Vitamins
Back Clinic Vitamins. They help our bodies grow and develop normally. The best way to get enough vitamins is to eat a balanced diet with a variety of foods. Knowing about the different types and what they do can help make sure the body gets enough overall wellness. They are nutrients that the human body needs to function and fight off disease.
The body cannot produce vitamins independently, so they must be acquired through food or supplements. There are 13 that are essential to the human body to work well. They are used in many different ways inside your body. While they do not directly serve as a source of energy, they help the enzymes that generate energy from nutrients such as carbohydrates and fats. Knowledge of the different types and understanding the purpose of these are important for optimal health.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Diets, Epigenetic's, Functional Medicine, Health, Holistic Medicine, Natural Health, Nutrition, Nutritional Genomics, Supplements, Vitamins, Wellness
Folate is a B vitamin naturally found in a variety of foods. The body can’t produce folate, that’s why it’s important to get it from folate-rich foods. Folate is naturally found in various plant and animal foods, including citrus fruits, avocado, spinach, kale, broccoli, eggs, and beef liver. Folate is also added to foods, such as bread, flours, and cereals, in the form of folic acid or the synthetic, water-soluble version of folate. Folate and folic acid have different effects on the body.
Our body utilizes folate for a variety of essential functions, including cell division, development of red blood cells, conversion of homocysteine to methionine, an amino acid used for protein synthesis, production of SAMe, and DNA methylation. Folic acid is also important for various metabolic processes. Folate deficiency has ultimately been associated with a variety of health issues, such as the increased risk of heart disease, birth defects, megaloblastic anemia, and cancer.
Daily Intake of Folate and Folic Acid
Our body stores between 10 to 30 mg of folate, most of which is stored in your liver while the remaining amount is stored in your blood and tissues. Normal blood folate levels range from 5 to 15 ng/mL. The main form of folate in the bloodstream is known as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. Daily intake of this essential nutrient is different for people of different ages. The recommended daily allowance of folate for infants, children, teens, adults, and pregnant women are as follows:
- 0 to 6 months: 65 mcg
- 7 to 12 months: 80 mcg
- 1 to 3 years: 150 mcg
- 4 to 8 years: 200 mcg
- 9 to 13 years: 300 mcg
- over 14 years: 400 mcg
- during pregnancy: 600 mcg
- during lactation: 500 mcg
Folic acid supplements play an important role in making sure that people who are in greater need of folate are getting enough of their daily intake. Increasing the daily intake of folate-rich foods is also important because these foods generally offer plenty of other nutrients that all act together to support overall health. Recommended folate daily intake increases during pregnancy and breastfeeding to promote rapid growth and help prevent neural tube defects in the fetus.
Folic acid is available in dietary supplements and fortified foods, including bread, flours, cereals, and several types of grains. It is also added to B-complex vitamins. Folate is also naturally found in a variety of foods, including:
- oranges
- orange juice
- grapefruit
- bananas
- cantaloupe
- papaya
- canned tomato juice
- avocado
- boiled spinach
- mustard greens
- lettuce
- asparagus
- Brussels sprouts
- broccoli
- green peas
- black-eyed peas
- dry-roasted peanuts
- kidney beans
- eggs
- Dungeness crab
- beef liver
Uses of Folate and Folic Acid
Both folate and folic acid are frequently utilized for a variety of reasons. Although folate and folic acid supplements are generally used to treat similar health issues, they do offer different effects in the body and, therefore, it may affect our overall health in different ways. Moreover, getting the proper daily intake of folate and folic acid can improve overall health. The following are several of the most common uses of folate and folic acid supplements, including:
- folate deficiency
- inflammation
- diabetes
- brain health
- heart disease
- kidney disease
- mental health issues
- fertility problems
- birth defects and pregnancy complications
For information regarding the importance of folate and folic acid, please review the following article:
The Importance of Folic Acid
Folate is a B vitamin that is naturally found in many different types of food. Because we can’t produce folate, it’s important to get it from foods that are high in folate. Various folate-rich foods include citrus fruits, avocado, spinach, kale, broccoli, eggs, and beef liver. Folate is also added to foods like bread, flours, and cereals, in the form of folic acid, the synthetic version of this essential nutrient. Folate and folic acid have different effects on the body. Our body uses folate for many important functions, including cell division, development of red blood cells, conversion of homocysteine to methionine, an amino acid used for protein synthesis, production of SAMe, and DNA methylation. Folic acid is also essential for many metabolic processes. Folate deficiency has ultimately been associated with a variety of health issues, such as heart disease, birth defects, megaloblastic anemia, and even cancer. Daily intake of this essential nutrient is different for people of different ages. Furthermore, folate is also naturally found in a variety of foods, such as bananas, avocado, boiled spinach, and eggs. Both folate and folic acid supplements have a variety of uses and they can help improve various health issues, including inflammation, diabetes, heart disease, birth defects, and pregnancy complications. Adding healthy foods to a smoothie is a fast and easy way to get your daily intake of folate. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight

Ginger Greens Juice
Servings: 1
Cook time: 5-10 minutes
� 1 cup pineapple cubes
� 1 apples, sliced
� 1-inch knob of ginger, rinsed, peeled, and chopped
� 3 cups kale, rinsed, and roughly chopped or ripped
� 5 cups Swiss chard, rinsed, and roughly chopped or ripped
Juice all ingredients in a high-quality juicer. Best served immediately.

Eating cholesterol-rich foods doesn�t increase your cholesterol
According to research studies, eating foods with HDL cholesterol or “good” cholesterol doesn’t increase your overall blood cholesterol levels. When you eat healthy cholesterol-rich foods, such as prawns and eggs, your blood cholesterol levels decrease, so your blood cholesterol levels stay balanced, or they’re only raised minimally. It’s actually saturated fats that you have to look out for when it comes to high blood cholesterol levels. Simply choose healthier food options.
