injury
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. A TBI happens when an outside force injures the brain, often from a blow to the head, a fall, a car accident, or a sports collision (Maas et al., 2022). These injuries range from mild concussions to severe trauma that can change someone’s life forever. In the United States alone, TBI is a leading cause of death and disability, affecting approximately 5.3 million Americans who live with long-term challenges from their injuries (Conti et al., 2024). When the brain experiences trauma, the damage goes far beyond the initial impact. The injury triggers a cascade of biological events within the brain that can persist for days, weeks, or even months afterward. These processes include inflammation, oxidative stress (damage from unstable molecules called free radicals), changes in how brain cells communicate, and disruptions to the brain’s energy systems (Wu et al., 2007). Understanding these mechanisms is crucial because it enables us to identify effective ways to support recovery, particularly through targeted nutrition and lifestyle adjustments.
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, a dual-licensed chiropractor and board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner in El Paso, Texas, brings over 25 years of expertise to treating patients with traumatic brain injuries and other complex injuries (A4M, n.d.). His unique clinical approach combines the biomechanical focus of chiropractic care with the diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities of a nurse practitioner, allowing him to address both the structural and systemic aspects of brain injury recovery. Dr. Jimenez’s practice emphasizes non-invasive treatment protocols, functional medicine assessments, and personalized care plans that incorporate nutrition, targeted supplementation, and rehabilitative therapies to support natural healing processes.
Common Symptoms of TBI: Focus on Nausea
The symptoms of traumatic brain injury vary depending on the severity of the injury, but several common signs appear across different types of TBI. These symptoms can be grouped into physical, sensory, and cognitive categories (Mayo Clinic, 2021). Physical symptoms often include headaches, which are the most frequently reported complaint after a brain injury. Nausea and vomiting are also extremely common, affecting many people immediately after the injury and sometimes persisting for weeks or months (Brain Injury Law of Seattle, 2025). Other physical symptoms include fatigue, drowsiness, speech difficulties, and dizziness or loss of balance. Sensory symptoms can involve blurred vision, double vision, ringing in the ears, sensitivity to light or sound, and changes in the ability to smell or taste. Cognitive symptoms may include confusion, memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes such as anxiety or depression.
Why Nausea Occurs After TBI
Nausea is particularly troubling for people recovering from TBI because it can interfere with eating, taking medications, and participating in rehabilitation activities. Understanding why nausea happens after a brain injury helps us develop better strategies to manage it.
Several mechanisms contribute to nausea following TBI (Brain Injury Law of Seattle, 2025; Complete Concussions, 2024):
- Brainstem involvement: The brainstem controls many automatic bodily functions, including the vomiting reflex. When trauma affects this area, it can cause persistent nausea that continues long after the initial injury. If nausea lasts for weeks or gets worse over time, it may signal serious brainstem dysfunction that requires immediate medical evaluation.
- Vestibular dysfunction: The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, helps control balance and spatial orientation. TBI can disrupt this system, leading to dizziness, motion sensitivity, and nausea. People with vestibular problems after TBI often feel worse when they move their heads or bodies in certain ways.
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP): After a head injury, swelling or bleeding inside the skull can increase pressure on the brain. This elevated pressure triggers persistent nausea, vomiting, and severe headaches. Increased ICP is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
- Neurochemical imbalance: TBI disrupts the brain’s natural balance of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These imbalances can lead to nausea, dizziness, mood changes, and other symptoms. When these chemical imbalances persist, nausea can become chronic and difficult to treat.
Vomiting after a head injury deserves special attention. While a single episode of vomiting may not indicate serious problems, persistent or repeated vomiting can signal a brain bleed, dangerous pressure buildup, or other serious complications (Complete Concussions, 2024). Anyone experiencing persistent vomiting after a head injury should seek medical care immediately. At Dr. Jimenez’s Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic in El Paso, patients with TBI receive comprehensive assessments that evaluate the underlying causes of symptoms, including nausea, such as vestibular dysfunction, cervical spine misalignments, and neurological imbalances. Through targeted chiropractic adjustments, acupuncture, and electro-acupuncture techniques, Dr. Jimenez addresses the physical manifestations of brain injury while supporting the body’s natural healing mechanisms (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
How TBI Affects Nutritional Habits
Beyond the immediate symptoms, traumatic brain injury creates significant challenges for maintaining proper nutrition. These challenges can make recovery more difficult and slow the healing process.
Disrupted Communication Between Brain and Gut
Some TBI injuries affect appetite because the brain may not properly communicate with the digestive system (UCLA Health, 2022). The gut-brain axis—a bidirectional communication system between the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract—can be severely disrupted after brain trauma. This makes it difficult for people to recognize when they are hungry or full, leading to either inadequate food intake or excessive eating.
Research shows that digestive system disorders after TBI are closely related to cognitive function, depression, and other neurological conditions (PMC, 2024). The gut microbiome—the community of bacteria and other microorganisms living in the digestive tract—plays a crucial role in this relationship. After TBI, changes in the gut microbiome can worsen brain injury outcomes and even contribute to chronic neurological damage.
Swallowing Difficulties
After TBI, damage to the brainstem, cerebellum, or thalamus, or increased pressure inside the skull, can make swallowing difficult (PMC, 2024). Loss of consciousness and cognitive decline can also affect swallowing function. These swallowing disorders, called dysphagia, create serious risks because they can lead to choking, aspiration (food or liquid entering the lungs), and pneumonia.
People with dysphagia often need specialized diets with modified food textures to eat safely. The International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI) provides guidelines for thickening liquids and modifying solid foods to help individuals with swallowing difficulties eat safely during rehabilitation (PMC, 2024).
Weight Changes and Eating Disorders
Weight management becomes a major concern after TBI. Patients hospitalized with severe TBI often lose significant amounts of weight, even when they receive nutrition through feeding tubes (Consultant360, 2021). However, after discharge, many people gain excessive weight. Research shows that eating disorders are common after TBI, largely due to hyperphagia (excessive hunger or food intake) and dysexecutive syndrome (loss of brain function that impairs judgment, planning, and insight).
