Internal Abdominal Injuries: Athletes
Children, teens, and adults participate in organized and recreational sports activities for fun, exercise, and social benefits. Individuals and parents are used to scrapes, bumps, bruises, sprains, and strains. However, internal abdominal injuries from the body colliding with another player or object are less common but dangerous. Abdominal injuries make up less than 4 percent of sports injuries but can be severe when they occur. These injuries are common in sports like wrestling, gymnastics, soccer, basketball, football, skiing, snowboarding, BMX freestyle, motocross, skateboarding, ice/field hockey, and lacrosse. Early symptoms are not always obvious or apparent and can be mild or seem to go in a different direction away from the abdominal region, which is why it is essential to know what to look for.

Internal Abdominal Injuries Athletes
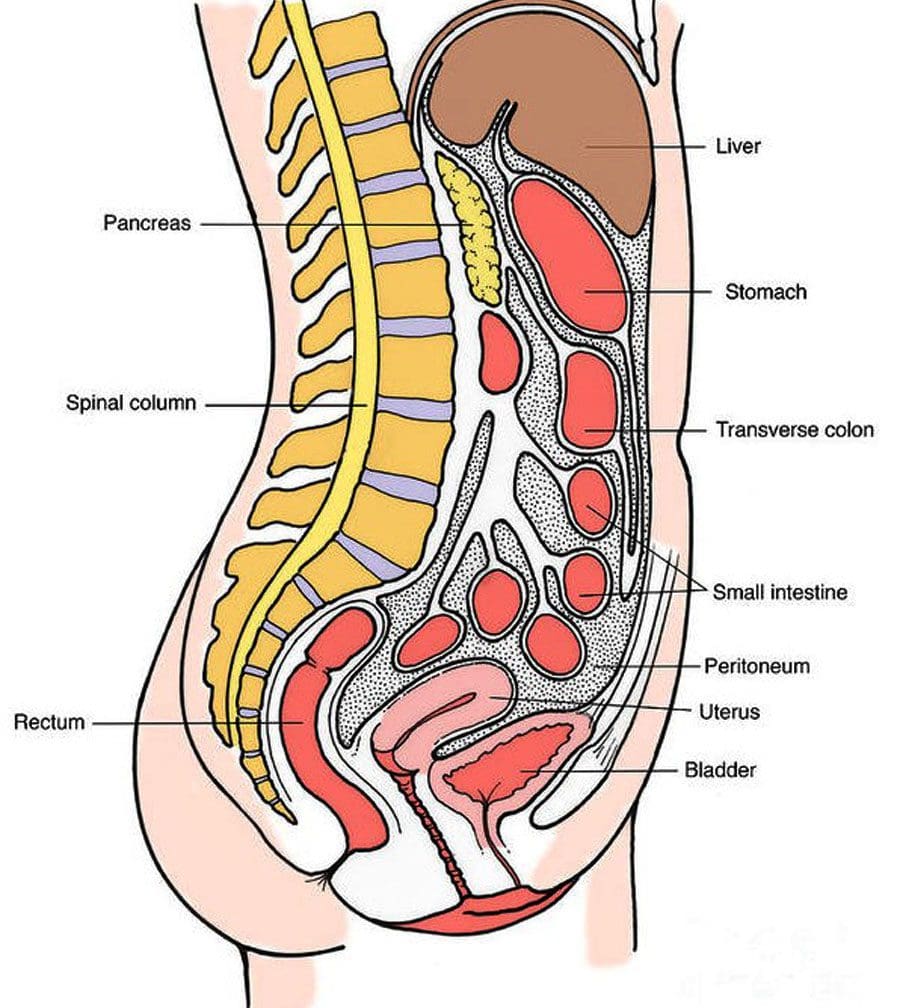
There are about 3oo 000 abdominal sports-related injuries. Kids and young athletes risk injuring their abdominal organs because their abdominal wall is thinner and still in development. However, internal abdominal injuries to the stomach, small and large intestine, spleen, liver, and kidneys can and do happen in adults.
Injury Types
Sports-related internal abdominal injuries are considered rare, but studies suggest they are increasing. The most common sites include:
Liver
- This causes pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- The liver has two lobes.
- The right lobe is the one that gets injured more often because it is bigger and presses against the ribcage.
- A torn liver can cause severe bleeding.
- Shock can develop from the bleeding, causing heart palpitations, rapid breathing, shortness of breath, and a pale, grey, and/or sweaty appearance.
The liver and spleen are the most commonly injured organs in sports. They are filled with blood and can get bruised, or ruptured, and can cause severe bleeding when torn or cut. Bleeding in the abdomen can irritate the diaphragm, which can cause pain in the shoulder. Sometimes shoulder pain is the only symptom making it difficult to diagnose and because bleeding can take time to develop, the symptoms might not present for several hours.
Spleen
- This causes pain in the upper left side of the abdomen.
- The spleen filters around 10% of the body’s blood supply every minute.
- A torn spleen can cause rapid and life-threatening internal bleeding.
Kidneys
- The kidneys can be injured by a blow/hit to the back or flank that causes bruising or laceration.
- This injury can cause flank/side pain, blood in the urine, nausea, and/or vomiting.
Abdominals
- A single organ or multiple organs can be injured.
- This can be the pancreas, diaphragm, stomach, gallbladder, bladder, or intestines.
- Bruising discoloration or bruising, particularly around the belly and flanks.
- This can cause abdominal pain with movement that does not get better that could be accompanied by fever, nausea, or vomiting.
Running into an object, another player, or falling hard can cause bruising, laceration, or create a tear/opening of a bowel wall. Symptoms can be delayed days to weeks after the injury when inflammation or infection develops.
Recognizing Internal Injuries
Signs and symptoms to look for include:
- Abdominal pain
- Bruising around the abdominal area.
- Tenderness over the injured area.
- Rigid abdomen.
- Left-arm and shoulder pain.
- Right-sided abdominal pain and right shoulder pain.
- Blood in the urine.
- Cold, sweaty skin.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Low blood pressure.
- Loss of consciousness.
Treatment
Chiropractic focuses on whole-body health and can help with abdominal injuries. The nervous and digestive systems are interconnected, meaning that damage could lead to viscerosomatic reflexes even if not directly injured. If internal damage or bleeding has occurred, individuals will be referred to a specialist, surgeon, or another emergency medical professional. If internal damage is ruled out, a chiropractic treatment plan that includes adjustments, massage therapy, manual and mechanical decompression, exercises, stretches, and health coaching will help with tissue injuries and problems that are causing gastrointestinal distress.
Spinal Non-Surgical Decompression
References
Arumugam, Suresh, et al. “Frequency, causes and pattern of abdominal trauma: A 4-year descriptive analysis.” Journal of emergencies, trauma, and shock vol. 8,4 (2015): 193-8. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.166590
Barrett, Cassie, and Danny Smith. “Recognition and management of abdominal injuries at athletic events.” International journal of sports physical therapy vol. 7,4 (2012): 448-51.
Kucera, K. L., Currie, D. W., Wasserman, E. B., Kerr, Z. Y., Thomas, L. C., Paul, S., & Comstock, R. D. (2019). Incidence of Sport-Related Internal Organ Injuries Due to Direct-Contact Mechanisms Among High School and Collegiate Athletes Across 3 National Surveillance Systems. Journal of athletic training, 54(2), 152–164. doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-271-17
Slentz, Cris A et al. “Effects of aerobic vs. resistance training on visceral and liver fat stores, liver enzymes, and insulin resistance by HOMA in overweight adults from STRRIDE AT/RT.” American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism vol. 301,5 (2011): E1033-9. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00291.2011