
by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
Actor Antonio Sabato, Jr., was suffering from depression, mood swings, and just feeling a tremendous loss of energy until he discovered hormone therapy that he says changed his life around.
Sabato, a staunch Republican who recently announced that he is running for Congress, was a vocal supporter of President Donald Trump during the 2016 campaign. The actor has long been interested in politics and public policy, but he tells Newsmax Health his health woes prevented him from performing his best.
The Italian-born heart throb best known for his role as Jagger Cates in the soap opera “General Hospital” and his work as a Calvin Klein model, discovered that his debilitating symptoms stemmed from hormone depletion, a condition that strikes one in four men over the age of 30.
The symptoms may also include low sex drive, sleep disturbances, depressed mood, lethargy, and diminished physical performance.
“For me, I couldn’t understand why I was feeling so low,” Sabato tells Newsmax Health. “I’ve always worked out to keep myself in top shape for my demanding roles in movies and on television and I just wasn’t bouncing back the way I used to. I suffered from terrible mood swings and insomnia. The doctors I went to wanted to give me pills, which I took at the beginning but then I felt trapped.
“I didn’t want to take sleeping pills and antidepressants. I just want to feel like myself again.”
Rather than throwing in the towel and chalking up his lethargy to aging, Sabato was determined to find an effective treatment for his condition.
After a great deal of searching he met Dr. Christopher Asandra, who is board-certified by the American Board of Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine and a leading anti-aging expert.
His program includes custom-tailored replacement therapy for both men and women to replace hormone levels diminished by the aging process, menopause and andropause, stress, diabetes, obesity, certain medications, and alcohol use.
“By careful testing and evaluating each patient’s blood work, I prescribe a formula that restores optimum hormone levels which soon translates into optimum health,” Asandra tells Newsmax Health.
After following Asandra’s protocol Sabato, 45, says he feels decades younger.
“I should have started his program in my 30s,” he laughs. “I have amazing energy and vitality and my mood swings are gone. I sleep like a baby and as an added benefit the brain fog disappeared and I have incredible mental clarity which is an asset when I need to memorize scripts.”
The therapy consists of inserting two tic-tac sized time-release pellets containing bio-identical testosterone hormones that slowly regulate the body over a 5-6 month period. Sabato also uses Asandra’s growth hormone called Sermorelin, a sequence of 29 vital amino acids taken daily at night to stimulate growth hormone production.
“This treatment helps improve bone density, strengthen the cardiovascular system, increase muscle mass and improve cognitive and memory function,” says Asandra.
But patients must also do their part, the expert insists.
“I can jump start their systems but they have to change their lifestyles to get off the couch, start exercising and eating right,” he says.”It’s like the old expression, I can lead the horse to water but I can’t make him drink!”
Sabato changed his diet to include 80 percent vegetables, fish, and chicken.
“I eat red meat once in a while but I usually stick to a huge salad with fish,” he says. “I eat no dairy, eggs or bread.”
Sabato, a self-professed workout enthusiast works out strenuously six days a week.
“I do resistance training, cardio and Jiu Jitsu, a form of martial arts,” he says. “Thanks to the hormone therapy I have far more energy than ever before.”
Asandra says that the secret to successful anti-aging therapy is to be judicious in replacing lost hormones.
“Some of my patients only need to have hormone therapy for a year to get back their energy, get off the couch and stay motivated to keep their bodies and minds healthy,” he says. “We customize all our therapies to ensure optimum levels which are carefully monitored by regular blood tests.”
“My patients say it is life changing not only for them, but also for the people around them,” he says, noting his treatment is generally not covered by insurance. “When you are on an even keel mentally, in top shape physically and can enjoy intimacy once again, a price tag similar to buying a Starbuck coffee daily is so worth it!”
Asandra says it is important to find the right doctor who will listen to your needs and treat the cause of your symptoms rather than use a Band-Aid approach.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
Although scientists have yet to develop an effective pill that will stop aging, a study from Brigham Young University says you can do it yourself — if you exercise a lot and don’t mind sweating. Heavy exercise can cut aging in your cells by nine years.