Dr. Jimenez’s functional medicine approach includes detailed nutritional assessments that evaluate how TBI has affected eating patterns, metabolism, and nutrient absorption. His clinic uses the Living Matrix Functional Medicine Assessment to identify nutritional deficiencies, metabolic imbalances, and digestive dysfunction that may be hindering recovery. By addressing these root causes, Dr. Jimenez helps patients restore healthy eating habits and support their brain’s healing process (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Impact on Cognitive Function
The relationship between TBI and cognitive function is complex and far-reaching. Cognitive impairments can persist long after the physical symptoms of injury have resolved, affecting memory, attention, processing speed, executive function, and emotional regulation.
Memory and Learning Difficulties
TBI damages the hippocampus and other brain regions critical for forming and storing memories. Research demonstrates that omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), can improve cognitive function after traumatic brain injury by supporting synaptic membrane fluidity and function (Wu et al., 2004). DHA is a major component of neuronal membranes at sites where brain cells communicate, making it vital for learning and memory.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays a crucial role in cognitive recovery after TBI. BDNF acts like a fertilizer for the brain, promoting the growth and survival of neurons, supporting the connections between brain cells, and facilitating learning and memory (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008). Dietary interventions can influence BDNF levels, offering a non-invasive approach to support cognitive recovery.
Attention and Processing Speed
People recovering from TBI often struggle with attention and mental processing speed. They may struggle to focus on tasks, filter out distractions, or process information efficiently. These difficulties can persist even after mild TBI (concussion) and can significantly impact work, school, and daily activities.
Executive Function Challenges
Executive functions are the high-level cognitive skills we use to plan, organize, make decisions, and control our behavior. TBI frequently impairs these abilities, resulting in difficulties with judgment, impulse control, planning, and problem-solving. These impairments can contribute to poor nutritional choices and difficulty adhering to healthy eating plans.
Emotional and Psychiatric Symptoms
Anxiety and depressive disorders are extremely common among people who have sustained a TBI, with as many as 70% of patients experiencing anxiety and up to 50% experiencing depression (Consultant360, 2021). These mood disorders can have a profound impact on eating patterns and food choices, often leading to weight gain and obesity. Depression symptoms can be intensified by a poor diet, creating a vicious cycle where inadequate nutrition worsens mental health, which in turn leads to poorer food choices.
Dr. Jimenez’s integrative treatment approach addresses the cognitive and emotional aspects of TBI recovery through a combination of chiropractic care, functional medicine, and stress management techniques. His clinic offers personalized wellness programs that include cognitive rehabilitation exercises, nutritional counseling, and natural therapies to support mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall brain health (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
The Non-Surgical Approach to Wellness with Chiropractic Care- Video
The Brain-Gut Connection in TBI Recovery
Understanding the brain-gut connection is key to optimizing nutrition after TBI. The gut and brain communicate constantly through multiple pathways, including the vagus nerve, immune system molecules, gut hormones, and the gut microbiome.
The Gut Microbiome’s Role
The gut microbiome comprises trillions of microorganisms that play crucial roles in metabolism, immune function, and neuronal function (Clark & Mach, 2016). Recent research shows that physical and emotional stress during recovery can change the composition of gut bacteria. These changes can impact brain function, intestinal barrier integrity, and immune responses—all of which are crucial for TBI recovery.
Studies in animal models demonstrate that exercise-induced stress decreased certain beneficial bacteria while increasing bacteria that degrade the intestinal mucus layer and affect immune function (Clark & Mach, 2016). In the context of TBI, maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through proper nutrition becomes even more crucial because gut health has a direct impact on brain recovery.
Gut Hormones and Cognitive Function
Several gut hormones influence emotions and cognitive processes (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008). Leptin, produced by fat tissue, helps regulate appetite and also supports synaptic plasticity—the brain’s ability to form and reorganize connections between neurons. Ghrelin, secreted by an empty stomach, not only stimulates appetite but also promotes the formation of new connections between brain cells, thereby enhancing learning and memory. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), produced by intestinal cells, regulates energy metabolism and has been shown to improve memory in animal studies.
Fermented Foods for Gut-Brain Health
Research increasingly shows that fermented foods support both gut health and brain health (UCLA Health, 2022). Fermented foods, such as sauerkraut, pickles, yogurt, and kefir, contain beneficial probiotics that help maintain a diverse and healthy gut microbiome. Prebiotic foods—such as onions, bananas, and whole grains—provide the fuel that good bacteria need to thrive.
Dr. Jimenez’s nutritional protocols emphasize the importance of gut health in neurological recovery. His functional medicine assessments often include evaluation of digestive function, gut microbiome diversity, and food sensitivities that may be contributing to inflammation and hindering brain healing (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
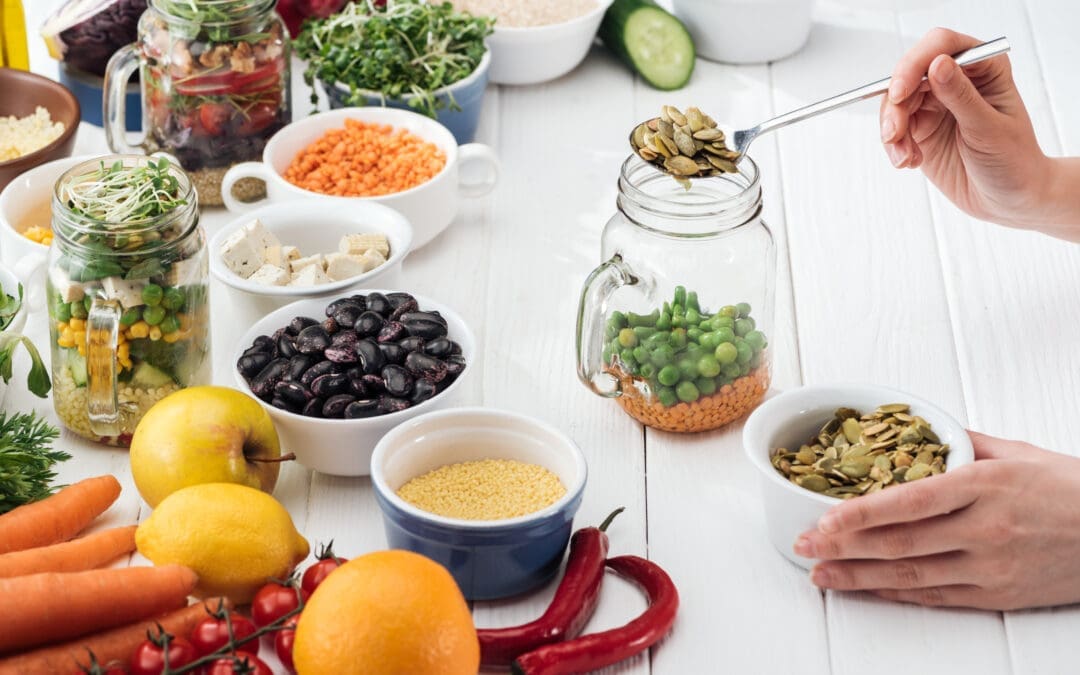
Nutritional Foods That Support Brain Function
Certain foods have been identified as particularly beneficial for brain health and recovery from TBI. Understanding which foods to emphasize can help people recovering from brain injuries make informed choices that support healing.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are among the most important nutrients for brain health (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008). These healthy fats are abundant in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, and trout. They serve multiple functions in brain recovery:
-
Membrane structure: DHA is a major component of neuronal membranes, making up a significant portion of the brain’s structure.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects: Omega-3s reduce inflammation in the brain, which is critical because inflammation contributes to ongoing damage after TBI.
