Managing Peptic Ulcers: A Comprehensive Guide
For individuals with chronic pain conditions, what are the risks of developing peptic ulcers?
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers
A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of the stomach or duodenum, the first area of the small intestine. The most common symptom is a burning stomach pain that may come and go for several days or weeks. Other symptoms include:
- Feeling full
- Feeling bloated
- Belching
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Stress and spicy foods can worsen ulcers but do not cause them.
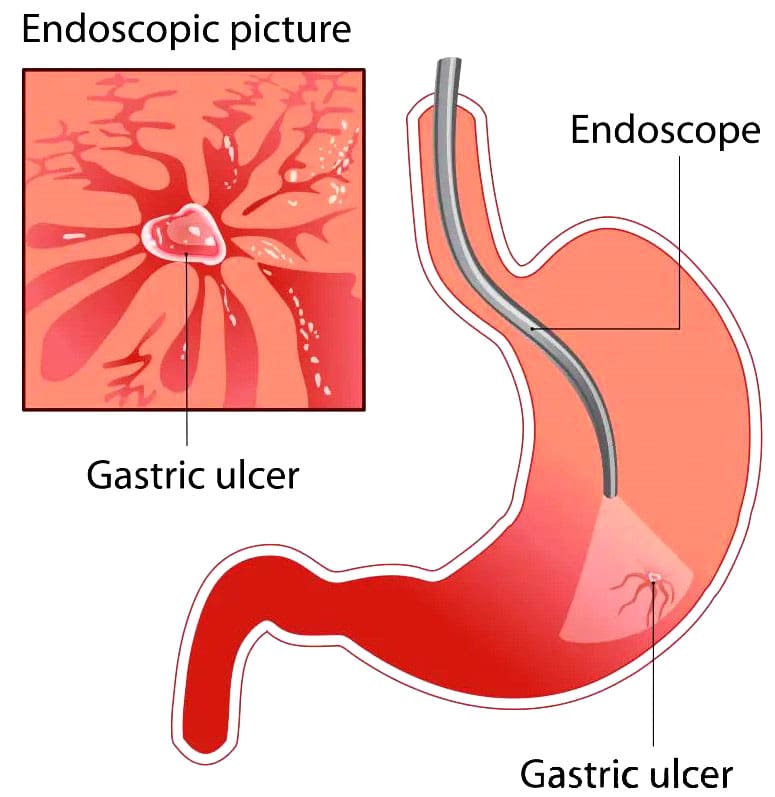
A peptic ulcer is a sore that occurs in the mucosal lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus. It is caused by stomach acids or other digestive juices damaging the stomach or duodenum lining. When the ulcer is in the stomach, it might also be called a gastric ulcer. The acid can create a painful open sore that may bleed. The most common cause of a peptic ulcer is a type of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). A second, less common cause of peptic ulcers is the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications or NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. (Fashner J. & Gitu A. C. 2015) Using over-the-counter NSAIDs for the occasional headache or achy back won’t cause a peptic ulcer. Rather, peptic ulcer disease is something that can occur with longer-term use, especially at high doses, such as for chronic pain associated with arthritis or other inflammatory conditions. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
NSAIDs and Ulcer Development
NSAIDs can cause ulcers because they can interfere with the stomach’s ability to protect itself from gastric acids as they slow the production of protective mucus in the stomach and change its structure. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022) While these acids are vital to the digestive process, they can compromise the stomach’s protective barriers. The stomach has three protections against gastric acid:
- Foveolar cells that line the stomach produce a protective mucus.
- Bicarbonate is produced by the foveolar cells, which help neutralize stomach acid.
- Blood circulation aids in repairing and renewing cells in the stomach’s mucosal layer.
Specific lipids called prostaglandins, which the body makes, affect pain receptors. NSAIDs work to reduce pain by blocking enzymes involved in the production of certain prostaglandins. Prostaglandins also protect the stomach’s mucosal layer, which can be broken when depleted. Suppressing the body’s natural defenses against gastric acids can lead to inflammation in the stomach lining. Over time, this can cause a capillary blood vessel to rupture, causing bleeding and the development of an open, ulcerative sore. (Bjarnason I. et al., 2018)
Symptoms
A peptic ulcer may cause symptoms in the digestive tract, but some individuals may have no symptoms. The most common symptom is upper abdominal pain, which can feel dull or burning. The pain can range in severity, with some experiencing mild discomfort and others having severe pain. Most of the time, the pain will occur after a meal, but it might also happen at night for some. It could go on from a few minutes to a few hours. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022) Other symptoms are less common but can include:
- Bloating
- Burping
- Gas
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Feeling sick in the stomach.
- Feeling full after even a small meal.
In rare cases, individuals with peptic ulcers may see blood in their stool or have black stools because blood is present. Blood coming from one or more peptic ulcers could also be visible in vomit. Call a healthcare provider right away if there is blood in stool or vomit, as this can be a sign of excessive bleeding or other serious problems. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
Diagnosis
When peptic ulcer symptoms occur, a healthcare provider may order several tests to determine the cause. For individuals who are receiving NSAIDs for chronic pain, a healthcare provider may already have a high suspicion that the medication is the cause or is contributing to peptic ulcer disease. Because infection with H. pylori is the most common cause, it is normally ruled out through a breath, blood, or stool test. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022) Tests to look for ulcers inside the upper digestive tract can include:
Upper GI Series
- Patients drink a barium substance to help the internal organs appear on imaging.
