The Role of Biomarkers for Depression
Depression is one of the most common mental health issues in the United States. Current research suggests that depression results from a combination of genetic, biological, ecological, and psychological aspects. Depression is a major psychiatric disorder worldwide with a significant economic and psychological strain on society. Fortunately, depression, even the most severe cases, may be treated. The earlier that treatment can begin, the more effective it is.
As a result, however, there’s a need for robust biomarkers that will aid in improving diagnosis in order to accelerate the drug and/or medication discovery process for each patient with the disorder. These are objective, peripheral physiological indicators which presence can be used to predict the probability of onset or existence of depression, stratify according to severity or symptomatology, indicate predict and prognosis or monitor response to therapeutic interventions. The purpose of the following article is to demonstrate recent insights, current challenges and future prospects regarding the discovery of a variety of biomarkers for depression and how these can help improve diagnosis and treatment.
Biomarkers for Depression: Recent Insights, Current Challenges and Future Prospects
Abstract
A plethora of research has implicated hundreds of putative biomarkers for depression, but has not yet fully elucidated their roles in depressive illness or established what is abnormal in which patients and how biologic information can be used to enhance diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. This lack of progress is partially due to the nature and heterogeneity of depression, in conjunction with methodological heterogeneity within the research literature and the large array of biomarkers with potential, the expression of which often varies according to many factors. We review the available literature, which indicates that markers involved in inflammatory, neurotrophic and metabolic processes, as well as neurotransmitter and neuroendocrine system components, represent highly promising candidates. These may be measured through genetic and epigenetic, transcriptomic and proteomic, metabolomic and neuroimaging assessments. The use of novel approaches and systematic research programs is now required to determine whether, and which, biomarkers can be used to predict response to treatment, stratify patients to specific treatments and develop targets for new interventions. We conclude that there is much promise for reducing the burden of depression through further developing and expanding these research avenues.
Keywords: mood disorder, major depressive disorder, inflammation, treatment response, stratification, personalized medicine
Introduction
Challenges in Mental Health and Mood Disorders
Although psychiatry has a disease-related burden greater than any single other medical diagnostic category,1 a disparity of esteem is still apparent between physical and mental health across many domains including research funding2 and publication.3 Among the difficulties that mental health faces is a lack of consensus surrounding classification, diagnosis and treatment that stems from an incomplete understanding of the processes underlying these disorders. This is highly apparent in mood disorders, the category which comprises the single largest burden in mental health.3 The most prevalent mood disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), is a complex, heterogeneous illness in which up to 60% of patients may experience some degree of treatment resistance that prolongs and worsens episodes.4 For mood disorders, and in the broader field of mental health, treatment outcomes would likely be improved by the discovery of robust, homogeneous subtypes within (and across) diagnostic categories, by which treatments could be stratified. In recognition of this, global initiatives to delineate functional subtypes are now in progress, such as the research domain criteria.5 It has been posited that biologic markers are priority candidates for subtyping mental disorders.6
Improving Response to Treatments for Depression
Despite an extensive range of treatment options for major depression, only approximately a third of patients with MDD achieve remission even when receiving optimal antidepressant treatment according to consensus guidelines and using measurement-based care, and rates of treatment response appear to fall with each new treatment.7 Furthermore, treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is associated with increased functional impairment, mortality, morbidity and recurrent or chronic episodes in the long term.8,9 Thus, obtaining improvements in treatment response at any clinical stage would afford wider benefits for overall outcomes in depression. Despite the substantial burden attributable to TRD, research in this area has been sparse. Definitions of TRD are not standardized, in spite of previous attempts:4 some criteria require only one treatment trial that fails to achieve a 50% symptom score reduction (from a validated measure of depression severity), while others require non-achievement of full remission or nonresponse to at least two adequately trialed antidepressants of different classes within an episode to be considered TRD.4,10 Furthermore, the staging and prediction of treatment resistance is improved by adding the key clinical features of severity and chronicity to the number of failed treatments.9,11 Nevertheless, this inconsistency in definition renders interpreting the research literature on TRD an even more complex task.
In order to improve response to treatments, it is clearly helpful to identify predictive risk factors of nonresponse. Some general predictors of TRD have been characterized, including a lack of full remission after previous episodes, comorbid anxiety, suicidality and early onset of depression, as well as personality (particularly low extraversion, low reward dependence and high neuroticism) and genetic factors.12 These findings are corroborated by reviews synthesizing the evidence separately for pharmacologic13 and psychological14 treatment for depression. Antidepressants and cognitive-behavioral therapies show approximately comparable efficacy,15 but due to their differing mechanisms of action might be expected to have different predictors of response. While early-life trauma has long been associated with poorer clinical outcomes and reduced responses to treatment,16 early indications suggest that people with a history of childhood trauma might respond better to psychological than pharmacologic therapies.17 Despite this, uncertainty prevails and little personalization or stratification of treatment has reached clinical practice.18
This review focuses on the evidence supporting the utility of biomarkers as potentially useful clinical tools to enhance treatment response for depression.
Biomarkers: Systems and Sources
Biomarkers provide a potential target for identifying predictors of response to various interventions.19 The evidence to date suggests that markers reflecting the activity of inflammatory, neurotransmitter, neurotrophic, neuroendocrine and metabolic systems may be able to predict mental and physical health outcomes in currently depressed individuals, but there is much inconsistency between findings.20 In this review, we focus on these five biologic systems.
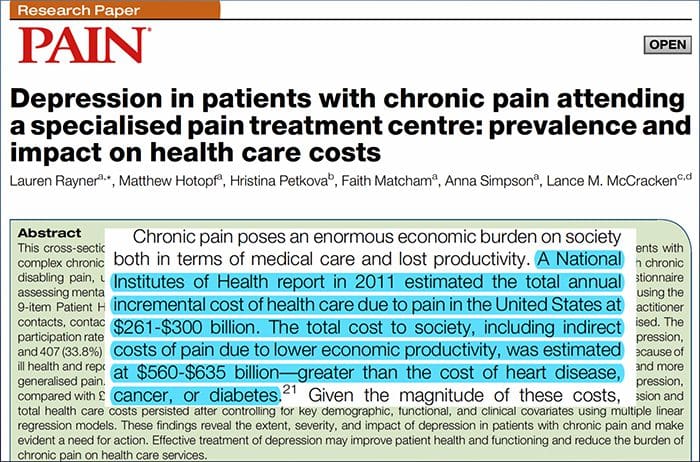
To attain a full understanding of molecular pathways and their contribution in psychiatric disorders, it is now considered important to assess multiple biologic �levels�, in what is popularly referred to as an �omics� approach.21 Figure 1 provides a depiction of the different biologic levels at which each of the five systems can be assessed, and the potential sources of markers on which these assessments can be undertaken. However, note that while each system can be inspected at each omics level, the optimal sources of measurement clearly vary at each level. For example, neuroimaging provides a platform for indirect assessment of brain structure or function, while protein examinations in blood directly assess markers. Transcriptomics22 and metabolomics23 are increasingly popular, offering assessment of potentially huge numbers of markers, and the Human Microbiome Project is now attempting to identify all microorganisms and their genetic composition within humans.24 Novel technologies are enhancing our ability to measure these, including through additional sources; for example, hormones such as cortisol can now be assayed in hair or fingernails (providing a chronic indication) or sweat (providing a continuous measurement),25 as well as in blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and saliva.
