Intercostal muscles are the muscles within the rib cage, commonly called the intercostals, which connect the ribs and make up the chest wall. An intercostal muscle strain refers to an injury between two or more ribs. If these muscles become overstretched, restricted, or suffer damage, it can cause inflammation and significant pain in the middle and upper back. Intercostal muscle strain is a common injury in athletes and physically demanding jobs. Chiropractic care and massage therapy can realign the vertebrae with the ribs and loosen and relax the muscles to increase circulation and restore mobility and function.
Contents
Intercostal Muscle Strain
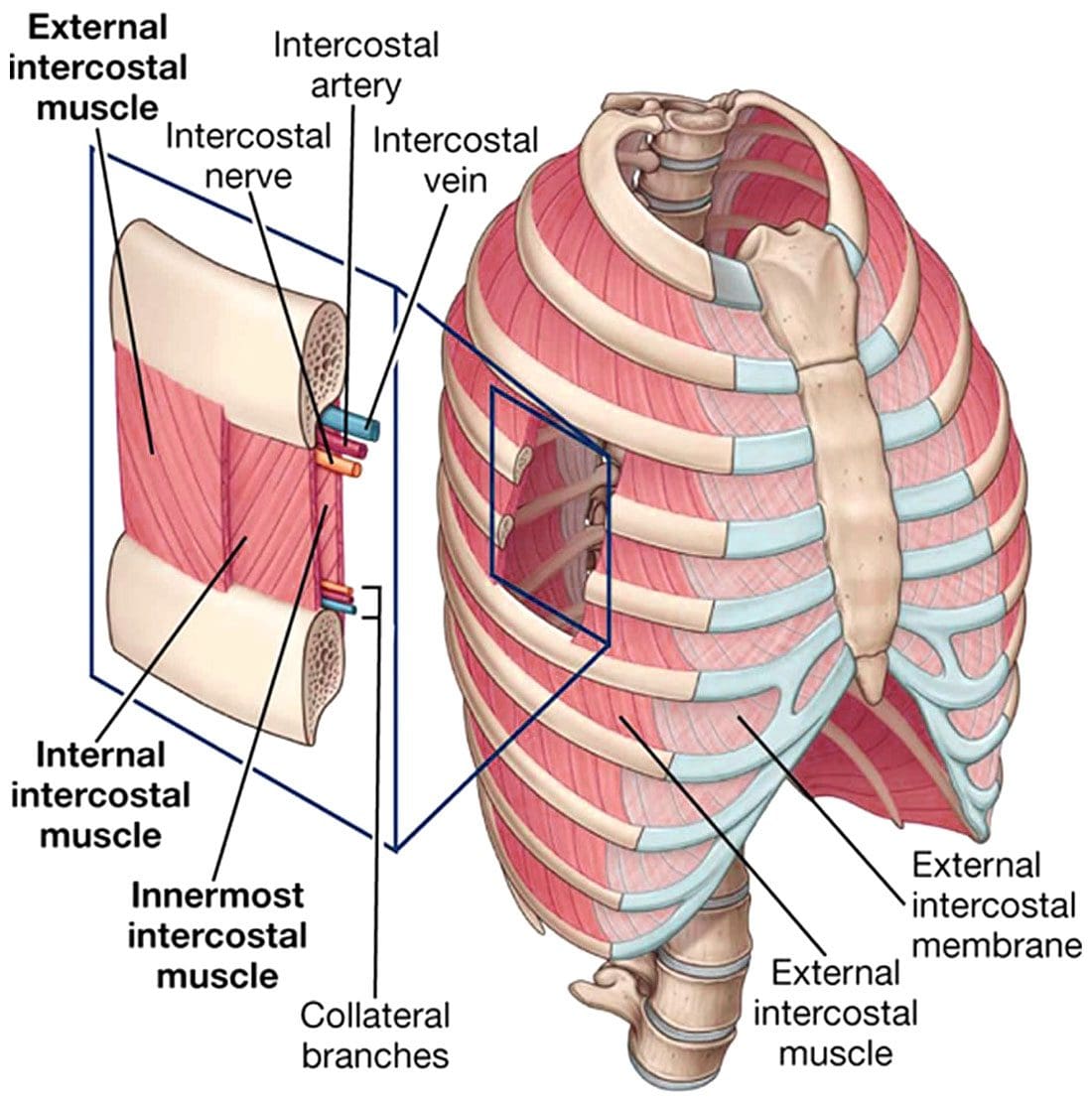
The intercostal muscles have different layers attached to the ribs to help build the chest wall and assist in breathing. There are 11 intercostal muscles on each side of the rib cage. Each set is located between connected ribs in the upper and mid-back and consists of the following:
External
- These are the outermost intercostals, responsible for expanding the chest during breathing to help inhale air and allow full deep breaths.