-
Oxidative stress reduction: Research indicates that omega-3 supplementation can reduce oxidative damage resulting from trauma (Wu et al., 2004).
-
BDNF support: Omega-3 fatty acids elevate levels of BDNF, supporting cognitive function and neural recovery.
For people who don’t eat fish, alternative sources include walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and microalgae supplements. However, the omega-3s found in plant sources (alpha-linolenic acid, or ALA) are not as readily used by the brain as the EPA and DHA found in fish (UCLA Health, 2022).
Berries and Antioxidants
Berries—particularly blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries—contain powerful antioxidants called flavonoids that give them their vibrant colors (Harvard Health, 2021). Research shows that women who consumed two or more servings of strawberries and blueberries per week experienced a delay in memory decline of up to two and a half years.
Flavonoids work through several mechanisms:
-
They increase blood flow to the brain
-
They improve neuronal function
-
They promote neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections
-
They reduce oxidative stress and inflammation
Leafy Green Vegetables
Green, leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, collards, and broccoli are rich in brain-healthy nutrients like vitamin K, lutein, folate, and beta-carotene (Harvard Health, 2021). Research suggests these plant-based foods may help slow cognitive decline. Vitamin K plays a role in forming certain fats that are concentrated in brain cells, while lutein and folate support cognitive function in older adults.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts are excellent sources of protein, healthy fats, and vitamin E—all important for brain health (Harvard Health, 2021). Walnuts deserve special attention because they contain high levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid. Research from UCLA linked higher walnut consumption to improved cognitive test scores. Walnuts, along with other nuts like almonds and hazelnuts, are also rich in vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that protects brain cells from oxidative damage. Pumpkin seeds provide zinc, magnesium, iron, and tryptophan—an amino acid that helps produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation (Salmon Health, 2023).
Whole Grains
Complex carbohydrates from whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread, provide steady energy for the brain (Headway UK, n.d.). Unlike refined grains and sugars that cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar, whole grains release energy slowly, helping to maintain stable energy levels throughout the day. This is especially helpful for people experiencing fatigue after TBI.
Healthy Fats: Olive Oil and Avocados
Olive oil, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, has been shown to have a range of health benefits, including protective effects on memory function (Headway UK, n.d.). Avocados provide healthy monounsaturated fats, along with potassium and lutein, which support brain health (Rezilir Health, 2025).
Eggs and Choline
Eggs are one of the best dietary sources of choline, a vital nutrient essential for producing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, mood regulation, and muscle control (UCI Health, 2025). Adequate choline intake has been linked to enhanced cognitive performance and may help protect against age-related memory decline. Eggs also contain B vitamins like B12, which help reduce homocysteine levels—an amino acid that, when elevated, can damage blood vessels and increase risk for stroke and dementia.
Turmeric and Curcumin
Turmeric, a yellow curry spice, contains curcumin, which has been shown to enhance recovery after brain trauma (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008). Curcumin displays particular effectiveness in preserving cognitive function through several mechanisms:
-
Reducing oxidative stress
-
Protecting against lipid peroxidation (damage to cell membranes)
-
Neutralizing harmful free radicals
-
Reducing inflammation in the brain
Studies have shown that curcumin supplementation reduced the effects of experimental concussive injury on cognitive function in animal models (Wu et al., 2006).
Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate contains flavonoids, caffeine, and theobromine—compounds that can improve cognitive function (Senior Lifestyle, 2025). Flavonoids increase blood flow to the brain, improve neuronal function, and promote neuroplasticity. Moderate consumption of dark chocolate has been linked to improved memory, attention, and overall cognitive function.
The Mediterranean Diet for Brain Health
Among various dietary patterns studied for brain health, the Mediterranean diet has emerged as particularly beneficial for people recovering from TBI (UCLA Health, 2022). This eating pattern, traditionally followed in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, emphasizes:
-
High portions of fruits and vegetables
-
Whole grains
-
Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
-
Nuts and seeds
-
Fish and seafood (at least twice per week)
-
Olive oil is the primary source of added fat
-
Moderate consumption of poultry
-
Limited intake of red meat and dairy products
-
Herbs and spices for flavoring instead of salt
Research suggests that the Mediterranean diet is associated with fewer signs of Alzheimer’s disease in the brains of older adults (NIA, 2023). Green leafy vegetables, in particular, were associated with less brain pathology. The MIND diet—a hybrid of the Mediterranean and DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diets specifically designed to support brain health—builds on these principles with additional emphasis on berries and green leafy vegetables (Mass General Hospital, 2025).
Dr. Jimenez often recommends a Mediterranean dietary pattern to his TBI patients, recognizing that this style of eating provides comprehensive support for brain health while reducing inflammation throughout the body (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Essential Vitamins and Supplements
Beyond whole foods, certain vitamins and supplements have shown promise in supporting brain function and recovery after TBI.