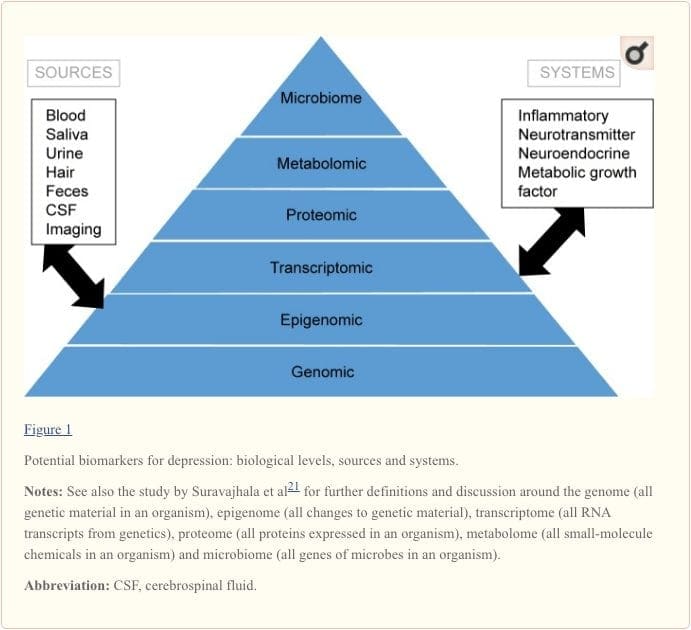
Given the number of putative sources, levels and systems involved in depression, it is not surprising that the scale of biomarkers with translational potential is extensive. Particularly, when interactions between markers are considered, it is perhaps unlikely that examining single biomarkers in isolation will yield findings fruitful for improving clinical practice. Schmidt et al26 proposed the use of biomarker panels and, subsequently, Brand et al27 outlined a draft panel based on prior clinical and preclinical evidence for MDD, identifying 16 �strong� biomarker targets, each of which is rarely a single marker. They comprise reduced gray matter volume (in hippocampal, prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia regions), circadian cycle changes, hypercortisolism and other representations of hypothalamic�pituitary�adrenal (HPA) axis hyperactivation, thyroid dysfunction, reduced dopamine, noradrenaline or 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, increased glutamate, increased superoxide dismutase and lipid peroxidation, attenuated cyclic adenosine 3?,5?-monophosphate and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activity, increased proinflammatory cytokines, alterations to tryptophan, kynurenine, insulin and specific genetic polymorphisms. These markers have not been agreed by consensus and could be measured in various ways; it is clear that focused and systematic work must address this enormous task in order to prove their clinical benefits.
Aims of this Review
As a deliberately broad review, this article seeks to determine the overall needs for biomarker research in depression and the extent to which biomarkers hold real translational potential for enhancing response to treatments. We begin by discussing the most important and exciting findings in this field and direct the reader to more specific reviews pertaining to relevant markers and comparisons. We outline the current challenges faced in light of the evidence, in combination with needs for reducing the burden of depression. Finally, we look ahead to the important research pathways for meeting current challenges and their implications for clinical practice.
Recent Insights
The search for clinically useful biomarkers for people with depression has generated extensive investigation over the last half a century. The most commonly used treatments were conceived from the monoamine theory of depression; subsequently, neuroendocrine hypotheses gained much attention. In more recent years, the most prolific research has surrounded the inflammatory hypothesis of depression. However, a large number of relevant review articles have focused across all five systems; see Table 1 and below for a collection of recent insights across biomarker systems. While measured at many levels, blood-derived proteins have been examined most widely and provide a source of biomarker that is convenient, cost-effective and may be closer to translational potential than other sources; thus, more detail is given to biomarkers circulating in blood.
In a recent systematic review, Jani et al20 examined peripheral blood-based biomarkers for depression in association with treatment outcomes. Of only 14 studies included (searched up until early 2013), 36 biomarkers were studied of which 12 were significant predictors of mental or physical response indices in at least one investigation. Those identified as potentially representing risk factors for nonresponse included inflammatory proteins: low interleukin (IL)-12p70, ratio of lymphocyte to monocyte count; neuroendocrine markers (dexamethasone nonsuppression of cortisol, high circulating cortisol, reduced thyroid-stimulating hormone); neurotransmitter markers (low serotonin and noradrenaline); metabolic (low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and neurotrophic factors (reduced S100 calcium-binding protein B). Further to this, other reviews have reported on associations between additional biomarkers and treatment outcomes.19,28�30 A brief description of putative markers in each system is outlined in the subsequent sections and in Table 2.
Inflammatory Findings in Depression
Since Smith�s seminal paper outlining the macrophage hypothesis,31 this established literature has found increased levels of various proinflammatory markers in depressed patients, which have been reviewed widely.32�37 Twelve inflammatory proteins have been evaluated in meta-analyses comparing depressed and healthy control populations.38�43
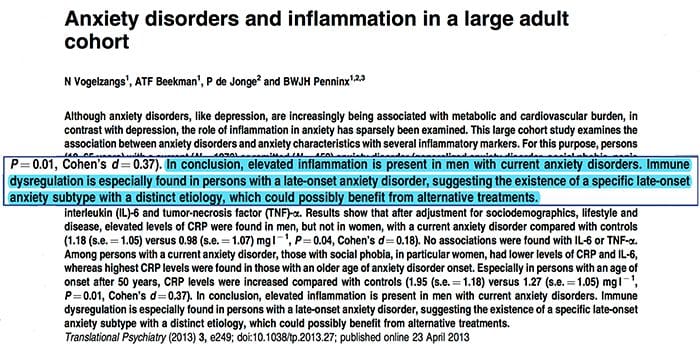
IL-6 (P<0.001 in all meta-analyses; 31 studies included) and CRP (P<0.001; 20 studies) appear frequently and reliably elevated in depression.40 Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF?) was identified in early studies (P<0.001),38 but substantial heterogeneity rendered this inconclusive when accounting for more recent investigations (31 studies).40 IL-1? is even more inconclusively associated with depression, with meta-analyses suggesting higher levels in depression (P=0.03),41 high levels only in European studies42 or no differences from controls.40 Despite this, a recent article suggested particular translational implications for IL-1?,44 supported by an extremely significant effect of elevated IL-1? ribonucleic acid predicting a poor response to antidepressants;45 other findings above pertain to circulating blood-derived cytokines. The chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 has shown elevations in depressed participants in one meta-analysis.39 Interleukins IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, IL-10 and interferon gamma were not significantly different between depressed patients and controls at a meta-analytic level, but have nonetheless demonstrated potential in terms of altering with treatment: IL-8 has been reported as elevated in those with severe depression prospectively and cross-sectionally,46 different patterns of change in IL-10 and interferon gamma during treatment have occurred between early responders versus nonresponders,47 while IL-4 and IL-2 have decreased in line with symptom remission.48 In meta-analyses, small decreases alongside treatment have been demonstrated for IL-6, IL-1?, IL-10 and CRP.43,49,50 Additionally, TNF? may only reduce with treatment in responders, and a composite marker index may indicate increased inflammation in patients who subsequently do not respond to treatment.43 It is notable, however, that almost all of the research examining inflammatory proteins and treatment response utilize pharmacologic treatment trials. Thus, at least some inflammatory alterations during treatment are likely attributable to antidepressants. The precise inflammatory effects of different antidepressants have not yet been established, but evidence using CRP levels suggests individuals respond differently to specific treatments based on baseline inflammation: Harley et al51 reported elevated pretreatment CRP predicting a poor response to psychological therapy (cognitive�behavioral or interpersonal psychotherapy), but a good response to nortriptyline or fluoxetine; Uher et al52 replicated this finding for nortriptyline and identified the opposite effect for escitalopram. In contrast, Chang et al53 found higher CRP in early responders to fluoxetine or venlafaxine than nonresponders. Furthermore, patients with TRD and high CRP have responded better to the TNF? antagonist infliximab than those with levels in the normal range.54
Together, the evidence suggests that even when controlling for factors such as body mass index (BMI) and age, inflammatory responses appear aberrant in approximately one-third of patients with depression.55,56 The inflammatory system, however, is extremely complex, and there are numerous biomarkers representing different aspects of this system. Recently, additional novel cytokines and chemokines have yielded evidence of abnormalities in depression. These include: macrophage inhibitory protein 1a, IL-1a, IL-7, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-15, eotaxin, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor,57 IL-5,58 IL-16,59 IL-17,60 monocyte chemoattractant protein-4,61 thymus and activation-regulated chemokine,62 eotaxin-3, TNFb,63 interferon gamma-induced protein 10,64 serum amyloid A,65 soluble intracellular adhesion molecule66 and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.67
Growth Factor Findings in Depression
In light of the potential importance of non-neurotrophic growth factors (such as those relating to angiogenesis), we refer to neurogenic biomarkers under the broader definition of growth factors.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is the most frequently studied of these. Multiple meta-analyses demonstrate attenuations of the BDNF protein in serum, which appear to increase alongside antidepressant treatment.68�71 The most recent of these analyses suggests that these BDNF aberrations are more pronounced in the most severely depressed patients, but that antidepressants appear to increase the levels of this protein even in the absence of clinical remission.70 proBDNF has been less widely studied than the mature form of BDNF, but the two appear to differ functionally (in terms of their effects on tyrosine receptor kinase B receptors) and recent evidence suggests that while mature BDNF may be reduced in depression, proBDNF may be overproduced.72 Nerve growth factor assessed peripherally has also been reported as lower in depression than in controls in a meta-analysis, but may not be altered by antidepressant treatment despite being most attenuated in patients with more severe depression.73 Similar findings have been reported in a meta-analysis for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor.74
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has a role in promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis along with other members of the VEGF family (eg, VEGF-C, VEGF-D) and has promise for depression.75 Despite inconsistent evidence, two meta-analyses have recently indicated elevations of VEGF in blood of depressed patients compared to controls (across 16 studies; P<0.001).76,77 However, low VEGF has been identified in TRD78 and higher levels have predicted nonresponse to antidepressant treatment.79 It is not understood why the levels of VEGF protein would be elevated, but it may partly be attributable to proinflammatory activity and/or increases in blood�brain barrier permeability in depressed states that causes reduced expression in cerebrospinal fluid.80 The relationship between VEGF and treatment response is unclear; a recent study found no relationship between either serum VEGF or BDNF with response or depression severity, despite decreases alongside antidepressant treatment.81 Insulin-like growth factor-1 is an additional factor with neurogenic functions that may be increased in depression, reflecting an imbalance in neurotrophic processes.82,83 Basic fibroblast growth factor (or FGF-2) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family and appears higher in depressed than control groups.84 However, reports are not consistent; one found that this protein was lower in MDD than healthy controls, but reduced further alongside antidepressant treatment.85
Further growth factors that have not been sufficiently explored in depression include tyrosine kinase 2 and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (also termed sVEGFR-1) which act in synergy with VEGF, and tyrosine kinase receptors (that bind BDNF) may be attenuated in depression.86 Placental growth factor is also part of the VEGF family, but has not been studied in systematically depressed samples to our knowledge.