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, and sensitive health issues and/or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate and support directly or indirectly our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation as to how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. The provider(s) Licensed in Texas*& New Mexico*�
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References:
- Kubala, Jillian. �Folic Acid: Everything You Need to Know.� Healthline, Healthline Media, 18 May 2020, www.healthline.com/nutrition/folic-acid#What-is-folic-acid?
- Ware, Megan. �Folate: Health Benefits and Recommended Intake.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 26 June 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/287677#recommended-intake.
- Felman, Adam. �Folic Acid: Importance, Deficiencies, and Side Effects.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 11 Mar. 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219853#natural-sources.
- Berg, M J. �The Importance of Folic Acid.� The Journal of Gender-Specific Medicine: JGSM: the Official Journal of the Partnership for Women’s Health at Columbia, U.S. National Library of Medicine, June 1999, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11252849/.
- Dowden, Angela. �Coffee Is a Fruit and Other Unbelievably True Food Facts.� MSN Lifestyle, 4 June 2020, www.msn.com/en-us/foodanddrink/did-you-know/coffee-is-a-fruit-and-other-unbelievably-true-food-facts/ss-BB152Q5q?li=BBnb7Kz&ocid=mailsignout#image=23.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Diets, Functional Medicine, Health, Holistic Medicine, Natural Health, Nutrition, Supplements, Vitamins, Wellness
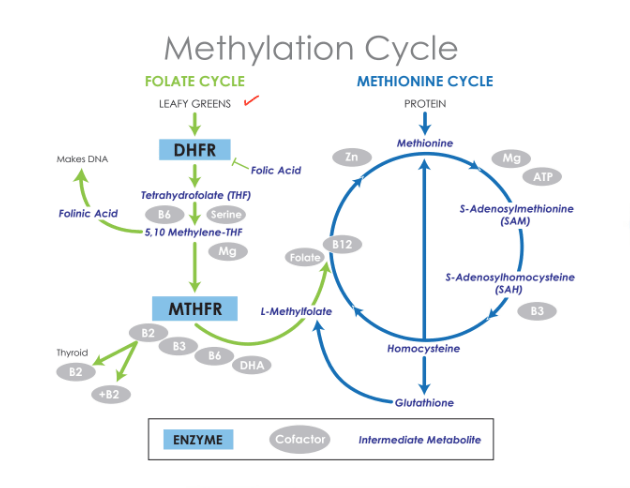
Folate, and its synthetic form folic acid, is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a fundamental role in a variety of functions in the human body. Folate is essential for cell division and homeostasis because it acts as a coenzyme in many biological pathways, including amino acid metabolism, methionine production, and DNA methylation. Folate metabolism happens together with the methionine cycle and the choline pathway. Most folate coenzymes are found in the liver.
Folate is also used as a coenzyme to convert methionine into homocysteine. Vitamin B6 and B12, together with folate, are also essential for DNA synthesis. Proper dietary intake of folate is fundamental for normal cell growth and DNA repair. Folate or vitamin B12 deficiency can ultimately cause a variety of health issues, including anemia. Oral supplementation may be necessary. In the following article, we will discuss folate metabolism and foods that are high in folate.
Folate Metabolism Overview
Several of the most important functions of folate metabolism are methylation and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) production, one of the most essential methyl donors in the cell. In the following diagram, we will explain folate metabolism.�
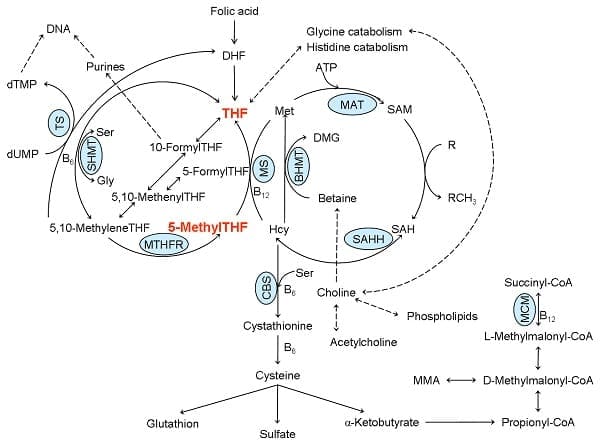
Figure 1: One carbon metabolism. ATP: adenosyl triphosphate, B6: vitamin B6, B12: vitamin B12, BHMT: betaine homocysteine methyltransferase, CBS: cystathionine-?-synthase, DHF: dihydrofolate, DMG: dimethylglycine, dTMP: deoxythymidine monophosphate, dUMP: deoxyuridine monophosphate, Gly: glycine, Hcy: homocysteine, MAT: methionine adenosyltransferase, Met: methionine, MCM: L-methylmalonyl CoA mutase, MM-CoA: L-methylmalonyl CoA, MMA: methylmalonic acid, MS: methionine synthase, MTHFR: 5,10-methyltetrahydrofolate reductase, SAH: S-adenosyl homocysteine, SAHH: S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase, SAM: S-adenosyl methionine, Ser: serine, SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, THF: tetrahydrofolate, TS: thymidylate synthase. Adapted from: Hypo- and hypervitaminosis of B and D vitamins � Diagnosis and clinical consequences. Herrmann W. et al. 2013. Uni-Med Verlag AG.
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is a component that converts folate to dihydrofolate (DHF) and DHF to the active form, THF. Folate metabolism consists of three cycles. One cycle starts with a component known as 10-formylTHF which is associated with purine production and two cycles utilize 5, 10-methyleneTHF in deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) and methionine production. 5-MethylTHF is one of the most predominant forms of folate found in the human body.
After cellular uptake, 5-methylTHF is converted into THF through the use of vitamin B12 in methionine synthase (MS). The methionine cycle is a fundamental pathway in SAM production. As previously mentioned above, B vitamin deficiencies, including folate, vitamin B6, and B12, as well as genetic birth defects can ultimately cause a variety of health issues. 5,10-MethyleneTHF is finally converted to 5-methylTHF by 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR).
