by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
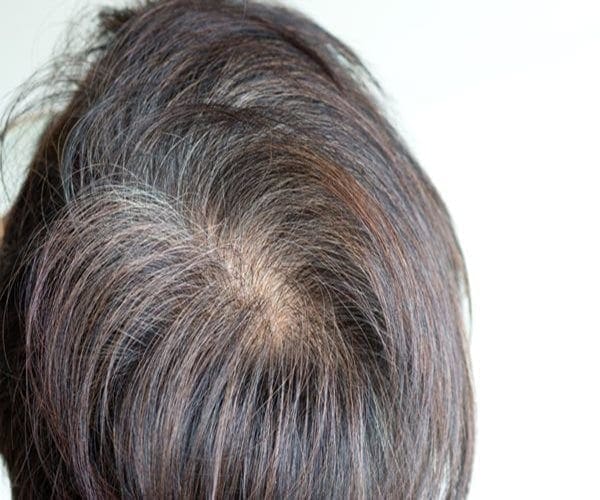
Changes in your hair — whether it’s graying hair or hair loss — are a bane of aging.
But if new research in mice pans out in humans, you could one day cross worries about your mane off your list of concerns about getting older.
That’s because researchers accidentally pinpointed skin cells linked to gray hair and balding while they were conducting research on a specific type of cancer that affects nerve cells. The investigators believe their discovery could someday lead to new treatments to stop baldness and graying hair.
“Although this project was started in an effort to understand how certain kinds of tumors form, we ended up learning why hair turns gray and discovering the identity of the cell that directly gives rise to hair,” said study author Dr. Lu Le. He is an associate professor of dermatology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
“With this knowledge, we hope in the future to create a topical compound or to safely deliver the necessary gene to hair follicles to correct these cosmetic problems,” he explained in a university news release.
The researchers found that a protein called KROX20 turns on skin cells that develop into the hair shaft. These cells are usually linked to nerve development.
These skin cells then produce a protein involved in hair color. This protein is called stem cell factor (SCF). When SCF was deleted from mice, their hair turned white, according to the report.
When KROX20 cells were deleted, the mice became bald, the researchers said.
Studies done on animals don’t always turn out the same in humans, so it remains to be seen if these results will look as promising in people.
The study team does want to learn if SCF and KROX20 stop working properly over time in people. And, because gray hair and balding are often among the first signs of aging, this research could also provide information on aging in general, the authors noted.
The study was published online May 2 in the journal Genes & Development.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Diets, Fitness
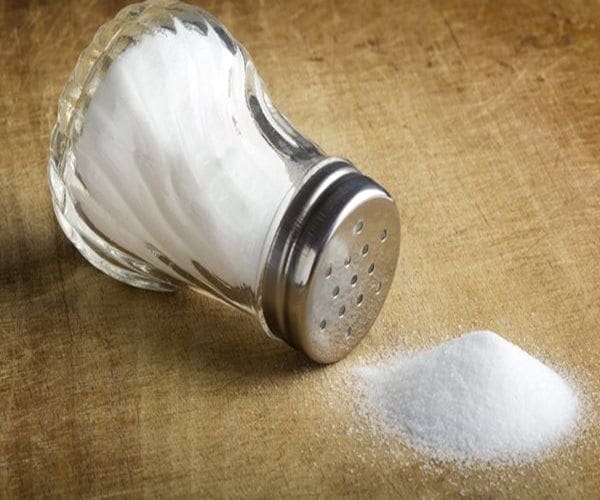
Tossing out the salt shaker may not be enough for your heart health. Most of the salt that Americans consume comes from processed foods and restaurant meals, a new study finds.
In a sampling of 450 U.S. adults, only 10 percent of salt, or sodium, in their diet came from food prepared at home. About half of that was added at the table.
Instead, restaurant meals and store-bought foods — including crackers, breads and soups — accounted for 71 percent of salt intake, the study found.
“Care must be taken when food shopping and eating out to steer clear of higher-sodium foods,” said lead researcher Lisa Harnack.
For prevent harmful high blood pressure, Americans are advised to limit salt intake to 2,300 milligrams (mg) daily, said Harnack, a professor at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health. That’s the equivalent of one teaspoon.
But, more than eight out of 10 Americans exceed this limit “by a mile,” she said.
Food diaries from study participants showed that about 3,500 mg of sodium was consumed a day on average.
The report was published online May 8 in the journal Circulation.
Kathryn Foti, an epidemiologist who wasn’t involved in the study, pointed out that high blood pressure is a leading cause of heart disease and stroke in the United States.
“Reducing salt reduces blood pressure and can help prevent cardiovascular disease,” said Foti, of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
“The most effective way to reduce salt is to reduce the content in commercially processed and prepared foods,” added Foti, co-author of an accompanying journal editorial.
She said gradual, voluntary reductions across the food supply could have a large public health benefit.
“Reducing average sodium intake by as little as 400 mg per day could prevent up to 32,000 heart attacks and 20,000 strokes annually,” she said.
The American Heart Association has launched a sodium-reduction campaign to encourage food companies and restaurants to reduce the salt in their products.
Harnack said food companies and restaurants that have pledged to comply “should be commended.”
But, Foti added, doctors should step up their efforts by educating patients about where their salt actually comes from.
“While it’s OK to encourage patients to go easy on the salt shaker, more importantly, physicians should emphasize product selection,” Foti suggested.
She and Harnack recommended reading the Nutrition Facts panel on packaged foods.
Swap out the high-sodium items with lower-salt options, Foti advised. Salt content in many foods varies widely across brands, she noted.
In restaurants where nutrition information isn’t posted, “consumers can request information about the salt content of menu items or ask how foods are prepared,” Foti added.
“And of course, choosing more fresh foods, such as fruits and vegetables, can help you reduce the salt in your diet,” she said.
The study involved 450 racially diverse adults, aged 18 to 74, living in Birmingham, Ala.; Minneapolis-St. Paul; or Palo Alto, Calif.
Between December 2013 and December 2014, the participants were asked to record their daily diet for four 24-hour periods. In addition, the study participants provided samples of salt equivalent to the amount they added at home.
Average salt consumption was over 50 percent more than the recommended 2,300 milligrams, the researchers found.
Salt added while cooking comprised only about 6 percent of sodium consumption, and salt added at the table from the salt shaker accounted for just 5 percent, according to the study.
Salt naturally found in foods made up about 14 percent of dietary sodium, while salt in tap water, dietary supplements and antacids made up less than 1 percent, according to the report.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Fitness, Health, Wellness
A new season means it’s time for a fresh new pair of kicks. And what better option to transition to spring in style than some bright white sneakers? Not only are they totally trendy right now, but this neutral footwear also matches (nearly) everything in your wardrobe. Plus, sneakers are the ultimate travel shoe—you can walk around in them all day without having to stop and deal with blisters or sore arches. (These comfortable ballet flats, stylish flats with arch support, and podiatrist-approved comfortable sandals are also great options for spring and summer travel, as well as everyday wear.) So whether you need sneaks to wear to work or to sport post-gym with your mesh-paneled leggings and cool hoodies, we’ve found nine fashionable white sneakers for women that will help you conquer the new season with a little extra pep in your step.
Converse Jack Purcell CP Canvas Low Top ($65; zappos.com)
If you’re looking for that quintessential pair of casual kicks, white Converse will do the trick. These classic sneakers are a super versatile choice—you can wear them on the weekends while running errands or rock them at the office for a cool, business-casual look.
Take your style game to a whole new level with these killer high-tops. You can rock them with rolled up jeans, shorts, or even a skirt for a truly on-point look.