B Vitamins
B vitamins play crucial roles in brain health (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008):
-
Vitamin B6: Supports neurotransmitter production and has positive effects on memory performance
-
Vitamin B12: Essential for neurological health; deficiency has been linked to cognitive decline
-
Folate (B9): Critical for neurotransmitter function and DNA repair; deficiency can lead to depression and cognitive impairment
Supplementation with B vitamins has been shown to prevent cognitive decline and dementia during aging and can enhance the effects of antidepressants (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008). Foods rich in B vitamins include leafy greens (folate), fish, poultry, eggs (B12), and fortified grains.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining cognitive function in older adults and appears to play a significant role in brain health (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008). Sources include fatty fish, mushrooms exposed to sunlight, and fortified products like milk and cereals. Many people, especially those recovering from TBI who may spend more time indoors, need vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E functions as an antioxidant, reducing free radicals in the brain that would otherwise impede optimal neuronal function (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008). Studies show that vitamin E ameliorates cognitive impairment after brain trauma in animal models and reduces cognitive decline in older adults. Food sources include nuts, seeds, spinach, avocado, and vegetable oils.
Magnesium
Magnesium plays a crucial role in nerve transmission and neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize (UCI Health, 2025). Magnesium deficiency is common and can contribute to anxiety, depression, and cognitive problems. Good sources include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Creatine
Creatine supplementation shows promise for improving brain health, particularly in conditions characterized by brain creatine deficits (Roschel et al., 2021). These deficits can be induced by acute stressors like sleep deprivation or chronic conditions like mild traumatic brain injury. Creatine supports cognitive processing and may help with recovery from brain trauma, though the optimal protocol for increasing brain creatine levels is still being determined (Conti et al., 2024).
Omega-3 Supplements
For individuals who don’t consume adequate amounts of fatty fish, omega-3 supplements (such as fish oil or microalgae-based DHA/EPA) can help ensure an adequate intake of these critical fatty acids (Conti et al., 2024). Research indicates that omega-3 supplementation can help decrease inflammation, mitigate neural damage, and maintain a sufficient energy supply to the brain following injury.
Melatonin
Melatonin supplementation may help alleviate sleep disturbances commonly experienced after TBI (Conti et al., 2024). Since quality sleep is essential for brain recovery and the consolidation of memories, addressing sleep problems through melatonin or other interventions is a crucial part of comprehensive TBI treatment.
Other Promising Supplements
Additional supplements being investigated for TBI recovery include (Conti et al., 2024):
-
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): An antioxidant that may reduce oxidative stress
-
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): May influence mental performance, though evidence is mixed
-
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): May help with migraine headaches common after TBI
-
Choline: Supports production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter critical for memory
-
Berry anthocyanins: Powerful antioxidants found in berries
-
Boswellia serrata: An anti-inflammatory botanical
-
Enzogenol: A pine bark extract with antioxidant properties
It’s essential to note that while supplements may be necessary for some individuals, it is crucial to consult your doctor or dietitian before taking them, as they could interact with medications or have other unintended effects (Headway UK, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez’s functional medicine approach includes comprehensive nutritional testing to identify specific deficiencies and imbalances that may be hindering recovery. His personalized supplementation protocols are based on individual patient needs, genetics, and the severity of injury, ensuring that each patient receives targeted nutritional support for optimal healing (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Just as certain foods support brain health, others can hinder recovery from TBI. While it’s important not to create overly restrictive diets that may be difficult to follow, being mindful of these foods can support better outcomes.
Saturated Fats and Trans Fats
Diets high in saturated fats have been shown to have an adverse effect on cognition (Gomez-Pinilla, 2008). Studies show that “junk food” diets—characterized by high contents of saturated fat and refined sugars—lead to a decline in cognitive performance and reduced levels of BDNF-related synaptic plasticity after just three weeks. Even more concerning, these diets elevated the neurological burden associated with experimental brain injury, resulting in worse performance in learning tasks.
Foods high in saturated fats include butter, cream, cheese, fatty meats, coconut oil, and palm kernel oil. Trans fats, found in many processed and fried foods, are particularly harmful and should be avoided.
Refined Sugars and Processed Foods
Sugar can cause weight gain and other health problems, and can cause “sugar crashes” where energy levels drop rapidly—a particular problem for people experiencing fatigue after TBI (Headway UK, n.d.). Highly processed foods often contain high amounts of salt and sugar, tend to have lower nutritional content, and may lead to weight gain.
Excessive Sodium
Salt is known to raise blood pressure and increase the risk of stroke (Headway UK, n.d.). Many people with taste and smell problems after TBI add more salt than they should. Using alternatives such as lemon juice, herbs, and spices can enhance flavor without the negative health effects associated with excess sodium.
Alcohol
Alcohol should be avoided or consumed very minimally during TBI recovery. Alcohol can interfere with healing processes, interact with medications, worsen cognitive symptoms, and increase fall risk.
Excessive Caffeine
While moderate caffeine consumption may offer cognitive benefits, excessive intake can have negative effects, particularly for people who experience urinary symptoms or sleep disturbances after brain injury (Headway UK, n.d.). Caffeine can also increase anxiety in some individuals.
Easy Brain-Boosting Recipes
Incorporating brain-healthy foods into daily meals doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some simple, nutritious recipes designed to support neurological recovery:
Blueberry Walnut Overnight Oats
This make-ahead breakfast is perfect for busy mornings and is packed with brain-boosting nutrients.
Ingredients:
-
1/2 cup rolled oats
-
1/2 cup milk (dairy or plant-based)
-
1/4 cup plain Greek yogurt
-
1/2 cup fresh blueberries
-
2 tablespoons chopped walnuts
-
1 teaspoon honey (optional)
-
1/2 teaspoon vanilla extract
Instructions:
-
In a mason jar or bowl, mix the oats, milk, yogurt, honey, and vanilla
-
Top with blueberries and walnuts
-
Cover and refrigerate overnight
-
Enjoy it cold in the morning
Why it’s good for your brain: Blueberries provide antioxidants that promote brain health, while walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids that support memory and focus. Oats provide steady energy, and Greek yogurt offers protein and probiotics for gut health.