Several of the most important functions of folate metabolism are methylation and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) production, one of the most essential methyl donors in the cell. In the following diagram, we will simplify folate metabolism.�
15 Foods That Are High in Folate
Folate, and its synthetic form folic acid, is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a fundamental role in a variety of functions in the human body. It�supports cell division and promotes fetal growth and development to reduce the risk of genetic birth defects. Folate is naturally found in many different types of foods. Doctors recommend 400 mcg of folate every day for adults to prevent deficiency. Here are 15 healthy foods that are high in folate or folic acid, including:
- avocado
- bananas
- citrus fruits
- papaya
- beets
- leafy greens
- asparagus
- Brussels sprouts
- broccoli
- nuts and seeds
- legumes
- eggs
- beef liver
- wheat germ
- fortified grains
In conclusion, folate, and its synthetic form folic acid, is an important micronutrient that can be naturally found in many different types of foods. Eating many different types of healthy foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, as well as fortified foods, is an easy way to increase your folate intake. These foods are not only high in folate but these are also high in other essential nutrients that can ultimately improve other aspects of your overall health.
For information regarding the nutritional role of folate, please review the following article:
Nutritional Role of Folate
Folate or folic acid is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a fundamental role in a variety of functions in the human body, including cell division and homeostasis. Folate also helps with amino acid metabolism, methionine production, and DNA methylation.�Folate or vitamin B12 deficiency can ultimately cause a variety of health issues. Oral supplementation may be necessary. In the diagrams above, we explain the process of folate metabolism.�Folate is naturally found in many different types of foods, including avocado, citrus fruits, leafy greens, broccoli, nuts and seeds, legumes, eggs, and fortified grains.�Eating many different types of healthy foods is an easy way to increase your folate intake. These foods are not only high in folate but these are also high in other essential nutrients that can ultimately improve other aspects of your overall health.�- Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insights

Berry Bliss Smoothie
Servings: 1
Cook time: 5-10 minutes
� 1/2 cup blueberries (fresh or frozen, preferably wild)
� 1 medium carrot, roughly chopped
� 1 tablespoon ground flaxseed or chia seed
� 1 tablespoons almonds
� Water (to desired consistency)
� Ice cubes (optional, may omit if using frozen blueberries)
Blend all ingredients in a high-speed blender until smooth and creamy. Best served immediately.
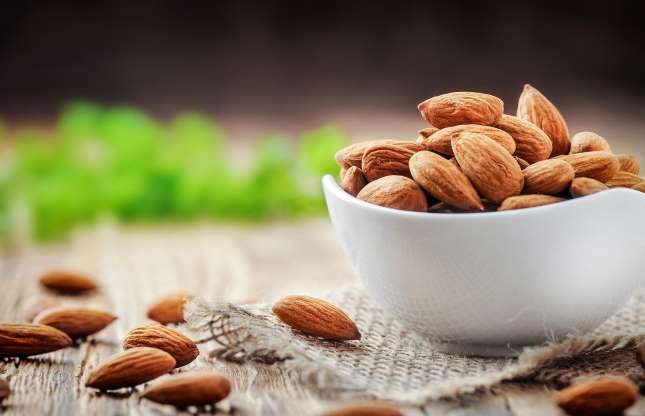

Almonds have twice as much calcium as milk
Gram for gram this is absolutely true! According to McCance and Widdowson’s Composition of Foods (the official guide to the nutrients in food used in the UK), about 100g of almonds have 240mg of bone-building calcium while semi-skimmed (2%) milk has 120mg per 100g (3.5oz). With that being said, however, we tend to drink milk in bigger quantities than we eat almonds (and the calcium from milk is easily absorbed), so the dairy option may be a better source day-to-day.
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, and sensitive health issues and/or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate and support directly or indirectly our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation as to how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. The provider(s) Licensed in Texas*& New Mexico*�
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References:
- Almas, Saneea. �Folic Acid: An Overview of Metabolism, Dosages, and Benefits of Optimal Periconception Supplementation: InfantRisk Center.� Infant Risk Center, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, www.infantrisk.com/content/folic-acid-overview-metabolism-dosages-and-benefits-optimal-periconception-supplementation.
- Homocysteine Expert Panel Staff. �Folate Metabolism.� Homocysteine Expert Panel, Homocysteine Expert Panel Media, www.homocysteine-panel.org/en/folatefolic-acid/basics/folate-metabolism/.
- Link, Rachael. �15 Healthy Foods That Are High in Folate (Folic Acid).� Healthline, Healthline Media, 27 Feb. 2020, www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods-high-in-folate-folic-acid.
- Shuhei, Ebara. �Nutritional Role of Folate.� Congenital Anomalies, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 11 June 2017, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28603928/?from_term=folate%2Bmetabolism&from_pos=3.
- MSN Lifestyle Staff. �Coffee Is a Fruit and Other Unbelievably True Food Facts.� MSN Lifestyle, MSN Lifestyle Media, 4 June 2020, www.msn.com/en-us/foodanddrink/did-you-know/coffee-is-a-fruit-and-other-unbelievably-true-food-facts/ss-BB152Q5q?li=BBnb7Kz&ocid=mailsignout#image=5.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Arthritis, Arthropathies, Diets, Functional Medicine, Health, Holistic Medicine, Natural Health, Nutrition, Supplements, Vitamins, Weight Loss, Wellness
Our diet can significantly affect inflammation in our bodies. Several foods can increase inflammation while other foods can reduce inflammation. According to healthcare professionals, a diet that is high in sugar may be associated with chronic inflammation. A systematic review in 2018 demonstrated that eating excess sugar can ultimately cause inflammation and a variety of other health issues, such as diabetes. Another 2014 research study showed that people who decreased their consumption of sugary or sweetened drinks had reduced inflammation. These research findings support the theory that eating excess sugar can cause chronic inflammation and various other diseases, including diabetes.