Metabolic Biomarker Findings in Depression
The main biomarkers associated with metabolic illness include leptin, adiponectin, ghrelin, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), glucose, insulin and albumin.87 The associations between many of these and depression have been reviewed: leptin88 and ghrelin89 appear lower in depression than controls in the periphery and may increase alongside antidepressant treatment or remission. Insulin resistance may be increased in depression, albeit by small amounts.90 Lipid profiles, including HDL-cholesterol, appear altered in many patients with depression, including those without comorbid physical illness, though this relationship is complex and requires further elucidation.91 Additionally, hyperglycemia92 and hypoalbuminemia93 in depression have been reported in reviews.
Investigations of overall metabolic states are becoming more frequent using metabolomics panels of small molecules with the hope of finding a robust biochemical signature for psychiatric disorders. In a recent study using artificial intelligence modeling, a set of metabolites illustrating increased glucose�lipid signaling was highly predictive of an MDD diagnosis,94 supportive of previous studies.95
Neurotransmitter Findings in Depression
While the attention paid to monoamines in depression has yielded relatively successful treatments, no robust neurotransmitter markers have been identified to optimize treatment based on the selectivity of monoamine targets of antidepressants. Recent work points toward the serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) 1A receptor as potentially important for both diagnosis and prognosis of depression, pending new genetic and imaging techniques.96 There are new potential treatments targeting 5-hydroxytryptamine; for example, using a slow-release administration of 5-hydroxytryptophan.97 Increased transmission of dopamine interacts with other neurotransmitters to improve cognitive outcomes such as decision making and motivation.98 Similarly, the neurotransmitters glutamate, noradrenaline, histamine and serotonin may interact and activate as part of a depression-related stress response; this might decrease 5-hydroxytryptamine production through �flooding�. A recent review sets out this theory and suggests that in TRD, this could be reversed (and 5-HT restored) through multimodal treatment targeting multiple neurotransmitters.99 Interestingly, increases in serotonin do not always occur conjunctively with therapeutic antidepressant benefits.100 Despite this, neurotransmitter metabolites such as 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol, of noradrenaline, or homovanillic acid, of dopamine, have often been found to increase alongside reduction in depression with antidepressant treatment101,102 or that low levels of these metabolites predict a better response to SSRI treatment.102,103
Neuroendocrine Findings in Depression
Cortisol is the most common HPA axis biomarker to have been studied in depression. Numerous reviews have focused on the various assessments of HPA activity; overall, these suggest that depression is associated with hypercortisolemia and that the cortisol awakening response is often attenuated.104,105 This is supported by a recent review of chronic cortisol levels measured in hair, supporting the hypothesis of cortisol hyperactivity in depression but hypoactivity in other illnesses such as panic disorder.106 Furthermore, particularly, elevated cortisol levels may predict a poorer response to psychological107 and antidepressant108 treatment. Historically, the most promising neuroendocrine marker of prospective treatment response has been the dexamethasone suppression test, where cortisol nonsuppression following dexamethasone administration is associated with a lower likelihood of subsequent remission. However, this phenomenon has not been considered sufficiently robust for clinical application. Related markers corticotrophin-releasing hormone and adrenocorticotropin hormone as well as vasopressin are inconsistently found to be overproduced in depression and dehydroepiandrosterone is found to be attenuated; the ratio of cortisol to dehydroepiandrosterone may be elevated as a relatively stable marker in TRD, persisting after remission.109 Neuroendocrine hormone dysfunctions have long been associated with depression, and hypothyroidism may also play a causal role in depressed mood.110 Furthermore, thyroid responses can normalize with successful treatment for depression.111
Within the above, it is important also to consider signaling pathways across systems, such as glycogen synthase kinase-3, mitogen-activated protein kinase and cyclic adenosine 3?,5?-monophosphate, involved in synaptic plasticity112 and modified by antidepressants.113 Further potential biomarker candidates that span biologic systems particularly are measured using neuroimaging or genetics. In response to the lack of robust and meaningful genomic differences between depressed and nondepressed populations,114 novel genetic approaches such as polygenic scores115 or telomere length116,117 could prove more useful. Additional biomarkers gaining popularity are examining circadian cycles or chronobiologic biomarkers utilizing different sources. Actigraphy can provide an objective assessment of sleep and wake activity and rest through an accelerometer, and actigraphic devices can increasingly measure additional factors such as light exposure. This may be more useful for detection than commonly used subjective reports of patients and could provide novel predictors of treatment response.118 The question of which biomarkers are the most promising for translational use is a challenging one, which is expanded upon below.
Current Challenges
For each of these five neurobiological systems reviewed, the evidence follows a similar narrative: there are many biomarkers that exist that are associated in some respects with depression. These markers are frequently interrelated in a complex, difficult-to-model fashion. The evidence is inconsistent, and it is likely that some are epiphenomena of other factors and some are important in only a subset of patients. Biomarkers are likely to be useful through a variety of routes (eg, those that predict subsequent response to treatment, those indicating specific treatments as more likely to be effective or those that alter with interventions regardless of clinical improvements). Novel methods are required to maximize consistency and clinical applicability of biologic assessments in psychiatric populations.
Biomarker Variability
Variation of biomarkers over time and across situations pertains more to some types (eg, proteomics) than others (genomics). Standardized norms for many do not exist or have not been widely accepted. Indeed, the influence of environmental factors on markers frequently depends on genetic composition and other physiologic differences between people that cannot all be accounted for. This makes the assessment of biomarker activity, and identifying biologic abnormalities, difficult to interpret. Due to the number of potential biomarkers, many have not been measured widely or in a complete panel alongside other relevant markers.
Many factors have been reported to alter the protein levels across biologic systems in patients with affective disorders. Along with research-related factors such as duration and conditions of storage (which may cause degradation of some compounds), these include time of day measured, ethnicity, exercise,119 diet (eg, microbiome activity, especially provided that most blood biomarker studies do not require a fasting sample),120 smoking and substance use,121 as well as health factors (such as comorbid inflammatory, cardiovascular or other physical illnesses). For example, although heightened inflammation is observed in depressed but otherwise healthy individuals compared to nondepressed groups, depressed individuals who also have a comorbid immune-related condition frequently have even higher levels of cytokines than either those without depression or illness.122 Some prominent factors with probable involvement in the relationship between biomarkers, depression and treatment response are outlined below.
