by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Crossfit, PUSH-as-Rx
Contact Us
Please fill out the form below to request more information or schedule your first session with one of our trainers.
If you’d like to reach us directly, please call one of our two locations, Central El Paso (915.203.8122) or West El Paso (915.740.2439), or email us at [email protected]
6440 Gateway East Bldg B, �El Paso, TX 79905

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Athletes
Related Articles
COLORADO SPRINGS, Colo. ��UTEP rifle team members Abby Monique (smallbore and air rifle) Mara Rouse, Maranda Nelson and Bailey Powell (air rifle only) recently had an amazing opportunity for growth by being invited to compete at the 2017 USA Shooting National Junior Olympic Shooting Championships at the Olympic Training Center in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
The Miners interacted with and shared the range with some of the best shooters in the sport, including 2016 Rio Olympics Women�s Air Rifle gold medalist Ginny Thrasher.
It marked the first such trip to the event for Rouse while Monique and Powell made their third and Nelson her fourth. The Miners performed admirably, placing three individuals among the top 75 (in a field of nearly 200) in the 10m air rifle.
In order to attend the Junior Olympics, athletes who are under the age of 20 (junior-aged athletes), must compete in a state junior Olympic Shooting championship match and receive an invitation to compete by meeting either an automatic score or win the athlete�s respective state title.
�It was very exciting to have all four of our junior aged athletes qualify and compete at the Junior Olympic Shooting Championships representing UTEP,� UTEP head coach Hannah Muegge said. �I�d like to thank our UTEP parents who came out and supported all of our athletes, in addition to those back home who followed along online. In the collegiate category, we definitely had one of the largest showings at this match. I could not ask for a better support system.�
Powell was exceptional, finishing in 14th place (out of a field of 180) in the 10m air rifle. She was particularly strong on the first day of action with her score (413) placing her eighth heading to the second day.
Monique represented the Orange and Blue in the smallbore. She recorded a score of 1120 to land in the upper-echelon of the field with a 31st-place finish. She also joined Powell in the 10m air rifle, tallying a total score of 804.8 to take 68th place.
Rouse, competing in the 10m air rifle, shot 401.3 in the first day before improving to 402.1 on day two. The total of 803.4 was good enough for 74th.
Nelson was saddled with a rifle malfunction on the first day and had to borrow an air rifle for the second day. Despite the challenges she held her head up high.
Like UTEP Rifle On Facebook
Follow UTEP Rifle On Instagram

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Crossfit, PUSH-as-Rx
MEET THE TEAM

DANIEL ALVARADO, OWNER & HEAD TRAINER

MIKE CONTRERAS, TRAINER

ETHAN PADILLA, TRAINER
LLUVIA MARTINEZ, TRAINER
IYLENE AVALOS
6440 Gateway East Bldg B, �El Paso, TX 79905

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Crossfit, PUSH-as-Rx
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
As a member of PUSH, you will have access to both locations. Each location is operated by different management, so the services offered at the Central and West location vary. The information on this website describes our Central El Paso location.
For more information about the West location, please visit https://www.facebook.com/Push2CrossFit or call (915) 740-2439.
Central El Paso
6440 Gateway East Bldg B,
El Paso, TX 79905
(915) 203-8122
PUSHasRx Central
6440 Gateway East Bldg B,
El Paso, TX 79905
(915) 203-8122
West El Paso
6100 Dew Drive
El Paso, TX 79912
(915) 740-2439
PUSH West
West El Paso
6100 Dew Drive
El Paso, TX 79912
(915) 740-2439
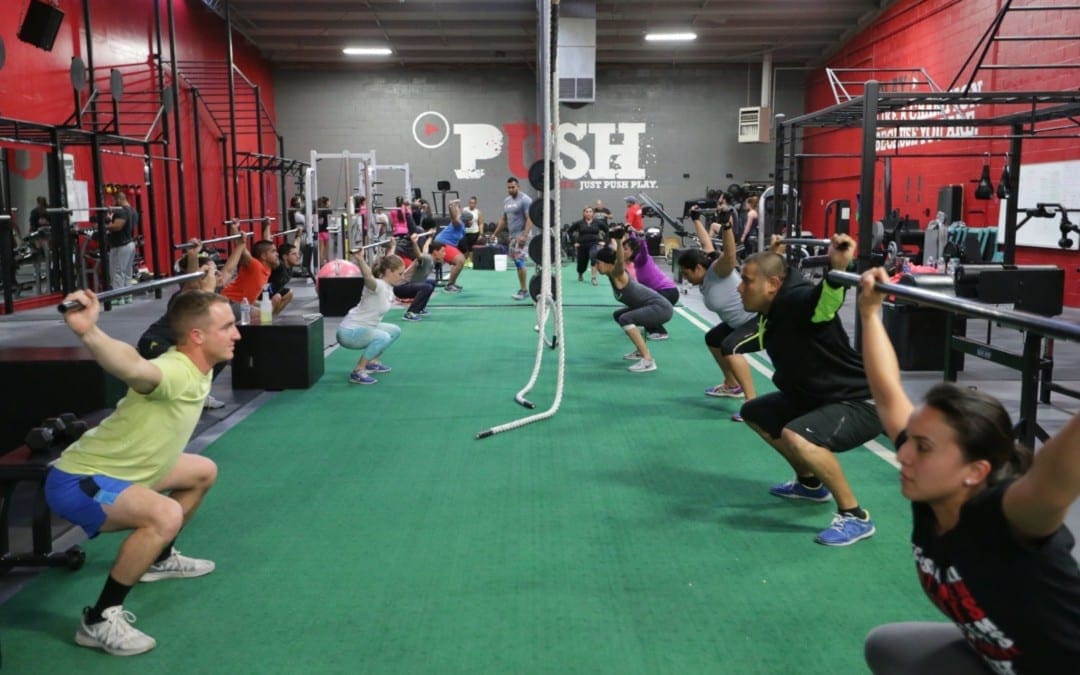

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Crossfit, PUSH-as-Rx
As a PUSH as Rx member, you have access to WODs (workouts of the day) every hour on the hour at our gym. Members have access to showers, making it very convenient for members to join a WOD before work, during lunch, or in between meetings. Our trainers are always available to you to help you improve your technique and help you reach your optimal fitness. Feel free to join the hourly WOD!
For PUSH members, we also offer childcare during certain hours so you can still train even if you have kids! Please call us for more information. We encourage PUSH families to become fit and healthy together, so we always make sure our facility is kid-friendly and safe.
As a PUSH as Rx member, you also have access to chiropractic services with Dr. Jimenez, which can support your fitness goals by ensuring you are pushing your limits safely! Enjoy a first free assessment as a PUSH as Rx member�just stop in any time!
We’ll periodically offer nutrition, flexibility and technique classes to our members at a discounted rate–follow us on Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram for regular updates!
We also offer personal training options at a discounted rate for our PUSH as Rx members�stop in any time to learn more about personal training! We�ll help you move at your own pace to reach your fitness goals.