
Why Staying Hydrated Is Crucial for Your Well-being
Can individuals maintain proper hydration levels in their bodies to prevent spinal pain and other musculoskeletal conditions?
Introduction
When making small changes to better their health and wellness, many understand that eating nutritional foods, exercising, and finding ways to reduce the pain and stress that environmental factors have affected the body. However, there is also another crucial component to a person’s health and wellness, and that is staying hydrated. Many individuals sometimes don’t realize that the human body contains about 60% of the water, which helps every vital organ, muscle, tissue, and vertebra in the body to function. However, many individuals who do not consume enough water due to a stressful event, exercising, or just wanting to drink sugary drinks will feel pain and discomfort in their bodies. This can range from mild headaches to back pain. Today’s article focuses on what spinal pain correlates with the back, why staying hydrated can reduce spinal pain and ways to stay hydrated. We talk with certified associated medical providers who inform our patients to maintain proper hydration to reduce the chances of spinal pain affecting their bodies. While asking their associated medical provider intricate questions, we advise patients to incorporate daily hydration levels as part of their routine to reduce the chances of spinal pain from returning. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
Spinal Pain Is Correlated With The Back
Do you feel constant aches or pains after a stressful day? Do you feel like chugging gallons of water but still feel thirsty? Or have you been noticing that you have been dealing with limited mobility that has been causing you pain and discomfort in your lower back? These pain-like scenarios are multifactorial and can correlate with spinal pain affecting the back. Now, many people wonder why spinal pain is associated with back pain. The spine is crucial in allowing the individual to be upright and move around during daily activities. The spinal vertebrae discs are between the bones, which would enable shock absorption when a person twists, bends, or flexes so the bones don’t rub together. However, when the body ages, the spine does, too, which causes the intervertebral disc to gradually fall and change the dynamics of the affected spine segments. (Kos et al., 2019) To that point, when the intervertebral disc becomes compressed due to degeneration, it can lead to the development of back pain.
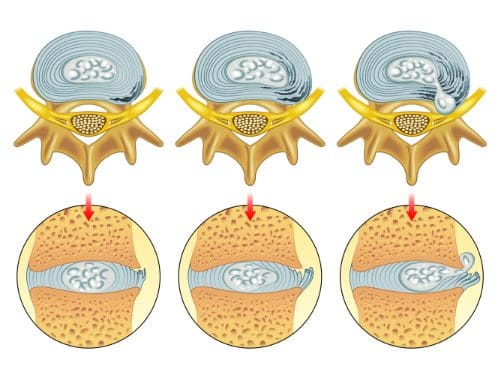
Since low back pain is a multifactorial musculoskeletal condition, many individuals often develop low back pain from numerous environmental risk factors like physical labor, excessive sitting or standing, poor dieting, and physical inactivity, which can cause individuals to have a loss of sensation, reduced reflexes, limited range of movements and tenderness can affect a person’s gait and posture. (Kabeer et al., 2023) When the spinal discs are being compressed, the water inside the disc becomes dehydrated and is linked to lower back pain. (Cheung et al., 2023) When the spinal discs are dehydrated in the spine due to improper hydration, it can lead to immobility, cause the disc to degenerate, and cause spinal structural defects that cause the surrounding muscles and tissues to have biomechanical instability and inflammation. (Hauser et al., 2022) When the body starts dehydrating, it retrieves water from the spine and other parts to sustain life and keep the vital organs functioning.
Eating Right To Feel Better- Video
Why Staying Hydrated Can Reduce Spinal Pain

Proper hydration is key to reducing the chances of spinal pain. By staying hydrated with plain, pure water, individuals can stay focused, remove toxins from the body, aid in weight reduction, and reduce muscle and low back pain. (Nsiah-Asamoah & Buxton, 2021) Drinking at least 64 ounces of water a day can rehydrate the body and prevent future issues that can cause pain. Proper hydration allows the body to maintain cell activity and regulate body temperature, reducing the chances of pain affecting the body.
Ways to Stay Hydrated
There are ways to stay hydrated and allow the body to have proper hydration levels. Incorporating hydrating fruits and vegetables can help aid in proper hydration as these fruits and vegetables contain about 90% water and the essential nutrients. Additionally, when individuals try to get their hydration levels back up, they are encouraged to drink more fluids as they prefer, especially if they feel unwell. This is to ensure that the body is hydrated enough so that individuals can receive subcutaneous or intravenous fluid supplements combined with regular fluid intake. (Li et al., 2023) Another way many individuals can stay hydrated is to combine non-surgical treatments like chiropractic care and spinal decompression to help realign and lengthen the spine to reduce unwanted pressure on the spinal discs and rehydrate them. The combination of non-surgical treatments and drinking plenty of hydrating fluids can help many individuals dealing with back pain associated with the spine as they start to make small changes to their routine and can live a life pain-free.
References
Cheung, S. T. Y., Cheung, P. W. H., & Cheung, J. P. Y. (2023). Why Are Some Intervertebral Discs More Prone to Degeneration?: Insights Into Isolated Thoracic “Dysgeneration”. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 48(12), E177-E187. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000004632
Hauser, R. A., Matias, D., Woznica, D., Rawlings, B., & Woldin, B. A. (2022). Lumbar instability as an etiology of low back pain and its treatment by prolotherapy: A review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil, 35(4), 701-712. https://doi.org/10.3233/BMR-210097
Kabeer, A. S., Osmani, H. T., Patel, J., Robinson, P., & Ahmed, N. (2023). The adult with low back pain: causes, diagnosis, imaging features and management. Br J Hosp Med (Lond), 84(10), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2023.0063
Kos, N., Gradisnik, L., & Velnar, T. (2019). A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch, 73(6), 421-424. https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2019.73.421-424
Li, S., Xiao, X., & Zhang, X. (2023). Hydration Status in Older Adults: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges. Nutrients, 15(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112609
Nsiah-Asamoah, C. N. A., & Buxton, D. N. B. (2021). Hydration and water intake practices of commercial long-distance drivers in Ghana: what do they know and why does it matter? Heliyon, 7(3), e06512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06512




 We Welcome You ??. Purpose & Passions: I am a Doctor of Chiropractic specializing in progressive, cutting-edge therapies and functional rehabilitation procedures focused on clinical physiology, total health, practical strength training, and complete conditioning. We focus on restoring normal body functions after neck, back, spinal and soft tissue injuries.
We Welcome You ??. Purpose & Passions: I am a Doctor of Chiropractic specializing in progressive, cutting-edge therapies and functional rehabilitation procedures focused on clinical physiology, total health, practical strength training, and complete conditioning. We focus on restoring normal body functions after neck, back, spinal and soft tissue injuries.