The study, which was published in the medical journal Preventive Medicine, found that people who have consistently high levels of physical activity have significantly longer telomeres than those who have sedentary lifestyles, as well as those who are moderately active.
Telomeres are the pieces of DNA at the end of chromosomes that act as protective caps. Chromosomes, which protect our genes, get shorter every time a cell divides. Once a chromosome gets too short, it dies. Shortened chromosomes are associated with the diseases of aging and death.
“Just because you’re 40, doesn’t mean you’re 40 years old biologically,” said exercise science professor Larry Tucker. “We all know people that seem younger than their actual age. The more physically active we are, the less biological aging takes place in our bodies.”
Tucker analyzed data from 5,823 adults who participated in the CDC’s National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, one of the few indexes that includes telomere length values for study subjects. The index also includes data for 62 activities participants might have engaged in over a 30-day window. Tucker used the data to calculate levels of physical activity.
Tucker found adults with high physical activity levels have telomeres with a biological aging advantage of nine years over those who are sedentary, and a seven-year advantage compared to those who are moderately active. To be highly active, women had to engage in 30 minutes of jogging per day (40 minutes for men), five days a week.
“If you want to see a real difference in slowing your biological aging, it appears that a little exercise won’t cut it,” he said. “You have to work out regularly at high levels.
“We know that regular physical activity helps to reduce mortality and prolong life, and now we know part of that advantage may be due to the preservation of telomeres,” Tucker said.
Researchers have been searching for other means to extend the length of telomeres. Scientists at Stanford University have found that a modified RNA protein can extend their lives.
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, helps transfer genetic information. Scientists modified RNA to contain the coding for an enzyme called telomerase, which is expressed by stem cells. When scientists treated skin cells with the modified RNA, the treated cells acted like much younger cells, multiplying as many as 40 times more than untreated cells.
“We have found a way to lengthen human telomeres by as much as 1,000 nucleotides, turning back the internal clock in these cells by the equivalent of many years of human life,” said Helen Blau, Ph.D., professor of microbiology and immunology at Stanford.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging, Seniors, Veterans
Richard Overton, the oldest living U.S. World War II veteran, turned 111 on Thursday in Texas.
Overton, an Austin resident, served with the Army’s 1887th Engineer Aviation Battalion in the Pacific Theater from 1942 to 1945.
He celebrated his 111th birthday with a lunch party at the University of Texas club, which was attended by Austin Mayor Steve Adler and other dignitaries. Overton received many gifts, including an autographed football from the University of Texas, ABC News reported.
The mayor declared May 11 Richard Overton Day and temporarily renamed Hamilton Avenue, where Overton lives, Richard Overton Avenue in his honor.
A GoFundMe campaign in January raised funds to allow Overton to stay in the home where he has lived for more than 70 years since he came home from the war, rather than be moved to an assisted living facility.
“111, that’s pretty old, ain’t it,” Overton said, USA Today reported. “I can still get around, I can still talk, I can still see, I can still walk.” Overton credits “cigars and God” for his longevity, admitting he had already had a few cigars that day.
Overton, a sharpshooter in the war, has been honored numerous times for his service, including for his 107th birthday having breakfast with President Barack Obama in the White House.
Overton was born May 11, 1906, in Bastrop County, Texas, Fox News reported.
Twitter users in his community and from far beyond it shared their appreciation and good wishes with Overton to mark his special day.

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
Grating, cracking or popping sounds around joints may predict future arthritis, especially in the knees, according to a recent U.S. study.
Among thousands of people with no knee pain who were followed for three years, one quarter had noisy knees yet they made up three quarters of the cases of symptomatic knee arthritis that emerged by the end of the study period, researchers found.
“Many people who have signs of osteoarthritis on X-rays do not necessarily complain about pain. Presently, there are no known strategies for preventing the development of pain in this group,” said lead study author Grace Lo of Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas.
Especially when people have joint space loss or other arthritis-related changes visible on X-rays, their also having noisy knees can be considered a sign of higher risk for developing pain within the next year, she said.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting more than 30 million adults in the United States, Lo and colleagues write in Arthritis Care and Research. Symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, which means X-ray evidence of arthritis plus pain or stiffness, affects about 16 percent of adults older than 60, they note.