Wild Salmon and Greens Power Bowl
This nutrient-dense bowl combines multiple brain-healthy ingredients in one satisfying meal.
Ingredients:
-
4 oz wild-caught salmon
-
2 cups mixed greens (arugula, spinach, romaine)
-
1/2 cup steamed broccoli
-
1/4 avocado, sliced
-
1/4 cup blueberries
-
1 tablespoon walnuts, chopped
-
2 teaspoons ground flaxseed
For the Turmeric-Tahini Dressing:
-
1 tablespoon tahini
-
1 teaspoon turmeric
-
Pinch of black pepper
-
1 teaspoon fresh lemon juice
-
1 teaspoon extra-virgin olive oil
-
Water to thin
Instructions:
-
Season salmon with salt and pepper; heat 1 teaspoon olive oil in a skillet over medium heat
-
Place salmon skin-side down; cook 4-5 minutes, flip and cook 3-4 minutes more until flaky
-
Steam broccoli florets for 4-5 minutes until bright green and tender
-
Whisk together dressing ingredients, adding water to reach the desired consistency
-
Layer greens in a bowl; top with broccoli, avocado, blueberries, walnuts, and flaxseed
-
Add salmon and drizzle with dressing
Why it’s good for your brain: Salmon provides EPA and DHA omega-3s that build neuronal membranes and reduce inflammation. Leafy greens offer folate, vitamin K, and natural nitrates that boost blood flow to the brain. Broccoli contains sulforaphane, which triggers antioxidant defenses. Turmeric’s curcumin helps reduce inflammation, while blueberries offer powerful antioxidants.
Spinach and White Bean Frittata
This protein-rich breakfast or lunch option is loaded with brain-healthy nutrients.
Ingredients:
-
6 eggs
-
1/4 cup milk
-
2 cups fresh spinach, chopped
-
1 cup cooked white beans (cannellini)
-
1/2 cup cherry tomatoes, halved
-
1/2 teaspoon turmeric
-
1/4 cup feta cheese (optional)
-
2 tablespoons olive oil
-
Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
-
Preheat oven to 375°F
-
In a bowl, whisk eggs, milk, turmeric, salt, and pepper
-
Heat olive oil in an oven-safe skillet over medium heat
-
Add spinach and cook until wilted
-
Add white beans and tomatoes; cook for 2 minutes
-
Pour the egg mixture over the vegetables
-
Cook without stirring for 4-5 minutes until edges begin to set
-
Sprinkle with feta if using
-
Transfer to oven and bake 12-15 minutes until center is set
Why it’s good for your brain: Eggs provide choline for memory and acetylcholine production, plus B vitamins to reduce homocysteine. Spinach offers folate, vitamin K, and lutein to slow cognitive decline. White beans provide magnesium for nerve transmission and plant-based protein to support stable blood sugar levels.
Mediterranean Chickpea and Vegetable Stew
This hearty, flavorful stew is perfect for meal prep and freezes well.
Ingredients:
-
2 tablespoons olive oil
-
1 onion, diced
-
3 cloves garlic, minced
-
2 sweet potatoes, cubed
-
2 cans (15 oz each) chickpeas, drained
-
1 can (14 oz) diced tomatoes
-
4 cups vegetable broth
-
2 cups fresh spinach
-
1 teaspoon cumin
-
1 teaspoon paprika
-
1/2 teaspoon turmeric
-
1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
-
Juice of 1 lemon
-
Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
-
Heat olive oil in a large pot over medium heat
-
Add onion and cook until softened, about 5 minutes
-
Add garlic and spices; cook 1 minute until fragrant
-
Add sweet potatoes, chickpeas, tomatoes, and broth
-
Bring to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer 20-25 minutes until the sweet potatoes are tender
-
Stir in spinach until wilted
-
Add lemon juice and adjust seasonings
-
Serve warm
Why it’s good for your brain: Chickpeas provide fiber, folate, iron, and magnesium. Sweet potatoes offer antioxidants, B vitamins, and vitamin C. Spinach adds more folate and antioxidants. The spices (cumin, turmeric) provide anti-inflammatory compounds.
Brain-Boosting Berry Smoothie
A quick, easy option for breakfast or snacks.
Ingredients:
-
1 cup mixed berries (blueberries, strawberries, blackberries)
-
1/2 banana
-
1 cup spinach
-
1 tablespoon almond butter
-
1 tablespoon ground flaxseed
-
1 cup unsweetened almond milk
-
1/2 cup plain Greek yogurt
-
1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
-
Ice cubes
Instructions:
-
Add all ingredients to a blender
-
Blend until smooth
-
Add more liquid if needed for the desired consistency
-
Pour into a glass and enjoy immediately
Why it’s good for your brain: Berries provide flavonoids and antioxidants for brain health. Spinach adds folate and vitamin K without affecting taste. Almond butter and flaxseed provide healthy fats and omega-3s. Greek yogurt offers protein and probiotics.
Walnut-Crusted Baked Salmon
An elegant but simple preparation that maximizes brain-healthy nutrients.
Ingredients:
-
1 lb skinless salmon fillet
-
2 teaspoons Dijon mustard
-
1 clove garlic, minced
-
1/4 teaspoon lemon zest
-
1 teaspoon lemon juice
-
1 teaspoon chopped fresh rosemary
-
1/2 teaspoon honey
-
1/4 teaspoon crushed red pepper
-
3 tablespoons panko breadcrumbs
-
3 tablespoons finely chopped walnuts
-
1 teaspoon extra-virgin olive oil
-
Olive oil cooking spray
Instructions:
-
Preheat oven to 425°F
-
Line a baking sheet with parchment paper
-
Mix mustard, garlic, lemon zest, lemon juice, rosemary, honey, and red pepper in a small bowl
-
In another bowl, combine breadcrumbs, walnuts, and olive oil
-
Place salmon on the prepared baking sheet
-
Spread mustard mixture over salmon
-
Top with the breadcrumb-walnut mixture
-
Spray lightly with cooking spray
-
Bake 8-12 minutes until salmon is cooked through
Why it’s good for your brain: Salmon provides omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA. Walnuts provide more omega-3s, as well as vitamin E. Garlic offers antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Pumpkin Seed and Berry Trail Mix
A convenient brain-boosting snack for on-the-go.