Stress. Both endocrine and immune responses have well-known roles in responding to stress (physiologic or psychological), and transient stress at the time of biologic specimen collection is rarely measured in research studies despite the variability of this factor between individuals that may be accentuated by current depressive symptoms. Both acute and chronic psychological stressors act as an immune challenge, accentuating inflammatory responses in the short and longer term.123,124 This finding extends to the experience of early-life stress, which has been associated with adult inflammatory elevations that are independent of stress experienced as an adult.125,126 During childhood traumatic experience, heightened inflammation has also been reported only in those children who were currently depressed.127 Conversely, people with depression and a history of childhood trauma may have blunted cortisol responses to stress, compared to those with depression and no early-life trauma.128 Stress-induced HPA axis alterations appear interrelated with cognitive function,129 as well as depression subtype or variation in HPA-related genes.130 Stress also has short- and long-term impairing effects on neurogenesis131 and other neural mechanisms.132 It is unclear precisely how childhood trauma affects biologic markers in depressed adults, but it is possible that early-life stress predisposes some individuals to enduring stress reactions in adulthood that are amplified psychologically and/or biologically.
Cognitive functioning. Neurocognitive dysfunctions occur frequently in people with affective disorders, even in unmedicated MDD.133 Cognitive deficits appear cumulative alongside treatment resistance.134 Neurobiologically, the HPA axis129 and neurotrophic systems135 are likely to play a key role in this relationship. Neurotransmitters noradrenaline and dopamine are likely important for cognitive processes such as learning and memory.136 Elevated inflammatory responses have been linked with cognitive decline, and likely affect cognitive functioning in depressive episodes,137 and in remission, through a variety of mechanisms.138 Indeed, Krogh et al139 proposed that CRP is more closely related to cognitive performance than to the core symptoms of depression.
Age, gender and BMI. The absence or presence, and direction of biologic differences between men and women has been particularly variable in the evidence to date. Neuroendocrine hormone variation between men and women interacts with depression susceptibility.140 A review of inflammation studies reported that controlling for age and gender did not affect patient-control differences in inflammatory cytokines (although the association between IL-6 and depression reduced as age increased, which is consistent with theories that inflammation generally heightens with age).41,141 VEGF differences between patients and controls are larger in studies assessing younger samples, while gender, BMI and clinical factors did not affect these comparisons at a meta-analytic level.77 However, the lack of adjustment for BMI in previous examinations of inflammation and depression appears to confound highly significant differences reported between these groups.41 Enlarged adipose tissue has been definitively demonstrated to stimulate cytokine production as well as being closely linked to metabolic markers.142 Because psychotropic medications may be associated with weight gain and a higher BMI, and these have been associated with treatment resistance in depression, this is an important area to examine.
Medication. Many biomarker studies in depression (both cross-sectional and longitudinal) have collected baseline specimens in unmedicated participants to reduce heterogeneity. However, many of these assessments are taken after a wash-out period from medication, which leaves the potentially significant confounding factor of residual changes in physiology, exacerbated by the extensive range of treatments available that may have had differing effects on inflammation. Some studies have excluded psychotropic, but not other medication use: in particular, the oral contraceptive pill is frequently permitted in research participants and not controlled for in analyses, which has recently been indicated to increase hormone and cytokine levels.143,144 Several studies indicate that antidepressant medications have effects on the inflammatory response,34,43,49,145�147 HPA-axis,108 neurotransmitter,148 and neurotrophic149 activity. However, the numerous potential treatments for depression have distinct and complex pharmacologic properties, suggesting there may be discrete biologic effects of different treatment options, supported by current data. It has been theorized that in addition to monoamine effects, specific serotonin-targeting medications (ie, SSRIs) are likely to target Th2 shifts in inflammation, and noradrenergic antidepressants (eg, SNRIs) effect a Th1 shift.150 It is not yet possible to determine the effects of individual or combination medications on biomarkers. These are likely mediated by other factors including the length of treatment (few trials assess long-term medication use), sample heterogeneity and not stratifying participants by response to treatment.
Heterogeneity
Methodological. As alluded to above, differences (between and within studies) in terms of which treatments (and combinations) the participants are taking and have taken previously are bound to introduce heterogeneity into research findings, particularly in biomarker research. In addition to this, many other design and sample characteristics vary across studies, thus augmenting the difficulty with interpreting and attributing findings. These include biomarker measurement parameters (eg, assay kits) and methods of collecting, storing, processing and analyzing markers in depression. Hiles et al141 examined some sources of inconsistency in the literature on inflammation and found that accuracy of depression diagnosis, BMI and comorbid illnesses were most important to account for in assessing peripheral inflammation between depressed and nondepressed groups.
Clinical. The extensive heterogeneity of depressed populations is well documented151 and is a critical contributor to contrasting findings within the research literature. It is probable that even within diagnoses, abnormal biologic profiles are confined to subsets of individuals that may not be stable over time. Cohesive subgroups of people suffering with depression may be identifiable through a combination of psychological and biologic factors. Below, we outline the potential for exploring subgroups in meeting the challenges that biomarker variability and heterogeneity pose.
Subtypes within Depression
Thus far, no homogenous subgroups within depression episodes or disorders have been reliably able to distinguish between patients based on symptom presentations or treatment responsiveness.152 The existence of a subgroup in whom biologic aberrations are more pronounced would help to explain the heterogeneity between previous studies and could catalyze the path toward stratified treatment. Kunugi et al153 have proposed a set of four potential subtypes based on the role of different neurobiological systems displaying clinically relevant subtypes in depression: those with hypercortisolism presenting with melancholic depression, or hypocortisolism reflecting an atypical subtype, a dopamine-related subset of patients who may present prominently with anhedonia (and could respond well to, eg, aripiprazole) and an inflammatory subtype characterized by elevated inflammation. Many articles focusing on inflammation have specified the case for the existence of an �inflammatory subtype� within depression.55,56,154,155 Clinical correlates of elevated inflammation are as yet undetermined and few direct attempts have been made to discover which participants may comprise this cohort. It has been proposed that people with atypical depression could have higher levels of inflammation than the melancholic subtype,156 which is perhaps not in line with findings regarding the HPA axis in melancholic and atypical subtypes of depression. TRD37 or depression with prominent somatic symptoms157 has also been posited as a potential inflammatory subtype, but neurovegetative (sleep, appetite, libido loss), mood (including low mood, suicidality and irritability) and cognitive symptoms (including affective bias and guilt)158 all appear related to biologic profiles. Further potential candidates for an inflammatory subtype involve the experience of sickness behavior-like symptoms159,160 or a metabolic syndrome.158
The propensity toward (hypo) mania may distinguish biologically between patients suffering from depression. Evidence now suggests that bipolar illnesses are a multifaceted group of mood disorders, with bipolar subsyndromal disorder found more prevalently than was previously recognized.161 Inaccurate and/or delayed detection of bipolar disorder has recently been highlighted as a major problem in clinical psychiatry, with the average time to correct diagnosis frequently exceeding a decade162 and this delay causing greater severity and cost of overall illness.163 With the majority of patients with bipolar disorder presenting initially with one or more depressive episodes and unipolar depression being the most frequent misdiagnosis, the identification of factors that might differentiate between unipolar and bipolar depression has substantial implications.164 Bipolar spectrum disorders likely have been undetected in some previous MDD biomarker investigations, and smatterings of evidence have indicated differentiation of HPA axis activity109 or inflammation165,166 between bipolar and unipolar depression. However, these comparisons are scarce, possess small sample sizes, identified nonsignificant trend effects or recruited populations that were not well characterized by diagnosis. These investigations also do not examine the role of treatment responsiveness in these relationships.
Both bipolar disorders167 and treatment resistance168 are not dichotomous constructs and lie on continua, which increases the challenge of subtype identification. Apart from subtyping, it is worth noting that many biologic abnormalities observed in depression are similarly found in patients with other diagnoses. Thus, transdiagnostic examinations are also potentially important.