How Sugar Can Cause Inflammation
Healthcare professionals have tried to understand how eating excess sugar can cause chronic inflammation. Sugar triggers the production of free fatty acids in the liver. When the human body digests these free fatty acids, the resulting compounds can trigger inflammation. Different types of sugar may also cause more inflammation. By way of instance, one research study found that fructose can cause more inflammation than glucose. However, a systematic review found that fructose didn’t cause more inflammation than glucose. Therefore, further research studies are still required to determine which types of sugar may cause more inflammation. Symptoms associated with chronic inflammation can include:
- pain and fatigue
- sleeping problems or insomnia
- anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders
- digestive problems like acid reflux, constipation, and/or diarrhea
- weight gain or obesity
- constant infections
People with chronic inflammation may also have an increased risk of developing a variety of other health issues, including diabetes and dementia. Chronic inflammation in older adults may also be associated with an increased risk of death.
Health Issues Caused by Chronic Inflammation
Observational research studies in humans have associated diets with high added sugar and refined carbohydrates to the increased risk of developing a variety of health issues, including diabetes, IBD, liver disease, dementia, and arthritis.
Diabetes
Research studies showed a connection between the increased consumption of added sugar and type 2 diabetes. A large analysis that included over 38,000 participants found that simply consuming one serving of sweetened drinks or beverages on a regular basis was associated with an 18 percent increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Another research study found that increasing the consumption of high-fructose corn syrup was also associated with diabetes.
Other Diseases
Increased consumption of added sugar and refined carbohydrates has also been associated with the development of other diseases, such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, liver disease, and dementia. Furthermore, excess fructose consumption has been associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Healthcare professionals believe this may be due to a combination of ongoing low-grade inflammation, increased gut permeability, and bacterial overgrowth in the gut.
Other Foods That Can Cause Inflammation
- sugary foods like pastries, desserts, and chocolate
- saturated fats from processed meats and dairy products
- trans fats found in fast, fried, foods
- vegetable and seed oils
- refined carbohydrates
- excessive alcohol
- MSG in prepared Asian foods and deli meats
For information regarding how excess sugar can cause chronic inflammation and various other health issues like diabetes, please review this article:
Diet can affect inflammation in our bodies. Several foods can increase inflammation while other foods can reduce inflammation. A diet that is high in sugar may be associated with inflammation. Numerous research studies have demonstrated that eating excess sugar can ultimately cause chronic inflammation and various other diseases, including diabetes. Because sugar triggers the production of free fatty acids in the liver, it can also trigger inflammation. Excess sugar can cause chronic inflammation. Different types of sugar may also cause different amounts of inflammation. There are many symptoms associated with chronic inflammation, including pain, fatigue, obesity, anxiety, and depression, among others. Inflammation can lead to a variety of health issues, such as diabetes and arthritis. Although excess sugar is associated with chronic inflammation, other foods like saturated fats and refined carbohydrates can also cause health issues. In the following article, we discuss how sugar can cause inflammation and a variety of other health issues, such as diabetes, in the human body. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insights

Sea Green Smoothie
Servings: 1
Cook time: 5-10 minutes
� 1/2 cup cantaloupe, cubed
� 1/2 banana
� 1 handful of kale or spinach
� 1 handful of Swiss chard
� 1/4 avocado
� 2 teaspoons spirulina powder
� 1 cup of water
� 3 or more ice cubes
Blend all ingredients in a high-speed blender until completely smooth and enjoy!

Leafy Greens Hold the Key to Gut Health
A unique type of sugar found in leafy greens can help feed our beneficial gut bacteria. Sulfoquinovose (SQ) is the only known sugar molecule to be made up of sulfur, an extremely essential mineral in the human body. The human body uses sulfur to produce enzymes, proteins, and a variety of hormones as well as antibodies for our cells. A fast and easy way to get leafy greens into your diet is to toss a couple of handfuls of them into a delicious smoothie!
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, and sensitive health issues and/or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate and support directly or indirectly our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation as to how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. The provider(s) Licensed in Texas*& New Mexico*�
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References:
- Spritzler, Franziska. �6 Foods That Cause Inflammation.� Healthline, Healthline Media, 12 Nov. 2019, www.healthline.com/nutrition/6-foods-that-cause-inflammation#1.
- Caporuscio, Jessica. �Does Sugar Cause Inflammation? What the Research Says.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 19 Sept. 2019, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326386.
- Brown, Mary Jane. �Does Sugar Cause Inflammation in the Body?� Healthline, Healthline Media, 12 Nov. 2017, www.healthline.com/nutrition/sugar-and-inflammation.
by Dr Alex Jimenez | Diets, Epigenetic's, Functional Medicine, Health, Natural Health, Nutrition, Nutritional Genomics, Supplements, Vitamins, Wellness
The MTHFR or methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is well-known due to a genetic mutation that may cause high homocysteine levels and low folate levels in the bloodstream, among other essential nutrients. Healthcare professionals believe that a variety of health issues, such as inflammation, may be associated with an MTHFR gene mutation. In the following article, we will discuss the MTHFR gene mutation and how it can ultimately affect your overall health.
What is an MTHFR Gene Mutation?
People can have single or multiple mutations, as well as neither, on the MTHFR gene. The different mutations are often referred to as “variants”. A variant occurs when the DNA of a specific part of a gene is different or varies from person to person. People that have a heterozygous or single variant of the MTHFR gene mutation have a decreased risk of developing health issues like inflammation and chronic pain, among other diseases. Moreover, healthcare professionals also believe that people that have homozygous or multiple variants of the MTHFR gene mutation may ultimately have an increased risk of disease. There are two MTHFR gene mutation variants. These specific variants include:
- C677T. Approximately 30 to 40 percent of people in the United States have a mutation at gene position C677T. About 25 percent of Hispanics and about 10 to 15 percent of Caucasians are homozygous for this variant.
