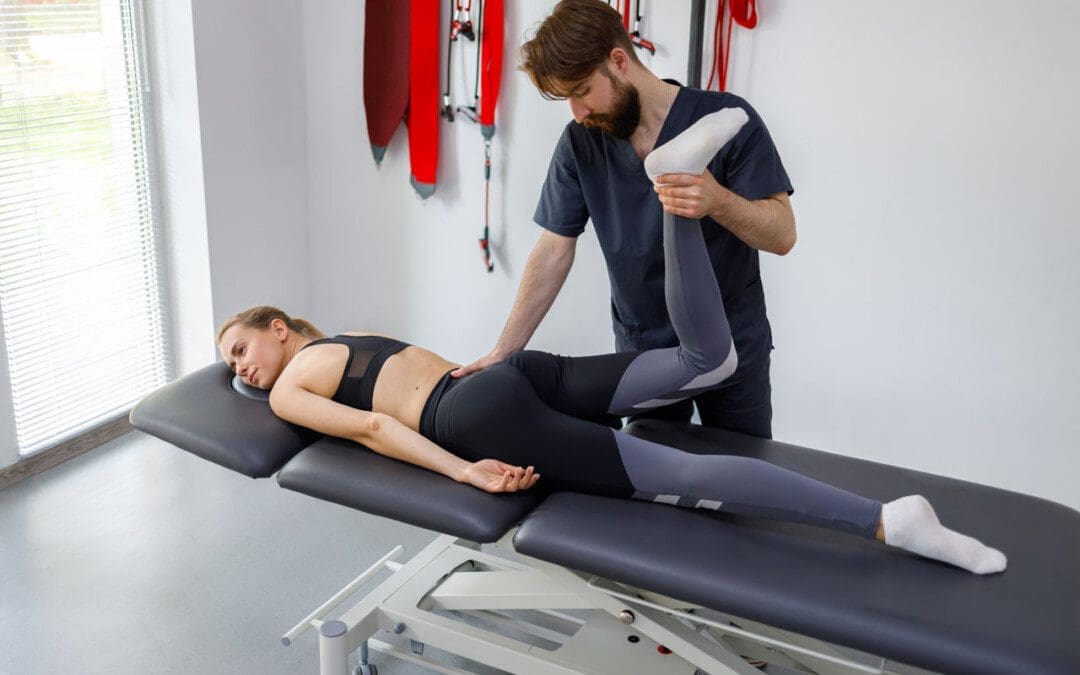
Athletes and physically active individuals who participate in activities, exercises, and sports that involve kicking, pivoting, and/or shifting directions can develop pelvis overuse injury of the pubic symphysis/joint at the front of the pelvis known as osteitis pubis. Can recognizing the symptoms and causes help in treatment and prevention?
Contents
Osteitis Pubis Injury
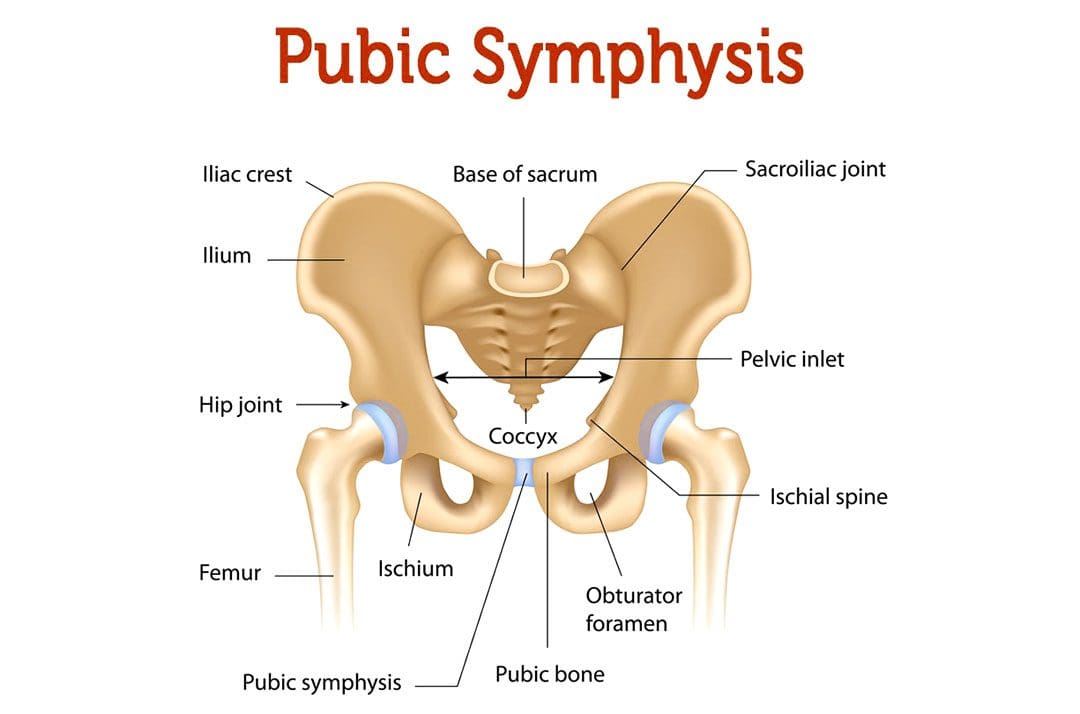
Osteitis pubis is the inflammation of the joint that connects the pelvic bones, called the pelvic symphysis, and the structures around it. The pubic symphysis is a joint in front of and below the bladder. It holds the two sides of the pelvis together in the front. The pubis symphysis has very little motion, but when abnormal or continued stress is placed on the joint, groin and pelvic pain can present. An osteitis pubis injury is a common overuse injury in physically active individuals and athletes but can also occur as the result of physical trauma, pregnancy, and/or childbirth.