Biomarker Measurement Challenges
Biomarker selection. The large number of potentially useful biomarkers presents a challenge for psychobiology in determining which markers are implicated in which way and for whom. To increase the challenge, relatively few of these biomarkers have been subject to sufficient investigation in depression, and for most, their precise roles in healthy and clinical populations are not well understood. Despite this, a number of attempts have been made to propose promising biomarker panels. In addition to Brand et al�s 16 sets of markers with strong potential,27 Lopresti et al outline an additional extensive set of oxidative stress markers with potential for improving treatment response.28 Papakostas et al defined a priori a set of nine serum markers spanning biologic systems (BDNF, cortisol, soluble TNF? receptor type II, alpha1 antitrypsin, apolipoprotein CIII, epidermal growth factor, myeloperoxidase, prolactin and resistin) in validation and replication samples with MDD. Once combined, a composite measure of these levels was able to distinguish between MDD and control groups with 80%�90% accuracy.169 We propose that even these do not cover all potential candidates in this field; see Table 2 for a nonexhaustive delineation of biomarkers with potential for depression, containing both those with an evidence base and promising novel markers.
Technology. Due to technologic advances, it is now possible (indeed, convenient) to measure a large array of biomarkers simultaneously at a lower cost and with higher sensitivity than has been the case previously. At present, this capability to measure numerous compounds is ahead of our ability to effectively analyze and interpret the data,170 something that will continue with the rise in biomarker arrays and new markers such as with metabolomics. This is largely due to a lack of understanding about the precise roles of and the interrelationships between markers, and an insufficient grasp of how related markers associate across different biologic levels (eg, genetic, transcription, protein) within and between individuals. Big data using new analytical approaches and standards will assist with addressing this, and new methodologies are being proposed; one example is the development of a statistical approach grounded in flux-based analysis to discover new potential metabolic markers based on their reactions between networks and integrate gene expression with metabolite data.171 Machine learning techniques are already being applied and will assist with models using biomarker data to predict treatment outcomes in studies with big data.172
Aggregating biomarkers. Examining an array of biomarkers simultaneously is an alternative to inspecting isolated markers that could provide a more accurate viewpoint into the complex web of biologic systems or networks.26 Also, to assist with disentangling contrasting evidence in this literature to date (particularly, where biomarker networks and interactions are well understood), biomarker data can then be aggregated or indexed. One challenge is in identifying the optimum method of conducting this, and it may require enhancements in technology and/or novel analytical techniques (see the �Big data� section). Historically, ratios between two distinct biomarkers have yielded interesting findings.109,173 Few attempts have been made to aggregate biomarker data on a larger scale, such as those using principal component analysis of proinflammatory cytokine networks.174 In a meta-analysis, proinflammatory cytokines have been converted into a single-effect size score for each study, and overall showed significantly higher inflammation before antidepressant treatment, predicting subsequent nonresponse in outpatient studies. Composite biomarker panels are both a challenge and opportunity for future research to identify meaningful and reliable findings that can be applied to improve treatment outcomes.43 A study by Papakostas et al took an alternative approach, selecting a panel of heterogeneous serum biomarkers (of inflammatory, HPA axis and metabolic systems) that had been indicated to differ between depressed and control individuals in a previous study and composited these into a risk score which differed in two independent samples and a control group with >80% sensitivity and specificity.169
Big data. The use of big data is probably necessary for addressing the current challenges outlined surrounding heterogeneity, biomarker variability, identifying the optimal markers and bringing the field toward translational, applied research in depression. However, as outlined above, this brings technological and scientific challenges.175 The health sciences have only recently begun using big data analytics, a decade or so later than in the business sector. However, studies such as iSPOT-D152 and consortia such as the Psychiatric Genetics Consortium176 are progressing with our understanding of biologic mechanisms in psychiatry. Machine-learning algorithms have, in very few studies, started to be applied to biomarkers for depression: a recent investigation pooled data from >5,000 participants of 250 biomarkers; after multiple imputation of data, a machine-learning boosted regression was conducted, indicating 21 potential biomarkers. Following further regression analyses, three biomarkers were selected as associating most strongly with depressive symptoms (highly variable red blood cell size, serum glucose and bilirubin levels). The authors conclude that big data can be used effectively for generating hypotheses.177 Larger biomarker phenotyping projects are now underway and will help to advance our journey into the future of the neurobiology of depression.
Future Prospects
Biomarker Panel Identification
The findings in the literature to date require replication in large-scale studies. This is particularly true for novel biomarkers, such as the chemokine thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and the growth factor tyrosine kinase 2 which, to our knowledge, have not been investigated in clinically depressed and healthy control samples. Big data studies must assay comprehensive biomarker panels and use sophisticated analysis techniques to fully ascertain the relationships between markers and those factors which modify them in clinical and nonclinical populations. Additionally, large-scale replications of principal component analysis might establish highly correlated groups of biomarkers and could also inform the use of �composites� in biologic psychiatry, which may enhance the homogeneity of future findings.
Discovery of Homogenous Subtypes
Regarding biomarker selection, multiple panels may be required for different potential pathways that research could implicate. Taken together, the current evidence indicates that biomarker profiles are assuredly, but abstrusely altered in a subpopulation of individuals currently suffering from depression. This may be established within or across diagnostic categories, which would account for some inconsistency of findings that can be observed in this literature. Quantifying a biologic subgroup (or subgroups) may most effectively be facilitated by a large cluster analysis of biomarker network panels in depression. This would illustrate within-population variability; latent class analyses could exhibit distinct clinical characteristics based on, for example, inflammation.
Specific Treatment Effects on Inflammation and Response
All commonly prescribed treatments for depression should be comprehensively assessed for their specific biologic effects, also accounting for the effectiveness of treatment trials. This may enable constructs relating to biomarkers and symptom presentations to predict outcomes to a variety of antidepressant treatments in a more personalized fashion, and may be possible in the context of both unipolar and bipolar depression. This is likely to be useful for new potential treatments as well as currently indicated treatments.
Prospective Determination of Treatment Response
Use of the above techniques is likely to result in an improved ability to forecast treatment resistance prospectively. More authentic and persistent (eg, long-term) measures of treatment response may contribute to this. Assessment of other valid measures of patient well-being (such as quality of life and everyday functioning) could provide a more holistic assessment of treatment outcome that may associate more closely with biomarkers. While biologic activity alone might not be able to distinguish treatment responders from nonresponders, concurrent measurement of biomarkers with psychosocial or demographic variables could be integrated with biomarker information in developing a predictive model of insufficient treatment response. If a reliable model is developed to predict response (either for the depressed population or a subpopulation) and is validated retrospectively, a translational design can establish its applicability in a large controlled trial.
Toward Stratified Treatments
At present, patients with depression are not systematically directed to receive an optimized intervention program. If validated, a stratified trial design could be employed to test a model to predict nonresponse and/or to determine where a patient needs to be triaged in a stepped care model. This could be useful in both standardized and naturalistic treatment settings, across different types of intervention. Ultimately, a clinically viable model could be developed to provide individuals with the most appropriate treatment, to recognize those who are likely to develop refractory depression and supply enhanced care and monitoring to these patients. Patients identified as being at risk for treatment resistance may be prescribed a concomitant psychological and pharmacologic therapy or combination pharmacotherapy. As a speculative example, participants with no proinflammatory cytokine elevations might be indicated to receive psychological rather than pharmacologic therapy, while a subset of patients with particularly high inflammation could receive an anti-inflammatory agent in augmentation to standard treatment. Similar to stratification, personalized treatment-selection strategies may be possible in the future. For example, a particular depressed individual might have markedly high TNF? levels, but no other biologic abnormalities, and could benefit from short-term treatment with a TNF? antagonist.54 Personalized treatment may also entail monitoring biomarker expression during treatment to inform possible intervention changes, the length of continuation therapy required or to detect early markers of relapse.
Novel Treatment Targets
There are a huge number of potential treatments that could be effective for depression, which have not been adequately examined, including novel or repurposed interventions from other medical disciplines. Some of the most popular targets have been in anti-inflammatory medications such as celecoxib (and other cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors), TNF? antagonists etanercept and infliximab, minocycline or aspirin. These appear promising.178 Antiglucocorticoid compounds, including ketoconazole179 and metyrapone,180 have been investigated for depression, but both have drawbacks with their side effect profile and the clinical potential of metyrapone is uncertain. Mifepristone181 and the corticosteroids fludrocortisone and spironolactone,182 and dexamethasone and hydrocortisone183 may also be effective in treating depression in the short term. Targeting glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists, including ketamine, might represent efficacious treatments in depression.184 Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids influence inflammatory and metabolic activity and appear to demonstrate some effectiveness for depression.185 It is possible that statins may have antidepressant effects186 through relevant neurobiological pathways.187
In this way, the biochemical effects of antidepressants (see the �Medication� section) have been utilized for clinical benefits in other disciplines: particularly gastroenterological, neurologic and nonspecific symptom illnesses.188 Anti-inflammatory effects of antidepressants may represent part of the mechanism for these benefits. Lithium has also been suggested to reduce inflammation, critically through glycogen synthase kinase-3 pathways.189 A focus on these effects could prove informative for a depression biomarker signature and, in turn, biomarkers could represent surrogate markers for novel drug development.