Keds Champion Original ($40; zappos.com)
Remember these? Keds are making a comeback and we’re definitely not mad about it—we love the versatility of these cute, simple sneaks. Plus, when they get scuffed, you can easily throw them in the wash—a major bonus when it comes to keeping white footwear fresh and clean.

Adidas Stan Smith Sneaker ($75; nordstrom.com)
These Adidas may be an old-school style, but modern-vintage sneakers are coming back in a big way. Plus, wearing them with stylish athleisure gives these sneakers an upgraded, hip look. Let them take you from a Saturday morning workout to brunch and beyond by pairing the sleek shoes with some bright, bold leggings.

New Balance 576 Made in UK Animal ($250; newbalance.com)
Mix up your wardrobe with a little dose of texture. These stylish monochromatic New Balance shoes, featuring an embossed leather upper, can easily be dressed up or down for any occasion.

DC Trase Slip-On TX ($45; zappos.com)
Looking for pair of shoes to easily throw on as you rush out the door? These slip-ons make getting dressed in the morning a total breeze. Not to mention, they look white-hot with skinny jeans, capris, shorts, dresses, and more.

Reebok Lifestyle Princess ($40; zappos.com)
This classic aerobics shoe has been updated for 2017 with breathable uppers and a terry lining designed to absorb moisture. They bring a preppy vibe to any active outfit.