Lo and colleagues analyzed data from 3,495 participants ranging in age from about 50 to 70 in a long-term study conducted in hospitals in Rhode Island, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Maryland. None had symptomatic knee arthritis at the start.
The researchers looked at how often people experienced knee pain, stiffness and “crepitus,” or noises and scraping feelings in their knees.
During clinic visits, people were asked questions like, “Do you feel grinding, hear clicking or any other type of noise when your right knee moves?” and “During the past 12 months, have you had pain, aching or stiffness in or around your right knee on most days for at least one month?” The patients were evaluated at the beginning of the study and again at 12, 24 and 36 months. X-rays were also taken once a year.
At the start, 65 percent of participants said they had no crepitus, 11 percent experienced it “rarely,” 15 percent had it “sometimes” and 9 percent had it “often” or “always.”
Overall, 635 participants, 18 percent, developed symptomatic arthritis of the knee during the study period.
Even after adjusting for weight and other factors, researchers found that odds of developing symptomatic arthritis rose along with the frequency of crepitus. Those who reported it “rarely” had 50 percent higher risk than those who never had it, and those with crepitus “sometimes” or “often” had about double the odds.
People with crepitus “always” were three times more likely to develop arthritis over four years than those who never had it.
Older age and having crepitus also increased the likelihood of developing arthritis, and men with crepitus were more likely than women with noisy knees to go on to develop arthritis.
“Differences across genders is interesting and unexplained. This may tell us about differences in symptom reporting or the biology of osteoarthritis,” said Daniel Solomon, the chair of arthritis and population health at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“Knowing how to predict who will develop symptomatic osteoarthritis may give patients and providers clues to who should receive earlier treatment or even prevention,” Solomon, who wasn’t involved in the study, told Reuters Health by email.
“It would be helpful to look at the MRIs of the people who had X-ray evidence, no pain and always had crepitus to understand what is happening in their knees,” Lo said. “This could help identify ways to decrease the risk for developing knee pain.”
Since MRI scans are more sensitive than X-rays, Lo added, researchers for future studies may be able to see osteophyte formations or other symptoms around the knee that they can’t usually see.
“Not all noises coming from a knee are a bad sign,” she said. “It might be helpful to ask your doctor for an X-ray to see if you have evidence of osteoarthritis and then take precautions from there.”

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
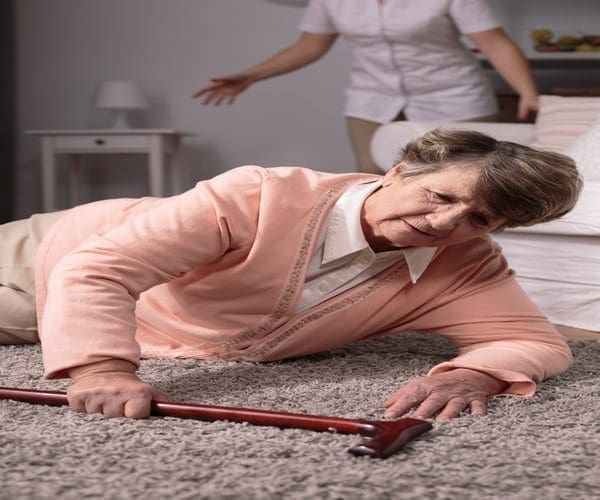
Scientists unveiled a lightweight, robotic, outer “skeleton” Thursday that can detect when someone loses their balance, correct their gait, and prevent their fall.
Designed to limit stumbles among the elderly, the device has sensors that can discern in real time when a limb starts to buckle or flail, and lightweight motors which exert instant force on both legs to restore balance.
“Wearable machines that enhance your movement and endurance no longer belong to the realm of science fiction,” the device’s creators said in a statement.
According to the World Health Organization, falls are the second cause of death from accidental or unintentional injuries worldwide.
Every year, more than 420,000 people die from falls — most of those are older than 65.
Nearly 40 million falls that require medical attention are reported annually, says the WHO, and this number is likely to skyrocket as people live to become ever older.
Dubbed the Active Pelvis Orthosis or APO, the new device could also help disabled people and amputees, said its designers from the Scuola Sant’Anna, an Italian University, and Switzerland’s EPFL polytechnical school.