Dr. Alex Jimenez’s Insight
Depression is a mental health disorder characterized by severe symptoms which affect mood, including loss of interest in activities. Recent research studies, however, have found that it may be possible to diagnose depression using more than just a patient’s behavioral symptoms. According to the researchers, identifying easily obtainable biomarkers which could more accurately diagnose depression is fundamental towards improving a patient’s overall health and wellness. By way of instance, clinical findings suggest that individuals with major depressive disorder, or MDD, have lower levels of the molecule acetyl-L-carnitine, or LAC, in their blood than healthy controls. Ultimately, establishing biomarkers for depression could potentially help better determine who is at risk of developing the disorder as well as help healthcare professionals determine the best treatment option for a patient with depression.
Conclusion
The literature indicates that approximately two-thirds of patients with depression do not achieve remission to an initial treatment and that the likelihood of nonresponse increases with the number of treatments trialed. Providing ineffective therapies has substantial consequences for individual and societal cost, including persistent distress and poor well-being, risk of suicide, loss of productivity and wasted health care resources. The vast literature in depression indicates a huge number of biomarkers with the potential to improve treatment for people with depression. In addition to neurotransmitter and neuroendocrine markers which have been subject to widespread study for many decades, recent insights highlight the inflammatory response (and the immune system more generally), metabolic and growth factors as importantly involved in depression. However, excessive contrasting evidence illustrates that there are a number of challenges needing to be tackled before biomarker research can be applied in order to improve the management and care of people with depression. Due to the sheer complexity of biologic systems, simultaneous examinations of a comprehensive range of markers in large samples are of considerable benefit in discovering interactions between biologic and psychological states across individuals. Optimizing the measurement of both neurobiological parameters and clinical measures of depression is likely to facilitate greater understanding. This review also highlights the importance of examining potentially modifying factors (such as illness, age, cognition and medication) in gleaning a coherent understanding of the biology of depression and mechanisms of treatment resistance. It is likely that some markers will show most promise for predicting treatment response or resistance to specific treatments in a subgroup of patients, and the concurrent measurement of biologic and psychological data may enhance the ability to prospectively identify those at risk for poor treatment outcomes. Establishing a biomarker panel has implications for boosting diagnostic accuracy and prognosis, as well as for individualizing treatments at the earliest practicable stage of depressive illness and developing effective novel treatment targets. These implications may be confined to subgroups of depressed patients. The pathways toward these possibilities complement recent research strategies to link clinical syndromes more closely to underlying neurobiological substrates.6 Apart from reducing heterogeneity, this may facilitate a shift toward parity of esteem between physical and mental health. It is clear that although much work is needed, establishment of the relationship between relevant biomarkers and depressive disorders has substantial implications for reducing the burden of depression at an individual and societal level.