Adidas Superstar Sneaker ($80; nordstrom.com)
The Adidas Originals Superstar is still a must-have after 48 years. Pair it with your basic leggings or even with a maxi skirt for a celeb status outfit.

Rebook Classic Leather Pearlized ($80; reebok.com)
A subtle shine makes the Reebok Classic Leather Pearlized that much more luxe. Padded foam sockliners keeps blisters at bay when you are working the no sock look.

Puma Basket Heart Patent ($85; puma.com)
Oversize laces—a nod to the 80s—give the Puma Basket Heart Patent a retro feel. This style was originally introduced in the 60s as a basketball warm-up shoe, so they’re great for hitting the courts too.


by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Fitness, Health, Wellness
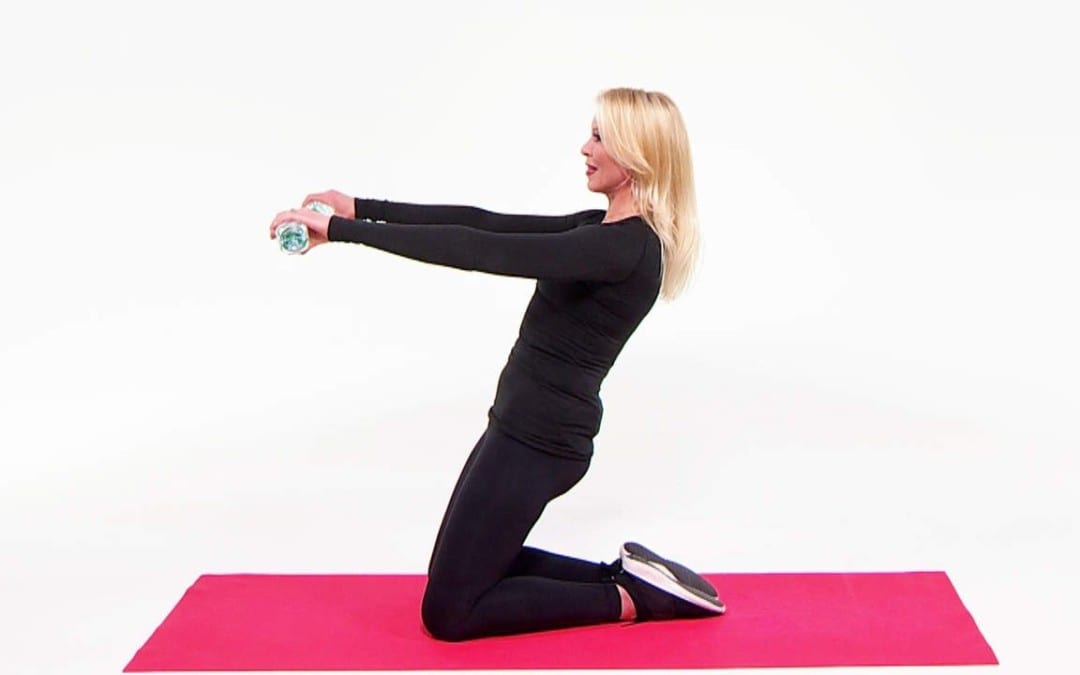
Pilates is known for building strength in your core—but that doesn’t mean it only works the abs. This popular workout can also lengthen your limbs and sculpt lean muscle all over. Take it from Julie Erickson, founder of the Endurance Pilates and Yoga studio in Boston. A certified Pilates instructor who’s trained pro athletes and dancers, Julie knows exactly how to use this workout to target each part of the body so you stay strong, no matter what type of activity you’re into (football, ballet, you name it!). In this video, Julie demonstrates six Pilates exercises that are specifically intended to help tone you from the waist up. Don’t have time to watch? Here are the six sculpting moves she shows us:
Shoulder opener: On a mat, rest on your knees holding a weight (or water bottle!) in each hand. Raise your arms out slightly behind the body, keeping them straight and pulsing your hands in towards your midsection behind the back for 45 seconds.