Symptoms
The most common symptom is pain over the front of the pelvis. The pain is most often felt in the center, but one side may be more painful than the other. The pain typically radiates/spreads outward. Other signs and symptoms include: (Patrick Gomella, Patrick Mufarrij. 2017)
- Lower abdominal pain in the center of the pelvis
- Limping
- Hip and/or leg weakness
- Difficulty climbing stairs
- Pain when walking, running, and/or shifting directions
- Clicking or popping sounds with movement or when shifting directions
- Pain when lying down on the side
- Pain when sneezing or coughing
Osteitis pubis can be confused with other injuries, including a groin strain/groin pull, a direct inguinal hernia, ilioinguinal neuralgia, or a pelvic stress fracture.
Causes
An osteitis pubis injury usually occurs when the symphysis joint is exposed to excessive, continued, directional stress and overuse of the hip and leg muscles. Causes include: (Patrick Gomella, Patrick Mufarrij. 2017)
- Sports activities
- Exercising
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Pelvic injury like a severe fall
Diagnosis
The injury is diagnosed based on a physical examination and imaging tests. Other tests may be used to rule out other possible causes.
- The physical exam will involve manipulation of the hip to place tension on the rectus abdominis trunk muscle and adductor thigh muscle groups.
- Pain during the manipulation is a common sign of the condition.
- Individuals may be asked to walk to look for irregularities in gait patterns or to see if symptoms occur with certain movements.
- X-rays will typically reveal joint irregularities as well as sclerosis/thickening of the pubic symphysis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging – MRI may reveal joint and surrounding bone inflammation.
- Some cases will show no signs of injury on an X-ray or MRI.
Treatment
Effective treatment can take several months or longer. Because inflammation is the underlying cause of symptoms, the treatment will often involve: (Tricia Beatty. 2012)
Rest
- Allows the acute inflammation to subside.
- During recovery, sleeping flat on the back may be recommended to reduce pain.
Ice and Heat Applications
- Ice packs help reduce inflammation.
- The heat helps ease pain after the initial swelling has gone down.
Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy can be extremely helpful in treating the condition to help regain strength and flexibility. (Alessio Giai Via, et al., 2019)
Anti-inflammatory Medication
- Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications – NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce pain and inflammation.
Assistive Walking Devices
- If the symptoms are severe, crutches or a cane may be recommended to reduce stress on the pelvis.
Cortisone
- There have been attempts to treat the condition with cortisone injections, but the evidence supporting its use is limited and needs further research. (Alessio Giai Via, et al., 2019)
Prognosis
Once diagnosed, the prognosis for full recovery is optimal but can take time. It can take some individuals six months or more to return to pre-injury level of function, but most return by around three months. If conservative treatment fails to provide relief after six months, surgery could be recommended. (Michael Dirkx, Christopher Vitale. 2023)
Sports Injuries Rehabilitation
References
Gomella, P., & Mufarrij, P. (2017). Osteitis pubis: A rare cause of suprapubic pain. Reviews in urology, 19(3), 156–163. https://doi.org/10.3909/riu0767
Beatty T. (2012). Osteitis pubis in athletes. Current sports medicine reports, 11(2), 96–98. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0b013e318249c32b
Via, A. G., Frizziero, A., Finotti, P., Oliva, F., Randelli, F., & Maffulli, N. (2018). Management of osteitis pubis in athletes: rehabilitation and return to training – a review of the most recent literature. Open access journal of sports medicine, 10, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.2147/OAJSM.S155077
Dirkx M, Vitale C. Osteitis Pubis. [Updated 2022 Dec 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556168/
General Disclaimer, Licenses and Board Certifications *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Comprehensive Guide to Recovery from Osteitis Pubis Injury" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those on this site and on our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on naturally restoring health for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card