Ingredients:
-
1 cup raw pumpkin seeds
-
1/2 cup walnuts
-
1/2 cup almonds
-
1/2 cup dried blueberries (unsweetened if possible)
-
1/4 cup dark chocolate chips (70% cacao or higher)
-
1/4 cup unsweetened coconut flakes
-
1 teaspoon cinnamon
-
1/4 teaspoon nutmeg
-
1 tablespoon maple syrup
Instructions:
-
Preheat oven to 325°F
-
Toss pumpkin seeds, walnuts, and almonds with maple syrup and spices
-
Spread on a baking sheet
-
Bake 10-12 minutes, stirring halfway through
-
Cool completely
-
Mix with dried blueberries, chocolate chips, and coconut
-
Store in an airtight container
Why it’s good for your brain: Pumpkin seeds provide zinc, magnesium, and iron. Nuts offer healthy fats and vitamin E. Blueberries add antioxidants. Dark chocolate contains flavonoids that support improved brain function.
Practical Tips for Eating Well After TBI
Making healthy food choices can be challenging when dealing with the effects of brain injury. These practical strategies can help:
Meal Planning and Preparation
-
Find and save simple recipes that you can return to regularly (Headway UK, n.d.)
-
Create a weekly meal plan so you know what to prepare each day
-
Make a shopping list or use online grocery ordering to avoid forgetting items
-
Batch cook and freeze meals when you have good energy; label containers with contents and date
-
Shop during optimal times when you feel most alert and when stores are less crowded
Managing Symptoms While Eating
-
Eat at regular intervals to avoid under-eating or over-eating; don’t skip breakfast (Headway UK, n.d.)
-
Set alarms as reminders to eat if you experience a loss of appetite
-
Pay attention to use-by dates if you have problems with taste and smell
-
Modify food textures if swallowing is difficult; work with a speech therapist or occupational therapist
-
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
Making Healthy Choices Easier
-
Keep healthy snacks visible and accessible: nuts, cut vegetables, fruit
-
Use herbs and spices instead of salt for flavor
-
Choose whole-grain versions of bread, pasta, and rice
-
Read nutrition labels to understand what’s in packaged foods
-
Ask for help when needed; use a Brain Injury Identity Card to start conversations about your needs
Dining Out Strategies
When eating at restaurants (Taste of Home, 2023):
-
Review menus online beforehand to plan your choices
-
Ask questions about ingredients and preparation methods
-
Request modifications: grilled instead of fried, dressing on the side, extra vegetables
-
Control portions by sharing an entrée or taking half home
-
Choose Mediterranean-style restaurants that emphasize vegetables, fish, and olive oil
Dr. Jimenez’s Clinical Approach to TBI and Injury Recovery
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic in El Paso, Texas, offers a comprehensive, integrative approach to treating patients recovering from traumatic brain injuries and other complex injuries. His dual licensure as both a chiropractor and board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner provides a unique perspective that addresses both the structural and systemic aspects of injury recovery.
Dual-Scope Diagnostic and Treatment Approach
Dr. Jimenez’s practice stands out due to his ability to integrate the biomechanical focus of chiropractic care with the diagnostic and therapeutic scope of a nurse practitioner (A4M, n.d.). As a chiropractor, he specializes in restoring musculoskeletal function, particularly after trauma affecting the neck, back, spine, and soft tissues. His chiropractic interventions emphasize non-invasive techniques such as spinal decompression, manual adjustments, and functional rehabilitation to alleviate pain and enhance mobility.
As a board-certified nurse practitioner, Dr. Jimenez employs evidence-based medicine to address systemic and metabolic dysfunctions. His expertise extends to managing chronic pain syndromes, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic disorders that often accompany brain injuries. This dual perspective enables him to identify the underlying causes of symptoms, ranging from biomechanical misalignments to physiological imbalances, and design treatment regimens that address both symptoms and their root causes.
Treatment of Various Injury Types
Dr. Jimenez’s clinic specializes in treating injuries from multiple sources (dralexjimenez.com, 2025):
- Motor vehicle accidents (MVAs): Whiplash, soft tissue injuries, and traumatic brain injuries from car crashes require comprehensive assessment and treatment. Dr. Jimenez provides both immediate injury care and long-term rehabilitation.
- Work injuries: Occupational injuries affecting the back, neck, and other body systems receive targeted treatment plans that support return to work while promoting complete healing.
- Sports injuries: Athletes recovering from concussions, sprains, strains, and other sports-related trauma benefit from protocols designed to restore function and prevent re-injury.
- Personal injuries, including falls, slip-and-fall accidents, and other types of personal injury cases, receive thorough evaluation and individualized treatment approaches.
Functional Medicine Assessments
Dr. Jimenez’s practice embraces Functional Integrative Medicine, a patient-focused approach that treats the whole person, not just symptoms (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). His comprehensive assessments evaluate:
-
Genetics: Understanding genetic predispositions to certain conditions
-
Lifestyle factors: Sleep, stress, exercise, and daily habits
-
Environmental exposures: Toxins and other environmental factors affecting health
-
Psychological factors: Mood, anxiety, depression, and stress responses
-
Nutritional status: Deficiencies, imbalances, and dietary patterns
The clinic utilizes the Living Matrix Functional Medicine Assessment and the Institute for Functional Medicine’s Collaborative Assessment Programs to create comprehensive health profiles for each patient.
Advanced Neuromusculoskeletal Imaging
Dr. Jimenez’s clinic utilizes advanced diagnostic imaging to assess the extent of injuries and track healing progress. This includes specialized neuromusculoskeletal imaging that can identify subtle changes in the spine, soft tissues, and nervous system that may not be apparent on standard imaging studies.