- A1298C. There are limited research studies for this variant. A 2004 study focused on 120 blood donors of Irish heritage. Of the donors, 56 or 46.7 percent were heterozygous for this variant and 11 or 14.2 percent were homozygous.
- Both C677T and A1298C. It�s also possible for people to have both C677T and A1298C MTHFR gene mutation variations, which includes one copy of each.
What are the Symptoms of an MTHFR Gene Mutation?
Symptoms of an MTHFR gene mutation can be different from person to person and from variant to variant. It’s important to remember that further research around MTHFR gene mutation variants and their effects on health are still needed. Evidence regarding how MTHFR gene mutation variants are associated with a variety of other health issues is currently lacking or it has been disproven. Conditions that have been suggested to be associated with MTHFR variants include:
- anxiety
- depression
- bipolar disorder
- schizophrenia
- migraines
- chronic pain and fatigue
- nerve pain
- recurrent miscarriages in women of child-bearing age
- pregnancies with neural tube defects, like spina bifida and anencephaly
- cardiovascular and thromboembolic diseases (blood clots, stroke, embolism, and heart attacks)
- acute leukemia
- colon cancer
What is the MTHFR Diet?
According to healthcare professionals, eating foods with high amounts of folate may help naturally support low folate levels in the bloodstream associated with MTHFR gene mutation variants.�Good food choices can include:
- fruits, such as strawberries, raspberries, grapefruit, cantaloupe, honeydew, banana.
- juices like orange, canned pineapple, grapefruit, tomato, or other vegetable juice
- veggies, such as spinach, asparagus, lettuce, beets, broccoli, corn, Brussels sprouts, and bok choy
- proteins, including cooked beans, peas, and lentils
- peanut butter
- sunflower seeds
People with MTHFR gene mutations may also want to avoid eating foods that have the synthetic form of folate, folic acid, however, the evidence is not clear if that�s beneficial or necessary. Supplementation may still be recommended for people with MTHFR gene mutation variants. Furthermore, always make sure to check the labels of the foods you buy, as this vitamin is added to many enriched grains like pasta, cereals, bread, and commercially produced flours.
For information regarding the MTHFR and its effects on health issues like cancer, please review this article:
Folate, Methyl-Related Nutrients, Alcohol, and the MTHFR 677C >T Polymorphism Affect Cancer Risk: Intake Recommendations
MTHFR, or methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, gene mutations may cause high homocysteine levels and low folate levels in the bloodstream. We believe that a variety of health issues, such as inflammation, may be associated with an MTHFR gene mutation. People can have single or multiple MTHFR gene mutations, as well as neither. The different mutations are often referred to as “variants”. People that have a heterozygous or single variant of the MTHFR gene mutation have a decreased risk of developing health issues like inflammation and chronic pain. Moreover, doctors also believe that people that have homozygous or multiple variants of the MTHFR gene mutation may ultimately have an increased risk of disease. The two MTHFR gene mutation variants are�C677T, A1298C, or both C677T and A1298C. Symptoms of an MTHFR gene mutation can be different from person to person and from variant to variant. Following what is referred to as the MTHFR diet can ultimately help improve overall health in people with MTHFR gene mutation variants. Also, adding these foods into a smoothie can be an easy way to add them into your diet. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insights
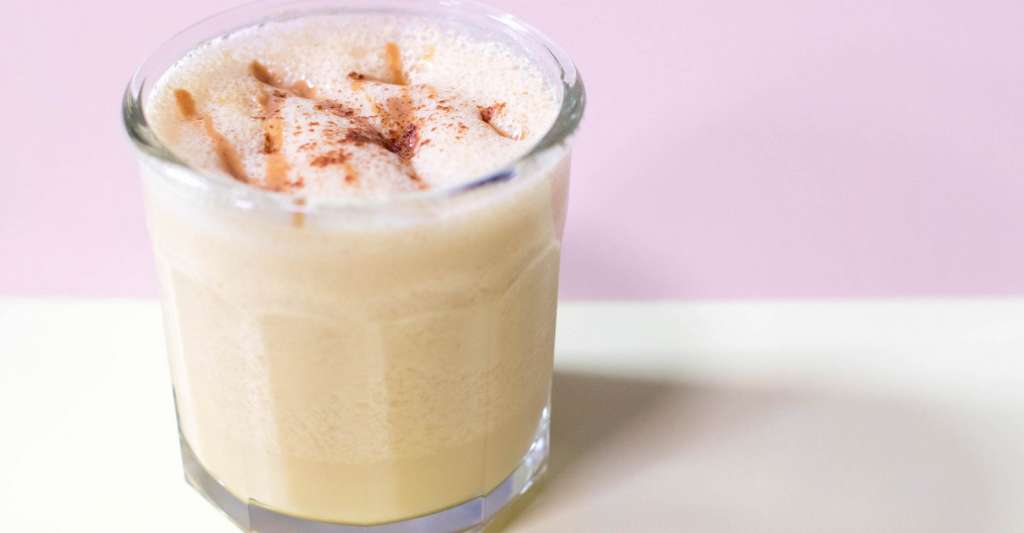

Protein Power Smoothie
Serving: 1
Cook time: 5 minutes
� 1 scoop protein powder
� 1 tablespoon ground flaxseed
� 1/2 banana
� 1 kiwi, peeled
� 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
� Pinch of cardamom
� Non-dairy milk or water, enough to achieve desired consistency
Blend all ingredients in a high-powered blender until completely smooth. Best served immediately!

Leafy Greens Hold the Key to Gut Health
A unique type of sugar found in leafy greens can help feed our beneficial gut bacteria. Sulfoquinovose (SQ) is the only known sugar molecule to be made up of sulfur, an extremely essential mineral in the human body. The human body uses sulfur to produce enzymes, proteins, and a variety of hormones as well as antibodies for our cells. A fast and easy way to get leafy greens into your diet is to toss a couple of handfuls of them into a delicious smoothie!