- The external intercostals originate at the lower edge of a rib and run diagonally to attach to the upper edge of the rib below.
- They are found in the rib cage’s back, sides, and front.
Internal
- These sit directly underneath the externals and help collapse the chest during breathing to exhale.
- The muscle fibers run perpendicular to the external intercostals, moving diagonally from front to back along the ribs, and are in the entire rib cage.
Innermost
- These sit directly underneath, run parallel to the internal intercostals, and run from the back of the rib cage to each side.
- The veins, arteries, and nerves lie between the internal and innermost intercostals.
When an intercostal muscle gets twisted, overused, or stretched too far, it can tear, causing muscle strain. Often radiating pain along the rib cage is experienced that extends to the back.
Causes
An intercostal muscle strain often occurs as the result of an injury or overexertion of the muscles. Common causes include:
- Trauma to the rib cage, such as from a fall or automobile collision.
- Impact trauma from sports or physical activities.
- Over twisting the torso beyond its normal range of motion from lifting weights, sports, yoga postures, or dance positions.
- Repeatedly reaching overhead for work or tasks like cleaning or painting.
- Lifting heavy objects above shoulder height.
- Repetitive torso movements.
- A sudden increase in physical activity that the body is not used to can also lead to intercostal muscle strain.
- This can happen when a lack of conditioning or unhealthy postures weaken muscles.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms can vary, depending on the severity and cause. Symptoms can include:
- Intercostal muscle spasms.
- Mobility difficulties.
- Inflammation, swelling, and sensitivity in the affected area.
- Stiffness and tension, causing upper back pain.
- Upper back and rib pain.
- Tenderness in the area between the ribs.
- Muscle rigidity when bending or twisting the upper body.
- Gradual worsening pain after repetitive movements.
- Worsening pain when coughing, sneezing, or breathing in deeply.
- Severe and sudden pain, particularly if caused by direct trauma to the chest or back.
Chiropractic
Diagnosis involves the individual’s medical history and a physical exam to check for movement limitations and assess affected and sensitive areas. Once the inflammation is reduced, chiropractic and physical therapy will focus on the following:
- Pain relief treatment.
- Breathing exercises.
- Posture training.
- Stretching under supervision.
- Strengthing exercises.
- Most cases fully heal within 6 to 8 weeks.
Rib Muscle Injury
References
De Troyer, A et al. “Mechanics of intercostal space and actions of external and internal intercostal muscles.” The Journal of clinical investigation vol. 75,3 (1985): 850-7. doi:10.1172/JCI111782
Lord, Michael J, and William G Carson Jr. “Multiple Rib Stress Fractures.” The Physician and sports medicine vol. 21,5 (1993): 80-91. doi:10.1080/00913847.1993.11947575
Morrison W. What is an intercostal muscle strain? Medical News Today. Jan 2020
Page P. Current Concepts in Muscle Stretching for Exercise and Rehabilitation. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 2012;7(1):109-119.
Park, Kyung-hee, et al. “Difference in selective muscle activity of thoracic erector spinae during prone trunk extension exercise in subjects with slouched thoracic posture.” PM & R: the Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation vol. 7,5 (2015): 479-84. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2014.10.004
Tran H. Causes of Intercostal Muscle Strain. Spine-health. October 2017
Yoo, Won-Gyu. “Effect of a combined thoracic and backward lifting exercise on the thoracic kyphosis angle and intercostal muscle pain.” Journal of physical therapy science vol. 29,8 (2017): 1481-1482. doi:10.1589/jpts.29.1481
Yoo, Won-Gyu. “Effect of thoracic stretching, thoracic extension exercise and exercises for cervical and scapular posture on thoracic kyphosis angle and upper thoracic pain.” Journal of physical therapy science vol. 25,11 (2013): 1509-10. doi:10.1589/jpts.25.1509
General Disclaimer, Licenses and Board Certifications *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Intercostal Muscle Strain: El Paso Back Clinic" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those on this site and on our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on naturally restoring health for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card