Acknowledgments
This report represents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King�s College London. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Footnotes
Disclosure. AHY has in the last 3 years received honoraria for speaking from Astra Zeneca (AZ), Lundbeck, Eli Lilly, Sunovion; honoraria for consulting from Allergan, Livanova and Lundbeck, Sunovion, Janssen; and research grant support from Janssen and UK funding agencies (NIHR, MRC, Wellcome Trust). AJC has in the last 3 years received honoraria for speaking from Astra Zeneca (AZ), honoraria for consulting from Allergan, Livanova and Lundbeck, and research grant support from Lundbeck and UK funding agencies (NIHR, MRC, Wellcome Trust).
The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
In conclusion,�while numerous research studies have found hundreds of biomarkers for depression, not many have established their role in depressive illness or how exactly biologic information could be utilized to enhance diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. However, the article above reviews the available literature on the biomarkers involved during other processes and compares the clinical findings to that of depression. Furthermore, new findings on biomarkers for depression may help better diagnose depression in order to follow up with better treatment. Information referenced from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).�The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic as well as to spinal injuries and conditions. To discuss the subject matter, please feel free to ask Dr. Jimenez or contact us at�915-850-0900�.
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez
Additional Topics: Back Pain
Back pain is one of the most prevalent causes for disability and missed days at work worldwide. As a matter of fact, back pain has been attributed as the second most common reason for doctor office visits, outnumbered only by upper-respiratory infections. Approximately 80 percent of the population will experience some type of back pain at least once throughout their life. The spine is a complex structure made up of bones, joints, ligaments and muscles, among other soft tissues. Because of this, injuries and/or aggravated conditions, such as herniated discs, can eventually lead to symptoms of back pain. Sports injuries or automobile accident injuries are often the most frequent cause of back pain, however, sometimes the simplest of movements can have painful results. Fortunately, alternative treatment options, such as chiropractic care, can help ease back pain through the use of spinal adjustments and manual manipulations, ultimately improving pain relief.

EXTRA IMPORTANT TOPIC: Low Back Pain Management
MORE TOPICS: EXTRA EXTRA:�Chronic Pain & Treatments





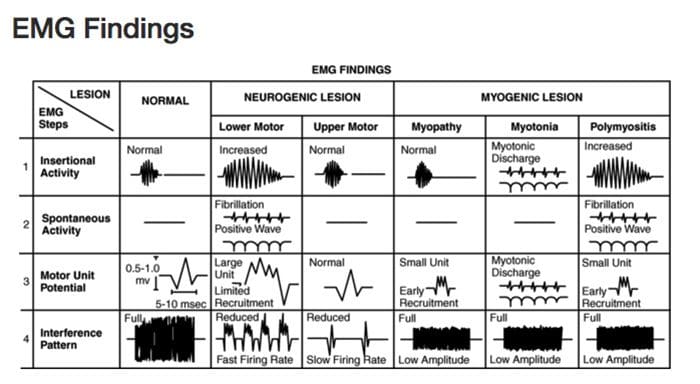 Diagnostic Needle EMG
Diagnostic Needle EMG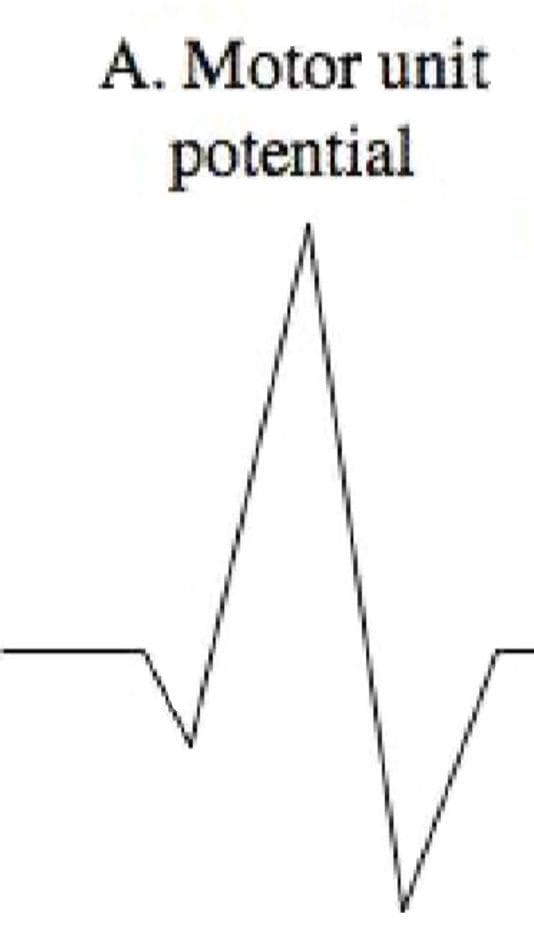 Polyphasic MUPS
Polyphasic MUPS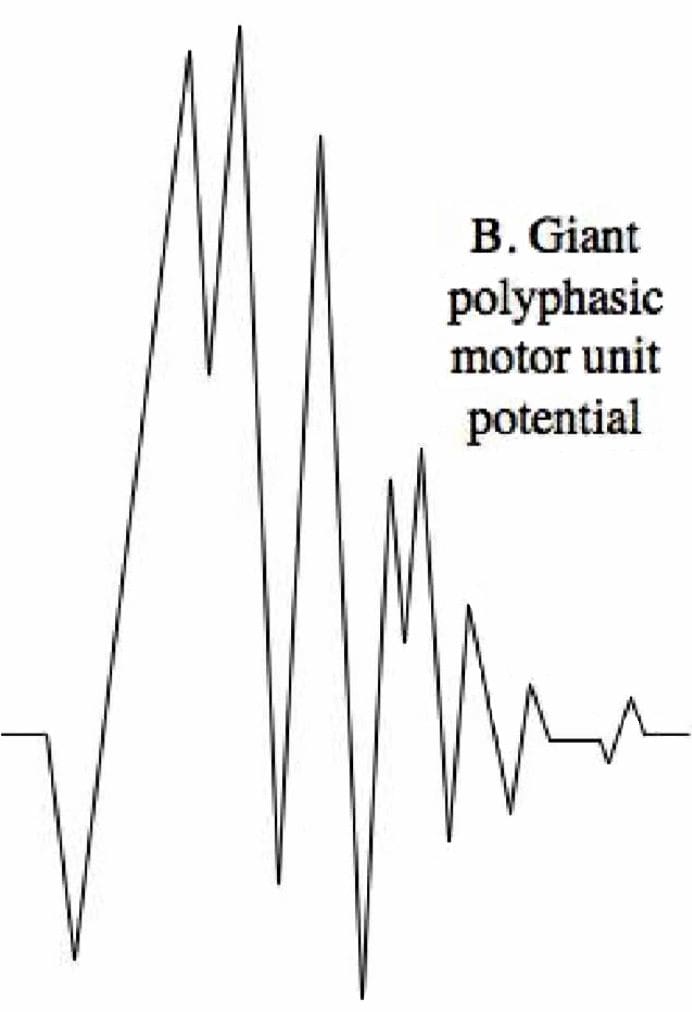 Complete Potential Blocks
Complete Potential Blocks Positive Sharp Waves
Positive Sharp Waves Abnormal Findings
Abnormal Findings



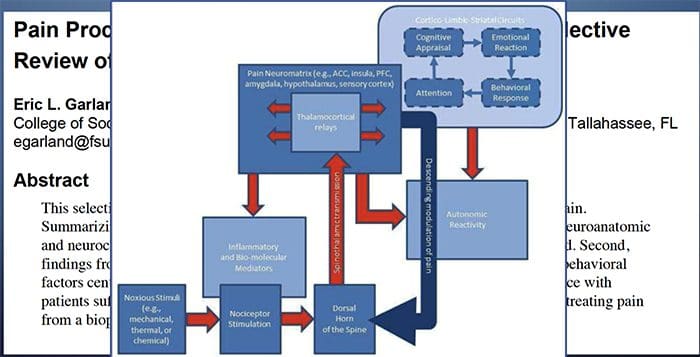
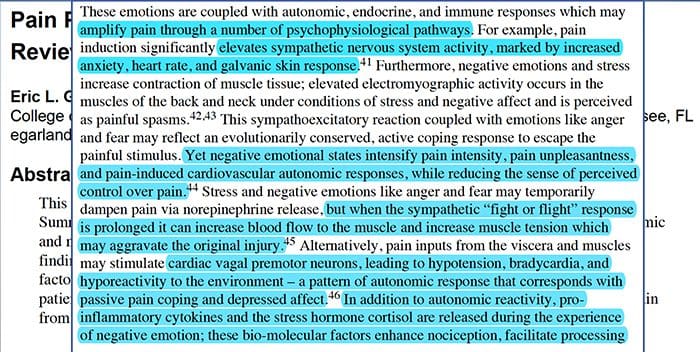
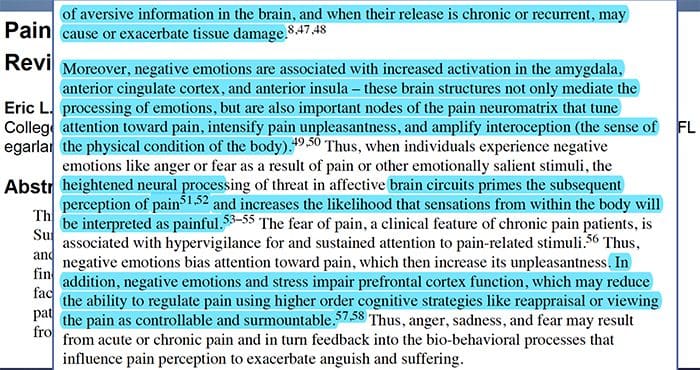
 Why Does My Shoulder Hurt? A Review Of The Neuroanatomical & Biochemical Basis Of Shoulder Pain