RELATED: This 10-Minute Ab-Sculpting Pilates Workout Targets Your Inner Core
Shave: On a mat, rest on your knees with your arms raised straight above your head. Create a diamond shape with hands above the head. With hands still in a diamond shape, bend at the elbows to lower the arms behind the head, then extend straight again. Continue this bend-and-extend movement for 45 seconds.
Arms wide: Standing tall with your back against a wall, slowly raise arms out to your sides until they create a wide “V” shape above your head. Return them down to the starting position and repeat this movement for 45 seconds.
RELATED: Get Sculpted Shoulders and Toned Arms with Emily Skye’s Upper-Body Workout
Goal: Standing tall with your back against a wall, raise your arms to a goal post position with each elbow creating a 90-degree angle at shoulder height. Keep arms raised and slowly shrug your shoulders up and down for 45 seconds.
Chest expansion: On a mat, rest on your knees with a weight in each hand. Slowly raise your arms straight out to chest height in front of you, then lower them back down. Turn your head to the right, then left, then return to center and repeat this sequence for 45 seconds.
Overhead side stretch: Standing tall, raise your right arm up overhead and lean your torso toward the left to stretch the side body. Return to center and repeat with the left arm raised, leaning your torso to the right to stretch the other side. Continue to switch off stretching to each side for 45 seconds.
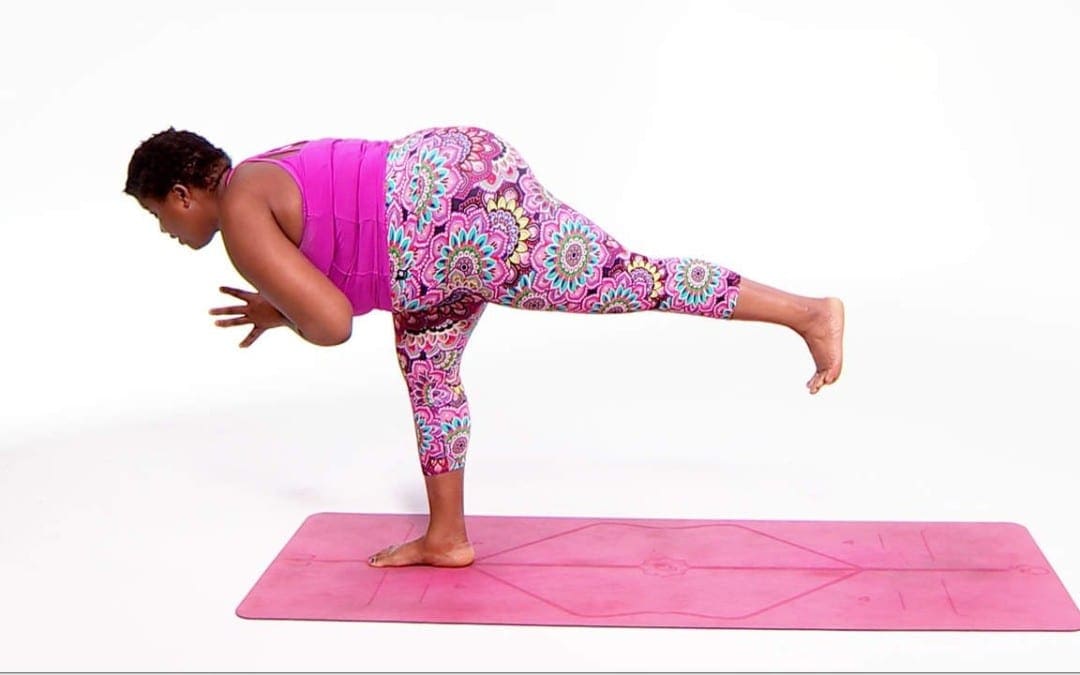