An Example of A TBI Symptom Questionnaire:
Integrated Treatment Modalities
The clinic offers multiple therapeutic approaches that work synergistically (dralexjimenez.com, 2025):
- Chiropractic adjustments: Manual adjustments to restore proper spinal alignment and nervous system function
- Acupuncture and Electro-Acupuncture: Traditional Chinese medicine techniques to reduce pain, decrease inflammation, and promote healing
- Functional rehabilitation: Targeted exercises and therapies to restore strength, flexibility, and function
- Nutritional counseling: Personalized dietary recommendations and supplementation protocols
- Stress management: Techniques to address the emotional and psychological impacts of injury
- Massage therapy: Soft tissue work to reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and support relaxation
Medical-Legal Documentation
For patients whose injuries resulted from accidents or the negligence of others, Dr. Jimenez provides comprehensive medical-legal documentation (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). His dual training allows him to prepare thorough medical reports that detail:
-
Mechanism of injury
-
Initial presentation and symptoms
-
Diagnostic findings
-
Treatment provided
-
Prognosis and long-term implications
-
Functional limitations and disabilities
This documentation supports patients in legal proceedings and insurance claims related to their injuries.
Collaborative Care Model
Dr. Jimenez recognizes that complex injuries often require input from multiple specialists. He has partnered with top surgeons, medical specialists, and rehabilitation providers in the El Paso area to ensure patients receive the highest standard of care (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). If he believes another specialist is better suited for a patient’s condition, he provides appropriate referrals while coordinating ongoing care.
Prevention and Long-Term Wellness
Beyond treating acute injuries, Dr. Jimenez’s practice emphasizes prevention and long-term wellness. Through education, lifestyle coaching, and ongoing support, patients learn how to:
-
Prevent re-injury
-
Maintain healthy spinal alignment
-
Support optimal brain and body function through nutrition
-
Manage stress effectively
-
Incorporate regular exercise and movement
-
Maintain a healthy body weight
-
Optimize sleep and recovery
Dr. Jimenez’s mission is to help patients not only recover from injuries but also thrive in El Paso’s beautiful community, achieving improved health, vitality, and quality of life (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
The Role of Exercise in Brain Recovery
While nutrition is crucial for brain health, combining dietary interventions with regular exercise can further enhance recovery. Research shows that diet and exercise work together synergistically, producing greater effects on brain plasticity and cognitive function than either intervention alone (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008).
Exercise Benefits for the Brain
Physical activity influences brain health through multiple mechanisms:
-
Increases BDNF levels: Exercise elevates brain-derived neurotrophic factor, promoting neuronal growth and survival
-
Reduces oxidative stress: Regular movement improves the body’s antioxidant defenses
-
Supports neurogenesis: Exercise promotes the birth of new neurons in the hippocampus
-
Improves blood flow: Enhanced circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the brain
-
Regulates neurotransmitters: Physical activity helps balance mood-regulating chemicals
Timing Considerations
The timing of exercise after TBI is important. Research indicates that exercise applied immediately following experimental traumatic brain injury can actually worsen outcomes (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008). However, exercise started at appropriate times during recovery facilitates healing and improves cognitive function. Patients should work with healthcare providers, such as Dr. Jimenez, to determine when and how to safely reintroduce physical activity after a brain injury. The rehabilitation programs at Dr. Jimenez’s clinic include carefully designed flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored to individual recovery stages (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Types of Exercise
Cardiovascular exercise appears most beneficial for brain recovery. Studies comparing different exercise types found treadmill running (walking or running) to be most effective for recovery (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008). Other beneficial activities include:
-
Walking
-
Swimming
-
Cycling
-
Dancing
-
Gentle yoga and tai chi (for balance and flexibility)
Combined Effects of Diet and Exercise
The combination of a healthy diet and exercise produces enhanced effects on brain recovery. Studies show that:
-
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation combined with exercise (DHA+Exercise) had greater effects on BDNF-mediated synaptic plasticity and cognition than either intervention alone (Gomez-Pinilla & Kostenkova, 2008)
-
Flavonoid-enriched diets combined with exercise increased the expression of genes supporting neuronal plasticity while decreasing genes involved in inflammation and cell death
-
Exercise can counteract some deleterious effects of high saturated fat diets on synaptic plasticity and cognitive function
Dr. Jimenez’s integrated approach acknowledges the synergistic relationship between nutrition and physical rehabilitation, resulting in treatment plans that optimize both components for optimal recovery (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Sleep and Recovery
Quality sleep is essential for brain recovery after TBI. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories, clears metabolic waste products, and repairs cellular damage. Many people experience sleep disturbances after brain injury, including:
-
Difficulty falling asleep
-
Frequent awakening during the night
-
Early morning awakening
-
Excessive daytime sleepiness
-
Altered sleep-wake cycles
Nutritional Support for Sleep
Certain dietary strategies can support better sleep:
-
Avoid caffeine in the afternoon and evening
-
Limit alcohol, which disrupts sleep architecture
-
Eat tryptophan-rich foods like turkey, eggs, cheese, nuts, and seeds
-
Consider magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains
-
Try tart cherry juice, a natural source of melatonin
-
Avoid heavy, spicy, or large meals close to bedtime
Sleep Hygiene
In addition to nutritional support, good sleep hygiene practices include:
-
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
-
Creating a dark, cool, quiet sleep environment
-
Limiting screen time before bed
-
Engaging in relaxing activities in the evening
-
Getting regular exercise (but not too close to bedtime)
Dr. Jimenez’s comprehensive approach to TBI recovery includes assessment and management of sleep disturbances, recognizing that quality rest is essential for healing (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Conclusion
Traumatic brain injury presents complex challenges that extend far beyond the initial impact. The symptoms—including nausea, cognitive impairments, nutritional difficulties, and emotional changes—can persist for months or years, significantly affecting quality of life. However, emerging research demonstrates that nutrition plays a powerful role in supporting brain recovery and cognitive function. The evidence is clear: what we eat matters for brain health. Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidant-rich berries, leafy greens, nuts, whole grains, and other nutrient-dense foods provide the building blocks and protective compounds the brain needs to heal. The Mediterranean dietary pattern, emphasizing these foods while limiting saturated fats and processed ingredients, offers a comprehensive nutritional approach supported by extensive research. Beyond whole foods, targeted supplementation with B vitamins, vitamin D, vitamin E, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids can address specific deficiencies and support recovery processes. The gut-brain connection underscores the significance of maintaining a healthy digestive system through the consumption of probiotics, prebiotics, and fermented foods. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s integrative approach in El Paso exemplifies how comprehensive care can support TBI recovery. By combining his expertise as both a chiropractor and nurse practitioner, Dr. Jimenez addresses the structural, metabolic, and nutritional aspects of brain injury. His functional medicine assessments identify root causes of symptoms, while his treatment protocols—including chiropractic adjustments, acupuncture, targeted nutrition, and rehabilitative therapies—support the body’s natural healing processes.
