Fermented Foods and Gut Health: Functional Back Clinic
Fermentation is a process where bacteria and yeast are used to break down foods. The fermentation process has been around for centuries and was initially produced to preserve foods, improve flavor and eliminate toxins. Research has found that eating fermented foods can also increase the beneficial bacteria/probiotics in the gut. Functional medicine practitioners recommend these foods for their health benefits, including improved digestion, increased immunity, and weight loss and maintenance.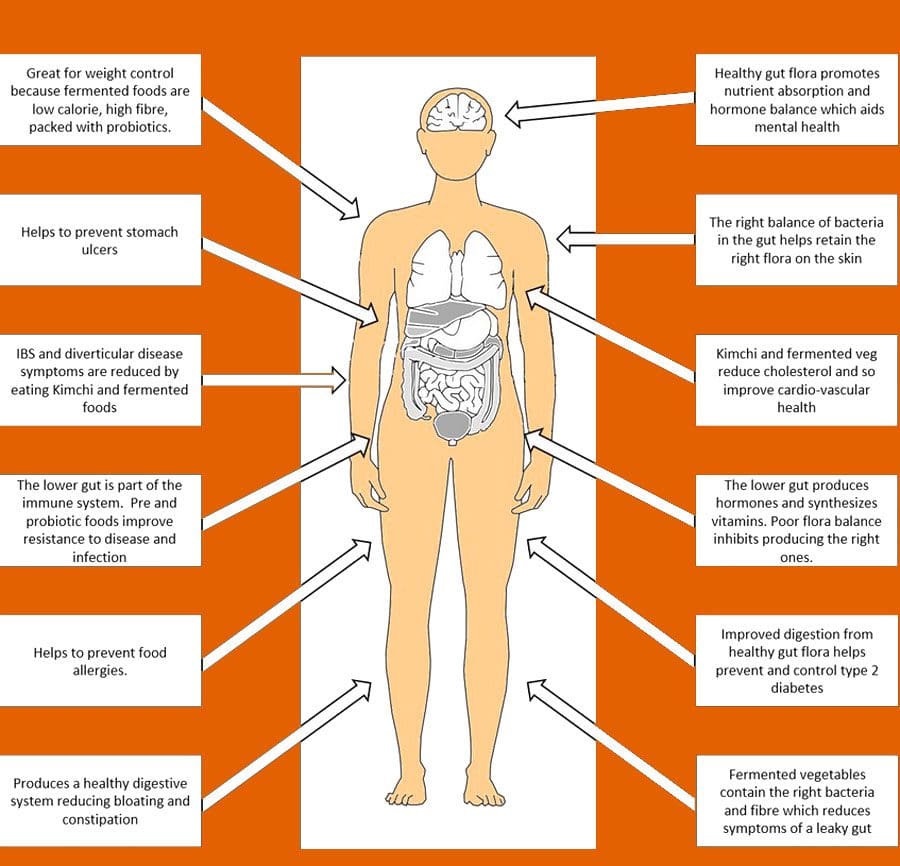
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods and beverages undergo controlled microbial growth and fermentation in which microorganisms like yeast and bacteria break down food elements like sugars/glucose into other products like organic acids, gases, or alcohol. The process gives fermented foods unique taste, aroma, texture, and appearance. There are many different types of fermented foods, including:
- Wine
- Kombucha
- Yogurt
- Cultured milk
- Cider
- Sauerkraut
- Fermented sausage
- Kimchi
- Miso
Whole foods like vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy, meat, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds can go through fermentation. These foods are nutritious in their original form, but through fermentation, they can provide probiotic and prebiotic health benefits.
Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that benefit the gut by creating a more favorable digestive environment. This helps:
- Digest food easier.
- Support a healthy immune system.
- Support organ health – lungs, reproductive organs, skin.
- Improves mood.
However, not all fermented foods contain probiotics, especially commercially produced foods that are pasteurized, killing bacteria and their associated health benefits.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are food ingredients that the microorganisms like gut bacteria consume to grow and live, leading to improving the digestive environment. These include:
- Milk
- Honey
- Tomato
- Garlic
- Onions
- Asparagus
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
However, most fruits, vegetables, and legumes contain prebiotics.
The Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods’ health benefits include reduced risk of:
- Diabetes
- Inflammation
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Obesity
They have also been linked to:
- Better weight management
- Improved brain activity
- Increased bone health
- Faster recovery after exercise and physical activity
There are currently no official guidelines regarding how often individuals should eat fermented foods. It is recommended to consult a nutritionist or dietician to figure out the best nutrition plan for the individual and their needs.
The Science
References
Aslam, Hajara, et al. “Fermented foods, the gut, and mental health: a mechanistic overview with implications for depression and anxiety.” Nutritional neuroscience vol. 23,9 (2020): 659-671. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2018.1544332
Dimidi, Eirini, et al. “Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease.” Nutrients vol. 11,8 1806. 5 Aug. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11081806
King, Sarah, et al. “Effectiveness of probiotics on the duration of illness in healthy children and adults who develop common acute respiratory infectious conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” The British journal of nutrition vol. 112,1 (2014): 41-54. doi:10.1017/S0007114514000075
Kok, Car Reen, and Robert Hutkins. “Yogurt and other fermented foods as sources of health-promoting bacteria.” Nutrition reviews vol. 76, Suppl 1 (2018): 4-15. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy056
Parker, Elizabeth A et al. “Probiotics and gastrointestinal conditions: An overview of evidence from the Cochrane Collaboration.” Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) vol. 45 (2018): 125-134.e11. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2017.06.024
Şanlier, Nevin, et al. “Health benefits of fermented foods.” Critical reviews in food science and nutrition vol. 59,3 (2019): 506-527. doi:10.1080/10408398.2017.1383355