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Fitness, Health, Wellness
Taking care of your mind and body can take tons of different forms, from settling in for a scented bubble bath to getting your heart rate sky-high in spin class. It all depends on what works best for you.
But if you ask us, practicing self-care while you stay active is the best of both worlds. That�s just what we�re doing in this eight-minute flow with body-positive yogi and Every Body Yoga author Jessamyn Stanley.
�This sequence is all about getting into your own body, finding your strength within, and remembering that you are self-confident all the time, no matter what obstacle, no matter where you are,� says Jessamyn. Preach.
There�s science to back up yoga�s mind-body benefits as well. The ancient activity comes with a wide range of healthy side effects, from lower stress levels to a stronger core, better sex, and fewer headaches (you know, just to name a few). Not to mention yoga is accessible for pretty much every body, as Jessamyn�s book demonstrates.
RELATED: This Invigorating Yoga Flow is the Best Way to Get Energized
In the video above, she�ll show you how to strengthen and lengthen your body using classic poses like Warrior I, Warrior II, Triangle, and more. You�ll also work on building better balance and eventually take time at the end of the practice to sit still, breathe, and appreciate all the amazing work your body has just allowed you to do.
Nervous because you�re a yoga novice? There�s no need. Jessamyn caters the flow to beginner and advanced yogis alike. Follow the yoga routine in the clip above to practice self-love and exercise at the same time. It�s really a win-win. And if you want to keep the self-love coming post-workout, go ahead and treat yourself to a DIY spa day. Because you deserve it.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | UTEP (Local) RSS
UTEP track and field will be hosting the 2017 Conference USA Outdoor Championships from May 11-14 at Kidd Field.
The Miners women’s team will be looking to win its first outdoor conference title in program history. The women’s team comes into the competition full steam after claiming its third consecutive C-USA indoor title.
The Fastest Kid in El Paso race will be taking place on Saturday, May 13. Kids ages 5-13 are invited to participate in the 100m dash at 3 p.m. at Kidd Field. To sign-up for the race please, contact UTEP Marketing at (915) 747-6065.
Leading the way for the Miners will be sophomore Tobi Amusan. The All-American opened the outdoor season with the second-fastest time in the nation of 12.63 in the 100m hurdles registered at the UTEP Springtime. The hurdler has claimed six first-places finishes this season, including a stellar performance in the 200m that rates her eighth nationally with a time of 22.60.
Lucia Mokrasova will also highlight the Miners kicking off the championships on Thursday with the heptathlon set to start at 2:45 p.m. MTMokrasova enters the meet ranked eighth nationally with 5,671 points registered at Texas Relays.
Highlighting the distance races will be Middle Tennessee Agnes Abu. The senior comes into the championships ranked sixth in the nation in the 800m.
On the men’s side, freshman Emmanuel Korir will be the Miner to watch. The mid-distance runner was named to The Bowerman Watch List after posting the fastest time in the nation of 1:43.73 in the 800m. Korir also ranks third in the nation in the 400m with a time of 44.67.
Tickets can be purchased at ticketmaster.com. A four-day pass can be purchased for $20 or a daily ticket can be purchased for $8 for adults or $4 for kids. Students are able to attend the championship free with their Miner ID.
For additional athletes to watch at the championship, click here. For information about parking, tickets and live results, click here.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Herbs, Natural Health, Remedies, Wellness
Many parents of children with debilitating gastrointestinal disorders may be frustrated by the lack of good treatment options and tempted to try herbal remedies at home, but a new study suggests they should proceed with caution.
Researchers examined data from 14 previously published studies with a total of 1,927 children suffering from problems like diarrhea, dehydration, colic, constipation, abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome. They didn’t have enough data to combine results from multiple small studies to offer definitive proof that herbal remedies might work for any of these health problems.
But some of the small studies did suggest certain herbal medicines might help ease diarrhea, abdominal pain and colic. And the studies didn’t find serious side effects associated with herbal remedies.
“The lack of conclusive research is unfortunately a general problem in pediatrics, but a special problem in herbal medicine is that for many herbal remedies no licensed and standardized products are available,” said lead study author Dr. Dennis Anheyer of the University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
In other words, even if evidence shows an herb may be safe and effective for a specific health problem, that doesn’t necessarily mean that every single version of that herb available for sale would work as well or be free of side effects.
When researchers looked at four studies with a total of 424 participants, they found some evidence suggesting that a variety of herbal remedies might help diarrhea: a plant in the rose family called potentilla erecta, carob bean juice, and an herbal compound preparation with chamomile.
One study with 120 participants also suggests that peppermint oil might help curb the duration, frequency and severity chronic abdominal pain that doesn’t have a clear medical explanation.
And, fennel might help ease colic symptoms in babies according to a review of five small studies of herbal remedies for infant colic.
While it’s possible herbal remedies might be used in addition to traditional medications or to help reduce reliance on drug therapy, parents should still see a doctor before trying out herbal therapies on their own, Anheyer said by email.
Another reason for caution is that even the studies in the current analysis that found herbal remedies effective don’t show how large the effects are, noted Dr. Peter Lucassen, a researcher at Radboud University Medical Center in the Netherlands who wasn’t involved in the study.
These small studies might get results that find herbs are statistically better than no treatment or alternative therapies, but the difference still might not be big enough to have a meaningful clinical impact on patients’ symptoms, Lucassen said by email.
“I would not advocate any of the herbal medicine because the article does not provide any data about how large the effects are,” Lucassen said.
Often, herbal remedies combine a variety of ingredients and use differing amounts of the main ingredients, which may alter how well they work and how safe they are for kids, Lucassen added. They might also contain chemicals not found in prescription medications that have dangerous side effects or a risk of overdose.
And there’s another reason parents shouldn’t try herbal remedies without seeing a doctor.
“Delayed diagnosis might be the result of herbal medications because parents seek help too late because they try the herbs first,” Lucassen said.




