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, and sensitive health issues and/or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our posts, topics, subjects and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate and support directly or indirectly our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require additional explanation as how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at�915-850-0900. The provider(s) Licensed in Texas*& New Mexico*�
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References:
- Marcin, Ashley. �What You Need to Know About the MTHFR Gene.� Healthline, Healthline Media, 6 Sept. 2019, www.healthline.com/health/mthfr-gene#variants.

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Diets, Functional Medicine, Health, Holistic Medicine, Natural Health, Nutrition, Supplements, Vitamins, Weight Loss, Wellness
Insulin is an essential hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. It is naturally produced in the pancreas and helps move excess glucose from the bloodstream into the cells to be used for energy. When the pancreas recognizes high blood sugar levels, it creates more insulin to reduce glucose. However, this can diminish the pancreas of insulin-producing cells which can eventually cause insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity. If the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin, it can lead to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. In the following article, we will discuss natural ways to improve insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity to prevent and regulate prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, among other health issues.
Foods to Avoid with Insulin Resistance
If you have insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity associated with prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, or any other health issue, there are several types of foods that can increase blood sugar levels. Frequently eating foods with high glucose content can diminish the insulin-producing cells that can ultimately affect the human body’s ability to produce enough insulin. When this occurs, high blood sugar levels remain elevated which can ultimately cause prediabetes and type 2 diabetes as well as lead to a variety of other health issues, including damage to organs such as the eyes and kidneys or limbs (neuropathy). Avoid eating the following types of foods if you have insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity:
- fried foods
- processed snacks and foods
- dairy products from cows, such as milk
- foods high in saturated fats, such as butter, and salt pork
- refined grains, such as white rice, pasta, bread, and flour-based foods
- sugary sweets and pastries, such as ice cream, chocolate bars, and cupcakes
- starchy vegetables, such as corn, potatoes and yams (without skin), and pumpkin
- sweetened drinks or beverages, such as fruit juices, fountain drinks, and sodas
- alcohol, such as beer and grain alcohol, in large quantities
Foods to Eat with Insulin Resistance
Many people are commonly deficient in essential nutrients, such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, and fiber. These nutrients are necessary for regulating blood sugar levels. People with insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity, or any other health issue, including prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, should eat foods that have plenty of these essential nutrients. According to the American Diabetes Association, people with insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity can eat from any of the basic food groups, however, it’s fundamental for individuals to understand which types of foods can increase blood glucose levels. Eat from the following types of foods if you have insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity:
- antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries
- citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and limes
- non-starchy vegetables, such as dark leafy greens, peppers, and broccoli
- protein-rich foods, such as legumes, nuts, soy, fish, and lean meats
- high-fiber foods, including beans, and lentils
- omega-3 fatty acid-rich foods, such as sardines, herring, and salmon
- certain types of whole grains, such as oats, quinoa, and barley
- water, especially as a substitute for sweetened drinks and
- unsweetened teas
Exercise to Improve Insulin Resistance
Eating good foods and avoiding bad foods can help improve insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity, however, there’s another natural way to improve this health issue: exercise. Participating and engaging in regular exercise helps improve insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity associated with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, among other health issues, by moving sugar from the bloodstream into the muscles to be used for energy. The American Heart Association recommends approximately 150 minutes of exercise every week for adults. Participating or engaging in exercise on a daily basis can improve high blood sugar levels as well as promote overall health and wellness.
For more information regarding how to naturally improve insulin resistance, please review this article:
Nutritional Modulation of Insulin Resistance
Insulin is an essential hormone that is naturally produced in the pancreas to help regulate blood sugar levels and move excess sugar from the bloodstream into the cells to be used for energy. When the pancreas senses high blood sugar levels in the blood, it creates more insulin to help reduce glucose. However, this can decrease the amount of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas which can cause insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity. If the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin, it can ultimately lead to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, among other health issues. There are several natural ways to improve insulin resistance or impaired insulin sensitivity to prevent and regulate prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, including eating good foods, avoiding bad foods, and exercising. Furthermore, adding a variety of good foods to a smoothie can be a fast and easy way to add nutrients to your diet. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insights
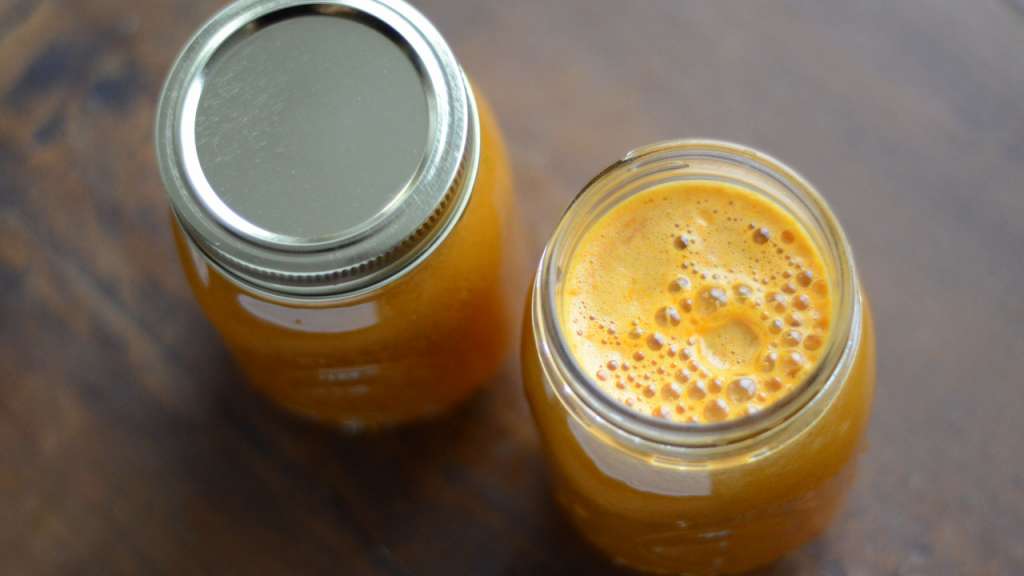

Sweet and Spicy Juice
Servings: 1
Cook time: 5-10 minutes
- 1 cup honeydew melons
- 3 cups spinach, rinsed
- 3 cups Swiss chard, rinsed
- 1 bunch cilantro (leaves and stems), rinsed
- 1-inch knob of ginger, rinsed, peeled, and chopped
- 2-3 knobs whole turmeric root (optional), rinsed, peeled, and chopped
Juice all ingredients in a high-quality juicer. Best served immediately.