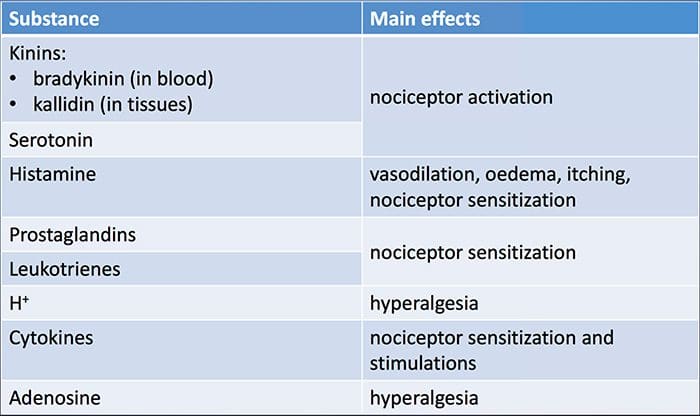
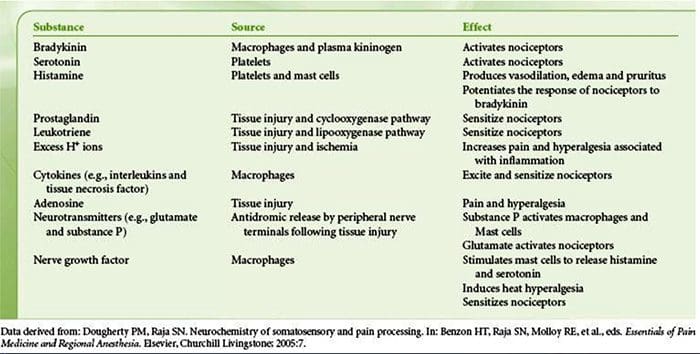
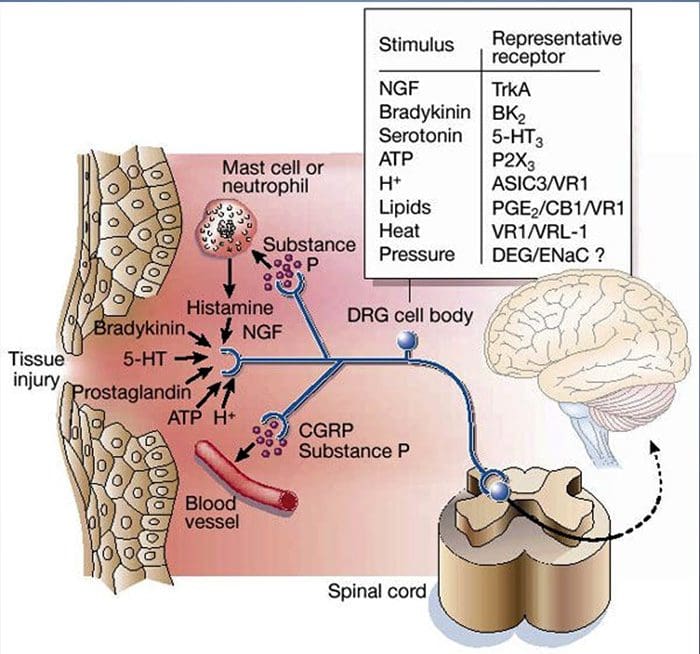
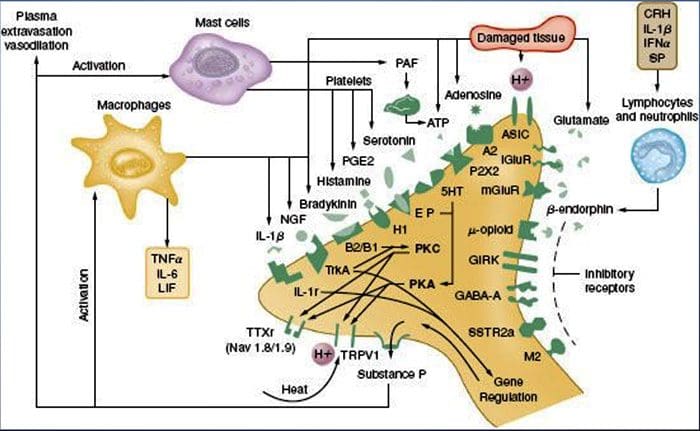
Why Does My Shoulder Hurt? A Review Of The Neuroanatomical & Biochemical Basis Of Shoulder Pain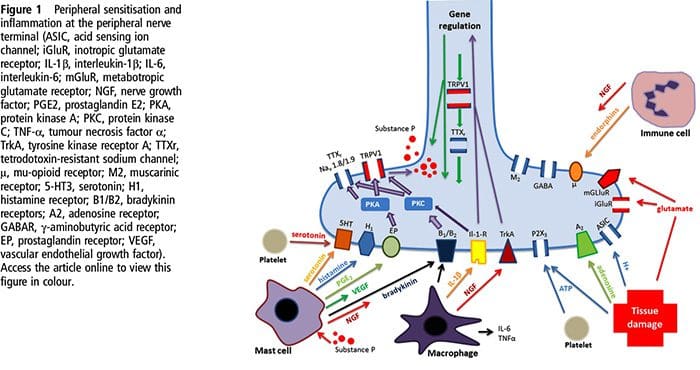 NGF and the transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) receptor have a symbiotic relationship when it comes to inflammation and nociceptor sensitization. The cytokines produced in inflamed tissue result in an increase in NGF production.19 NGF stimulates the release of histamine and serotonin (5-HT3) by mast cells, and also sensitizes nociceptors, possibly altering the properties of A? fibers such that a greater proportion become nociceptive. The TRPV1 receptor is present in a subpopulation of primary afferent fibers and is activated by capsaicin, heat and protons. The TRPV1 receptor is synthesized in the cell body of the afferent fibre, and is transported to both the peripheral and central terminals, where it contributes to the sensitivity of nociceptive afferents. Inflammation results in NGF production peripherally which then binds to the tyrosine kinase receptor type 1 receptor on the nociceptor terminals, NGF is then transported to the cell body where it leads to an up regulation of TRPV1 transcription and consequently increased nociceptor sensitivity.19 20 NGF and other inflammatory mediators also sensitize TRPV1 through a diverse array of secondary messenger pathways. Many other receptors including cholinergic receptors, ?-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors and somatostatin receptors are also thought to be involved in peripheral nociceptor sensitivity.
NGF and the transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) receptor have a symbiotic relationship when it comes to inflammation and nociceptor sensitization. The cytokines produced in inflamed tissue result in an increase in NGF production.19 NGF stimulates the release of histamine and serotonin (5-HT3) by mast cells, and also sensitizes nociceptors, possibly altering the properties of A? fibers such that a greater proportion become nociceptive. The TRPV1 receptor is present in a subpopulation of primary afferent fibers and is activated by capsaicin, heat and protons. The TRPV1 receptor is synthesized in the cell body of the afferent fibre, and is transported to both the peripheral and central terminals, where it contributes to the sensitivity of nociceptive afferents. Inflammation results in NGF production peripherally which then binds to the tyrosine kinase receptor type 1 receptor on the nociceptor terminals, NGF is then transported to the cell body where it leads to an up regulation of TRPV1 transcription and consequently increased nociceptor sensitivity.19 20 NGF and other inflammatory mediators also sensitize TRPV1 through a diverse array of secondary messenger pathways. Many other receptors including cholinergic receptors, ?-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors and somatostatin receptors are also thought to be involved in peripheral nociceptor sensitivity.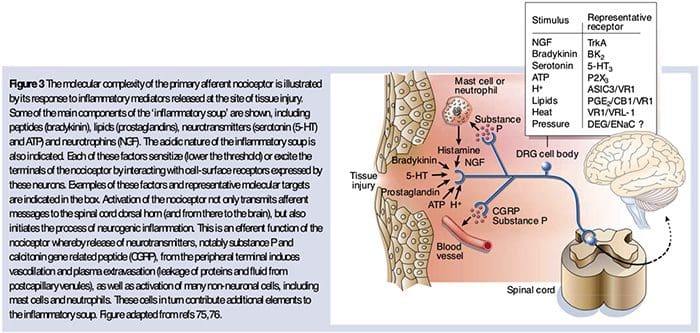 The Neurochemistry Of Nociceptors
The Neurochemistry Of Nociceptors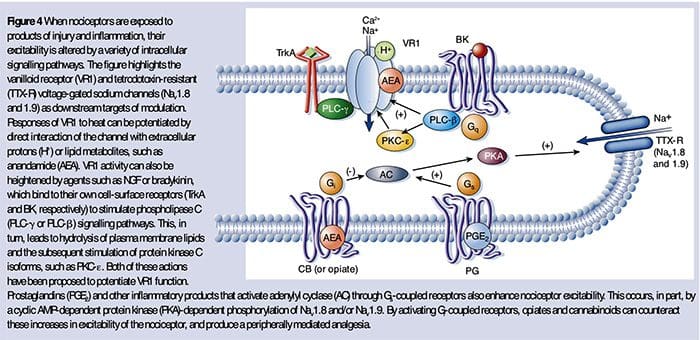 Cellular & Molecular Mechanisms Of Pain
Cellular & Molecular Mechanisms Of Pain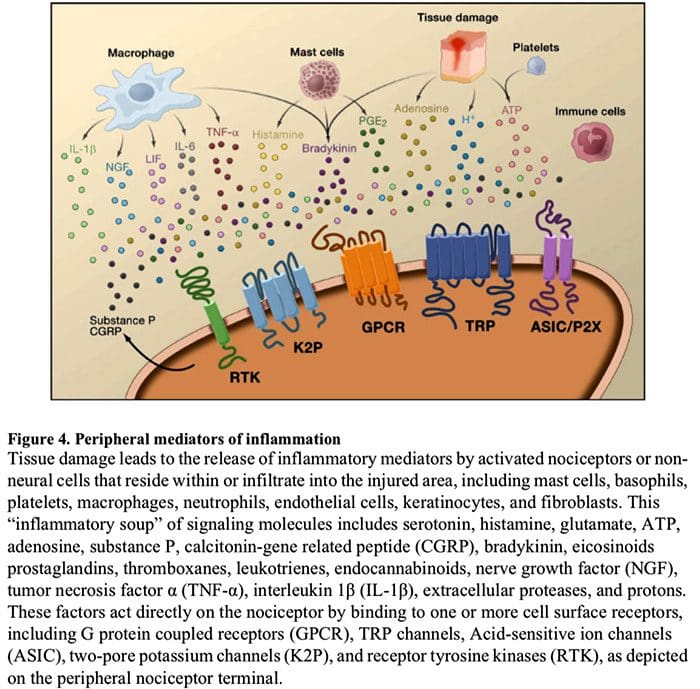
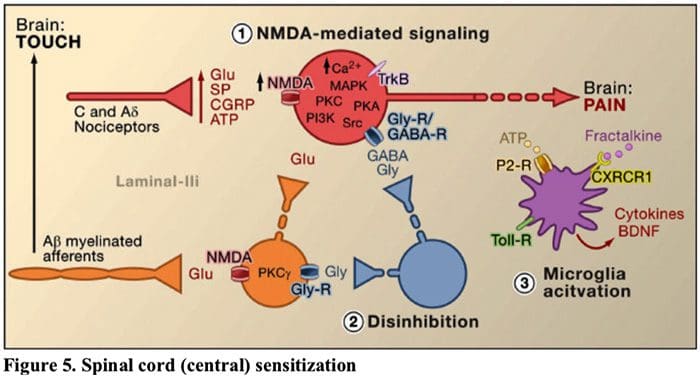 Figure 5. Spinal Cord (Central) Sensitization
Figure 5. Spinal Cord (Central) Sensitization