For anyone recovering from TBI, whether from a motor vehicle accident, sports injury, fall, or other trauma, the path to recovery involves multiple components: proper medical care, appropriate rehabilitation, adequate rest, stress management, and—critically—optimal nutrition. By incorporating brain-healthy foods into daily meals, staying hydrated, managing symptoms that interfere with eating, and working with knowledgeable healthcare providers, individuals can support their brain’s remarkable capacity for healing and adaptation. The recipes and strategies outlined in this article offer practical and accessible ways to nourish the brain during recovery. These nutritional interventions, combined with appropriate medical care, physical rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications, offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life after traumatic brain injury. Remember, recovery is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and comprehensive support. With the right nutritional foundation, expert medical care from practitioners like Dr. Jimenez, and a commitment to healing, individuals recovering from TBI can work toward restoring brain function, preventing long-term complications, and living vibrant, fulfilling lives.
References
- A4M. (n.d.). Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP. Retrieved from https://www.a4m.com/alex-jimenez-injury-medical-amp-chiropractic-clinic-el-paso-tx.html
- Brain Injury Law of Seattle. (2025). Nausea and traumatic brain injury (TBI): Symptoms & treatment. Retrieved from https://www.braininjurylawofseattle.com/traumatic-brain-injury-symptoms-tbi/nausea/
- Clark, A., & Mach, N. (2016). Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis, and diet: A systematic review for athletes. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 13, 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-016-0155-6
- Complete Concussions. (2024). Dealing with concussion symptoms: Nausea. Retrieved from https://completeconcussions.com/concussion-tips-information/dealing-with-concussion-symptoms-nausea/
- Conti, F., McCue, J. J., DiTuro, P., Galpin, A. J., & Wood, T. R. (2024). Mitigating traumatic brain injury: A narrative review of supplementation and dietary protocols. Nutrients, 16(15), 2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152430
- Consultant360. (2021). Feeding the brain: Nutrition for patients with traumatic brain injury. Retrieved from https://www.consultant360.com/article/nutrition411/emergency-medicine/feeding-brain-nutrition-patients-traumatic-brain-injury
- dralexjimenez.com. (2025). El Paso, TX, family practice nurse practitioner and chiropractor. Retrieved from https://dralexjimenez.com/
- Gómez-Pinilla, F. (2008). Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(7), 568-578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2421
- Gomez-Pinilla, F., & Kostenkova, K. (2008). The influence of diet and physical activity on brain repair and neurosurgical outcome. Surgical Neurology, 70(4), 333-336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2008.05.023
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2021). Foods linked to better brainpower. Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/foods-linked-to-better-brainpower
- Headway UK. (n.d.). Diet after brain injury: Healthy body, healthy mind? Retrieved from https://www.headway.org.uk/about-brain-injury/individuals/brain-injury-and-me/diet-after-brain-injury-healthy-body-healthy-mind/
- Maas, A. I. R., Menon, D. K., Manley, G. T., et al. (2022). Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. The Lancet Neurology, 21(11), 1004-1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00309-X
- Mass General Hospital. (2025). MIND diet 3-day sample meal plan. Retrieved from https://www.massgeneral.org/news/article/mind-diet-3-day-sample-meal-plan
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Traumatic brain injury – Symptoms & causes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20378557
- Meeusen, R., & Decroix, L. (2018). Nutritional supplements and the brain. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 28(2), 200-211. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2017-0314
- National Institute on Aging. (2023). MIND and Mediterranean diets linked to fewer signs of Alzheimer’s brain pathology. Retrieved from https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/mind-and-mediterranean-diets-linked-fewer-signs-alzheimers-brain-pathology
- PMC. (2024). Research progress on digestive disorders following traumatic brain injury. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11695231/
- Rezilir Health. (2025). Brain-boosting eats: A wild salmon & greens bowl that loves your mind. Retrieved from https://www.rezilirhealth.com/brain-boosting-eats-a-wild-salmon-greens-bowl-that-loves-your-mind/
- Roschel, H., Gualano, B., Ostojic, S. M., & Rawson, E. S. (2021). Creatine supplementation and brain health. Nutrients, 13(2), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020586
- Salmon Health. (2023). 10 brain-healthy foods for older adults. Retrieved from https://salmonhealth.com/brain-matters-10-foods-that-support-brain-health/
- Senior Lifestyle. (2025). Top 10 foods for senior brain health. Retrieved from https://www.seniorlifestyle.com/resources/blog/the-top-10-foods-for-a-healthy-brain/
- Taste of Home. (2023). 35 superfood recipes that are good for your brain. Retrieved from https://www.tasteofhome.com/collection/meals-that-give-your-brain-a-boost/
- Toader, C., Dobrin, N., Costea, D., et al. (2024). Mind, Mood, and Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063340
- UCLA Health. (2022). Nutrition may play a key role in supporting brain health for people recovering from a TBI. Retrieved from https://www.uclahealth.org/news/article/nutrition-may-play-a-key-role-in-supporting-brain-health-for-people-recovering-from-a-tbi
- UCI Health. (2025). MIND food: Blissful recipes to boost brain health. Retrieved from https://www.ucihealth.org/blog/2025/06/delicious-recipes-for-brain-health
- Wu, A., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2004). Dietary omega-3 fatty acids normalize BDNF levels, reduce oxidative damage, and counteract learning disability after traumatic brain injury in rats. Journal of Neurotrauma, 21(10), 1457-1467. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2004.21.1457
- Wu, A., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2006). Dietary curcumin counteracts the outcome of traumatic brain injury on oxidative stress, synaptic plasticity, and cognition. Experimental Neurology, 197(2), 309-317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.09.004
- Wu, A., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2007). Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation restores mechanisms that maintain brain homeostasis in traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 24(10), 1587-1595. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2007.0313
- Cerdó, T., Ruiz, A., Suárez, A., & Campoy, C. (2017). Probiotic, prebiotic, and brain development. Nutrients, 9(11), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111247