Eat Mushrooms
One simple thing we can do to improve the microbiome!
Mushrooms feed bacteria in the gut. They are rich in chitin, hemicellulose, ? and ?-glucans, mannans, xylans, and galactans. They are also amazing prebiotics that promotes the growth of gut microbiota, equalling health benefits.
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and nervous health issues or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health protocols to treat injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask�Dr. Alex Jimenez�or contact us at�915-850-0900.
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T.
References:
- Raman, Ryan. �14 Natural Ways to Improve Your Insulin Sensitivity.� Healthline, Healthline Media, 17 May 2017, www.healthline.com/nutrition/improve-insulin-sensitivity.
- Herrmann Dierks, Melissa. �Meal Planning & Exercise Tips for Insulin Resistance.� AgaMatrix, AgaMatrix Media, agamatrix.com/blog/insulin-resistance-diet/.
- Felman, Adam. �Diet and Insulin Resistance: Foods to Eat and Diet Tips.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 27 Mar. 2019, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/316569#foods-to-eat.
by Dr Alex Jimenez | Chiropractic, Functional Medicine, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Health Coaching, Integrative Functional Wellness, Nutrition, Nutritional Genomics, Vitamins, Wellness
With everything that is going on in today’s world immunity is especially important. Without a properly functioning immune system, our bodies can become inflamed and more susceptible to viruses. Inflammation can cause a weakened immune system, joint pain, headaches, fatigue and more!
So what can we do to build up our immunity and help give our bodies a fighting chance? First off, washing your hands is highly important. Not just now, but always. Be sure to wash your hands with warm water and scrub everywhere. Second, get plenty of sleep. Rest is how the body recovers. If you do not give your body adequate sleep, the strength you’re cells have to fight off infection lessens. Third, eat healthy food, hydrate, and exercise. Finally, last but not least help kick up your immune system by supplementing the body with all-natural supplements.
There are many supplements that will be beneficial to the body. However, two of the most important are NAC and Glutamine.
What Are They?
NAC stands for N-acetyl-Cystine. NAC is an amino acid that the body can produce but the body can also greatly benefit from taking additional NAC in supplemental form. NAC plays an important role in helping the liver to detox. In addition to this, NAC helps to replenish the glutathione levels in the lungs and can help to reduce the inflammation. This is highly beneficial in helping to relieve the symptoms of a respiratory infection.
NAC is also greatly beneficial in boosting brain health. NAC helps to regulate glutamate levels and replenish glutathione. However, one of the most important factors of NAC is its ability to boost Glutathione levels.
Glutamine is an amino acid that helps the body perform many functions. Glutamine plays a crucial part in the immune system.
The Connection & How It Impacts Immunity
However, one of the most important factors of NAC is its ability to booze Glutathione levels. NAC and glutathione can help to boost an individual’s immune health. In research studies shown, NAC has been shown to lessen the effects of a virus and its ability to replicate. When it comes to immunity NAC and Glutamine are powerful molecules. Stoping the replication of a virus can help reduce the spread and the length of the virus in an individual.
Many infections and diseases have been linked to low glutathione levels. When the glutathione levels are low this is typically due to enhanced oxygen radicals. Studies have been done and show that when supplementing NAC to those who have low glutathione levels, it directly boosts their levels and helps with infection.
Especially with everything happening today, we want to increase our immunity and decrease the inflammation in the body.� Essentially, think of the body as a road trip. For this trip we need two main things: the gas for the car, and the car to take you to the end destination.� NAC is the gas that drives the car. We need the gas to get to our end destination. Our end destination is being healthy and giving our body the best chance to fight off infection (increased Glutathione). So by giving our body gas (NAC) we provide it with what it needs to take us to where we want to go (increased Glutathione, leading to increased immunity).
How Can I Benefit?
Overall, NAC is great to decrease inflammation. Inflammation is an extremely common underlying issue relating to other health conditions individuals suffer from. By providing your body with additional supplements, you can help increase your immunity and decrease your chances of contracting a virus and/or the length of the virus. Always discuss supplements with your primary care doctor before you begin them, but consider adding these into your daily routine!
I always recommend talking to your primary care provider and taking supplements daily. Supplements, in general, are a great way to help provide the body with the essential vitamins and minerals you may be missing. However, now more than ever supplementation is key. By building up and providing the body with the nutrients it needs for proper function, it will help prepare your body to fight off an infection. Supplementation like NAC is great to have already running in your system to help combat an infection if you were to catch one. Remember to be smart, talk to a primary care doctor before beginning supplementation, and keep in mind that not all supplements are created equal.� -Kenna Vaughn, Senior Health Coach��
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and nervous health issues or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health protocols to treat injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900.�
References:
Dinicola S, De Grazia S, Carlomagno G, Pintucci JP. N-acetylcysteine as powerful molecule to destroy bacterial biofilms. A systematic review.�Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(19):2942�2948.
Goodson, Amy. �Top 9 Benefits of NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine).� Healthline, 2018, www.healthline.com/nutrition/nac-benefits#section3.
