Planks For Spine Support and Back Pain Prevention
Regularly doing planks can support/strengthen the spine and prevent back pain no matter the fitness level. It’s estimated that 70% of adults will experience back problems and pain. One of the best ways to keep the spine healthy is by strengthening the core muscles. The more these muscles are built up, the healthier the body will become. The plank position activates the entire core taking the pressure off of the spine.
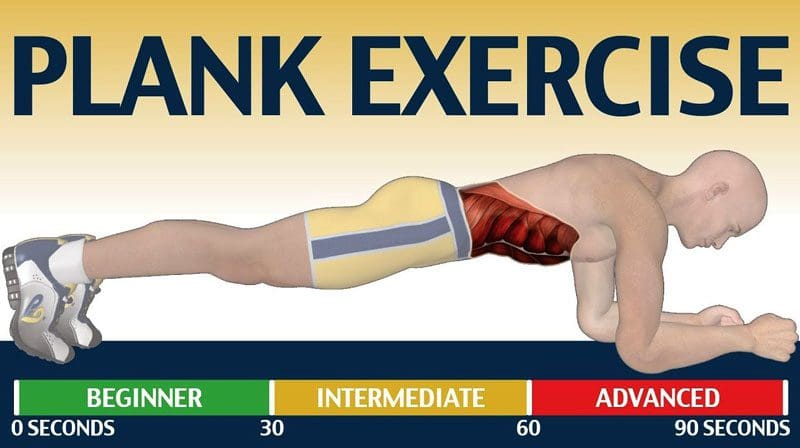
Core Anatomy
The core is the center of the body. It contains all the muscles surrounding the torso. These muscles work together to:
- Stabilize the body during movement.
- Prevent injury when engaged in physical activity/exercise.
- Provide spinal support.
The core is split into two groups of muscles: The inner core and the outer core.
Inner Core
The inner core consists of:
Multifidus Muscles
- Located in the deep layer of the back on either side of the spinal column.
Quadratus Lumborum
- The deep abdominal muscle in the lower back sits on either side of the lumbar region of the spine.
Transversus Abdominis
- Located between the lower ribs and the top of the pelvis.
Pelvic Floor
- This base group of muscles stretches from the tailbone to the pubic bone.
Diaphragm
- A dome-shaped muscle that rests below the lungs.
Outer Core
Rectus Abdominis
- These are more commonly known as the abs.
External Obliques
- These muscles are located on either side of the rectus abdominis.
Internal Obliques
- These muscles are located below the external obliques, inside the hip bones.
Erector Spinae
- These muscles surround the spine and extend up both sides of the vertebral column.
Planks and Back Pain Prevention
When the core is not strong enough, the spine and back muscles overcompensate to keep the body standing correctly. Studies have shown how planks effectively activate the muscles responsible for spinal stabilization. The exercise targets the entirety of the core and strengthens the shoulders and glutes. Strengthening these muscles improves posture, helping to alleviate back problems and pain. However, it’s recommended to talk to a doctor before beginning a plank regimen if back pain is present. If done incorrectly, they could aggravate the back muscles.
Proper Form
Choose an area clear of furniture where the whole body can stretch out. Follow these steps:
- Begin with hands and knees on the floor.
- Extend the legs back while keeping the elbows directly below the shoulders and the wrists below the elbows.
- Keep the head down, looking at the space just above the hands.
- Engage the abs and keep the body rigid.
- Imagine a perfectly straight line from the neck to the toes.
- Hold the position for 10 to 60 seconds, depending on fitness level.
- Lower the body gently to the floor.
- Make sure not to curve the back as curving means that the abdominal muscles are being engaged, and tilting the head up can strain the neck.
- Both can lead to injury, which is why maintaining proper form is essential.
Plank Variations
There are variations of this exercise for different levels of physical fitness. Once the modified and full plank has been mastered, various planks can target other areas of the body. These include:
Side Plank
- These involve shifting the weight to one forearm while extending the other arm into the air.
One-arm Plank
- These involve lifting one hand off the ground, then alternating.
Single-leg Plank
- These require lifting one leg off the ground, then alternating.
Walking Plank
- These shift the right hand and foot evenly, then bring the left hand and foot to the full plank position.
Reverse Plank
- These require facing the opposite direction and pushing upwards towards the ceiling.
Anybody can work up to a plank at any age at any fitness level; it just takes time. Once achieved, it is a great way to keep the body’s core strong, healthy and helps prevent back problems.
Body Composition
Band Lateral Raise
The lateral band raise is an excellent workout for the shoulders. It works out the lateral deltoid, anterior deltoid, and serratus anterior.
- Grasp one band in one hand.
- Step on the free end with the opposite foot.
- Right hand and left foot and vice versa.
- Slowly extend and raise the arm until they are parallel to the floor.
- Lower the arms in the same manner.
- If the shoulders are healthy and strong enough, try adding dumbbells or kettlebells to increase the resistance.
References
Calatayud, Joaquín et al. “Tolerability and Muscle Activity of Core Muscle Exercises in Chronic Low-back Pain.” International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 16,19 3509. 20 Sep. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijerph16193509
World Health Organization. (2013) “Low back pain.” www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/Ch6_24LBP.pdf
Youdas, James W et al. “Magnitudes of muscle activation of spine stabilizers in healthy adults during prone on elbow planking exercises with and without a fitness ball.” Physiotherapy Theory and practice vol. 34,3 (2018): 212-222. doi:10.1080/09593985.2017.1377792