- A series of X-rays are taken.
Upper Endoscopy
- A flexible tube with a camera is used to look inside the esophagus, the stomach, and the duodenum.
- Patients are sedated during the procedure, and small pieces of tissue are taken from the lining for further testing. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
Risk Factors
All NSAIDs have the potential to cause indigestion, gastric bleeding, and ulcers. However, some individuals are more susceptible to developing peptic ulcer disease than others. Peptic ulcers caused by NSAIDs are more likely to occur in individuals who: (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
- Are 70 or older
- Have a history of ulcers
- Take corticosteroids
- Take high-dose NSAIDs
- Take NSAIDs regularly for a long time
- Take more than two types of NSAIDs
- Use aspirin daily, including low-dose aspirin, for cardioprotective purposes.
- Take blood thinners
- Drink alcohol regularly
- Smoke
Studies suggest that 25% of those who use NSAIDs long-term will develop an ulcer, but only a small percentage will go on to develop serious complications. (Lanza F. L. et al., 2009)
Treatment
NSAID-induced ulcers usually heal once the NSAID is stopped. Certain treatments may be recommended to expedite the healing process depending on the severity of the peptic ulcer. In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to repair the damage.
Medications
A healthcare provider may recommend taking one or more medications. Over-the-counter options may include:
- Antacids help neutralize stomach acid.
- A proton pump inhibitor or PPI, such as omeprazole, lowers acid levels in the stomach. (Begg M. et al., 2023)
- Bismuth subsalicylate – Pepto-Bismol or Kaopectate. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
Prescription Medications
These might be recommended and can include the following:
- An H2-blocker, which prevents the production of stomach acid by blocking histamine
- Prescription PPIs such as Aciphex – rabeprazole or Konvomep – omeprazole and sodium bicarbonate.
- Mucosal protective agents, or MPAs, maintain the mucosal layer in the stomach. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022)
The bigger problem for individuals is how to manage pain when the medications are discontinued. For individuals with chronic pain, this may require the help of a physical therapy team, including a pain management healthcare provider. Certain medications called COX inhibitors could be used to control pain for some. COX inhibitors have been shown to work for pain relief and are associated with fewer digestive side effects than other types of NSAIDs. These meds have also been shown to have cardiovascular side effects, however, so it’s usually recommended they be used at the lowest dosage. (Scarpignato C. et al., 2015)
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle adjustments may be recommended to heal peptic ulcers, including:
- Avoiding foods that worsen symptoms.
- Avoiding caffeine
- Avoiding alcohol
- Quitting smoking
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be recommended, but this is more often the case when there are complications as a result of the ulcer, such as:
- Serious bleeding
- Perforation or a hole in the stomach or small intestine (Lee C. W. & Sarosi G. A. Jr 2011)
- Obstruction or bowel blockage
Prevention
Avoiding long-term and high-dose use of NSAIDs or not using these medications can help protect and prevent peptic ulcers. For individuals who have to take an NSAID due to a condition they are trying to manage, a healthcare provider may prescribe one of the meds used to treat peptic ulcers to prevent them from occurring. Some believe that spicy food and stress cause ulcers, but that has been discredited. (Cleveland Clinic, 2022) Most individuals who take NSAIDs will not experience peptic ulcer disease. (Drini M. 2017) However, those who have chronic pain and who are receiving high doses should be aware of the potential.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Individuals who have any concerns about the use of NSAIDs and how the digestive system will be affected should ask a healthcare provider if there are ways to prevent ulcers and if those measures should be implemented while receiving high doses of NSAIDs. Left untreated, ulcers can lead to complications, which is why it is important to get a diagnosis and receive treatment. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign naturally.
Root Causes of Gut Dysfunction
References
Fashner, J., & Gitu, A. C. (2015). Diagnosis and Treatment of Peptic Ulcer Disease and H. pylori Infection. American family physician, 91(4), 236–242.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2022). Peptic ulcers (stomach ulcers). Retrieved from www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/peptic-ulcers-stomach-ulcers
Bjarnason, I., Scarpignato, C., Holmgren, E., Olszewski, M., Rainsford, K. D., & Lanas, A. (2018). Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract From Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology, 154(3), 500–514. doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.049
Lanza, F. L., Chan, F. K., Quigley, E. M., & Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology (2009). Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. The American journal of gastroenterology, 104(3), 728–738. doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.115
Begg, M., Tarhuni, M., N Fotso, M., Gonzalez, N. A., Sanivarapu, R. R., Osman, U., Latha Kumar, A., Sadagopan, A., Mahmoud, A., & Khan, S. (2023). Comparing the Safety and Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists in the Management of Patients With Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus, 15(8), e44341. doi.org/10.7759/cureus.44341
Scarpignato, C., Lanas, A., Blandizzi, C., Lems, W. F., Hermann, M., Hunt, R. H., & International NSAID Consensus Group (2015). Safe prescribing of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with osteoarthritis–an expert consensus addressing benefits as well as gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks. BMC medicine, 13, 55. doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0285-8
Lee, C. W., & Sarosi, G. A., Jr (2011). Emergency ulcer surgery. The Surgical clinics of North America, 91(5), 1001–1013. doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2011.06.008
Cleveland Clinic. (2022). Can stress give you an ulcer? health.clevelandclinic.org/can-stress-give-you-an-ulcer
Drini M. (2017). Peptic ulcer disease and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Australian prescriber, 40(3), 91–93. doi.org/10.18773/austprescr.2017.037