Wessner B, Strasser EM, Spittler A, Roth E. Effect of single and combined supply of glutamine, glycine, N-acetylcysteine, and R,S-alpha-lipoic acid on glutathione content of myelomonocytic cells.�Clin Nutr. 2003;22(6):515�522. doi:10.1016/s0261-5614(03)00053-0

by Dr Alex Jimenez | Functional Medicine, Gastro Intestinal Health, Gut and Intestinal Health, Health, Nutrition, Vitamins, Wellness
Do you feel:
- Excessive belching, burping or bloating
- Gas immediately following a meal
- Stomach pain, burning or aching 1-4 hours after eating
- Feel hungry an hour or two after eating
- Digestive problems when lying down or bending forward
If you are experiencing any of these situations, then you should try some micronutrients for your GI tract health.
GI Tract Health

Over two thousand years ago, Hippocrates recognized that the gut plays a significant role in overall health and that modern scientific research has substantiated and solidified this view. With GI (gastrointestinal) health, advanced testing, and intricate healing protocols focused a lot when it comes to the GI tract. Some patients may benefit from the precise analysis of the makeup from their gut flora or the specific food elimination and reintroduction strategies, but not to overlook the fundamentals. Addressing the basics like general micronutrient repletion or supplementation with the foundational nutrients can be targeted for therapeutic purposes and can go a long way for an individual�s healing.
The Micronutrients
These are some of the fundamental micronutrients that the body needs to perform the everyday task. These can mostly be found in foods or in supplements and vitamins that are consumed, and even though high restriction diets can deplete these nutrients, they are still crucial for not only our gut health but for the entire body system as well.
Glutamine
The amino acid glutamine is a trusty workhorse for a healthy gut function in the body. Even though it is technically not an essential amino acid, it serves as an energy source for epithelial cells that makes up the intestinal lining for the intestines. Various circumstances like trauma, burns, or recovery from significant operations or illnesses can increase the body’s demand for glutamine.
Glutamine can be found in all protein foods like:
- Eggs
- Beef
- Skim milk
- Tofu
- White rice
- Corn
Taurine
Another amino acid is taurine is beneficial for individuals who need help with the digestion of dietary fats. Taurine is unique due to not being used in any structural protein; however, it has other roles in the body. Taurine can be synthesized from cysteine and can be obtained from animal foods specifically, sadly though it is nonexistent in plant food. Bile acids that are bound with taurine are secreted by the liver; the making of this compound is critical for bile acid function and proper fat absorption in the body.
Taurine can provide these health benefits to the body, which includes:
- Improve blood sugar control and fight diabetes
- Stop the occurrence of epilepsy
- Reduces seizure attacks
- Prevents cardiovascular diseases
- Regulates muscle contractions
- Controls and calms the central nervous system
Potassium
Potassium is the core nutrient that plays a role in a healthy GI function, especially when it comes to intestinal motility. Some disorders like fatigue and cardiac arrhythmias can be the result of potassium deficiency, and inadequate potassium may lead to delayed gastric emptying and intestinal paralysis. If the body is not treated soon, it can lead to chronic illnesses in the GI, causing unpleasant effects like bloating, abdominal pain, and constipation.
All food supplies have an abundance of potassium, but certain medications can reduce potassium levels. Factors like excessive alcohol consumption or strict chronic dieting for weight loss can be the result of inadequate potassium intake and the body status of a person.
Some of the health benefits that potassium can provide are:
- Maintains constant blood pressure
- Reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Maintains bone density
- Maintains muscle mass
Vitamin B6
B vitamins, especially vitamin B6, are highly essential to the GI tract because they make sure that the brain is also healthy as well. Deficiency of vitamin B6 can cause these symptoms:
- Tingling, numbness, and pain in the hands and feet
- Anemia
- Seizures
- Depression
- Confusion
- Weak immune system
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin that produces the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine and forming myelin for the body. This vitamin can help boost brain function and can improve memory function. Some of the other benefits it can provide to the body are:
- Lowers the risk of dementia
- Reduce the severity of nausea during pregnancy
- Protection from air pollution
- Ensures the normal functioning of digestive enzymes
Conclusion
Even though these are the necessary foundational micronutrients and amino acids for their roles in the GI tract, it is crucial for individuals who have these micronutrient deficiencies. Even though the popularity of highly restrictive diets emphasizes on caloric restrictions for weight loss for individuals, it can limit the intake of certain nutrient-dense foods. It can cause disruptions to the gastrointestinal tract. When a person surrounds themselves with an abundance of foods with these micronutrients can live a healthy life. Some products combined with these micronutrient foods can provide support to the gastrointestinal system and help boost the sugar metabolism for the body.
October is Chiropractic Health Month. To learn more about it, check out Governor Abbott�s declaration on our website to get full details on this historic moment.
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal and nervous health issues as well as functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health protocols to treat injuries or chronic disorders of the musculoskeletal system. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
References:
Brazier, Yvette. �Vitamin B-6: Benefits, Dosage, Food Sources, and Deficiency Symptoms.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 27 Mar. 2017, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219662.php.
Cadman, Bethany. �L-Glutamine for IBS: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 7 Feb. 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320850.php.
Caporuscio, Jessica. �What Is Taurine? Benefits and Side Effects.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 26 Sept. 2019, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326476.php.
Higdon, Jane. �Potassium.� Linus Pauling Institute, 14 Oct. 2019, lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/minerals/potassium#deficiency.
Mawer, Rudy. “What Is Taurine? Benefits, Side Effects, and More.” Healthline, 27 Nov. 2018, www.healthline.com/nutrition/what-is-taurine.
Megan Ware, RDN. �Potassium: Health Benefits and Recommended Intake.� Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 10 Jan. 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/287212.php.
Team, DFH. �Micronutrients in GI Health.� Designs for Health, 11 Oct. 2019, blog.designsforhealth.com/node/1123.
Tinsley, Grant. “Glutamine: Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects.” Healthline, 13 Jan. 2018, www.healthline.com/nutrition/glutamine.

