“It’s technology that will actually help people with their daily activities,” they added.
The team published the results of their lab experiments in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.
The “exoskeleton” is worn from the waist down, its creators explained, “and is vastly different from the armoured stuff you see in today’s science fiction movies”.
It is attached to a belt worn around the middle that holds small motors at the hips, and soft braces strapped to the thighs.
The device weighs about five kilogrammes (11 pounds), can be easily adjusted to a person’s individual height and girth, and does not interfere with normal walking, the team said.
The “assistive mode” is activated only when balance loss is detected.
“The robotic exoskeleton is able to identify an unexpected slippage and counteract it,” Peppino Tropea, one of the study authors, told AFP.
The APO “increases stiffness at hip joints against limb movements, indeed, the slipping leg is slowed down, while the other one is forced towards the ground. This strategy is effective for balance recovery.”
Tropea and the rest of the team tested their creation on eight elderly people and two amputees with prosthetic limbs — two groups particularly vulnerable to potentially devastating falls.
They were made to walk on a treadmill with a platform that would unexpectedly slip sideways, causing the walker to lose balance.
Repeated tests showed that the device “effectively” aided balance recovery, the paper reported.
“I feel more confident when I wear the exoskeleton,” a statement quoted 69-year-old Fulvio Bertelli, one of the trial participants, as saying.
A video explaining the invention can be watched here:

by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging, Probiotics
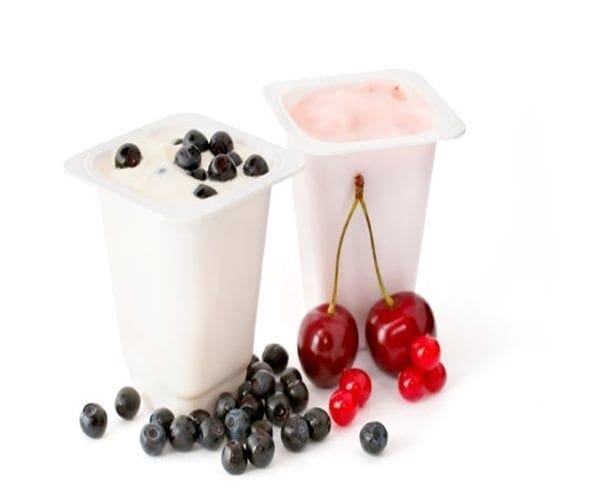
An Irish study that examined the relationship between dairy intake and bone density found that senior citizens who ate the most yogurt had denser hip bones than those who ate the least.
Researchers examined 1,057 women and 763 men who underwent a bone-mineral-density (BMD) assessment and 2,624 women and 1,290 men who had their physical function measured. All were older than 60 years of age.
Yogurt consumption information was gleaned from a questionnaire and categorized as never, two to three times per week, and more than one serving per day. Other factors that influence bone health were taken into consideration including daily intakes of other dairy products, meat, fish, smoking, alcohol, and other traditional risk factors that affect bone health.
After adjusting for all risk factors, each unit increase in yogurt consumption in women was associated with a 31 percent lower risk of osteopenia (a condition where old bone is reabsorbed into the body faster than it can make new bone) and a 39 percent lower risk of osteoporosis (weak, brittle bones).
In men, the risk of osteoporosis was 52 percent lower in those who ate the most yogurt.
“Yogurt is a rich source of different bone promoting nutrients,” said researcher Dr. Eamon Laird. “The data suggest that improving yogurt intakes could be a strategy for maintaining bone health.”
Other recent studies have found yogurt has some surprising health benefits. Scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles, found that good bacteria like the Lactobacillus strain found in yogurt battle inflammation and can slow, or even stop, the development of cancer. In addition, good bacteria reduced gene damage.
An analysis of 23 randomized studies at Vanderbilt University Medical Center found that using probiotics improved the symptoms of people with seasonal allergies. Researchers theorize probiotics change the composition of bacteria in the intestines in ways that modulate the body’s immune response and stop it from reacting to pollen and other allergens.
by Dr Alex Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP | Anti Aging
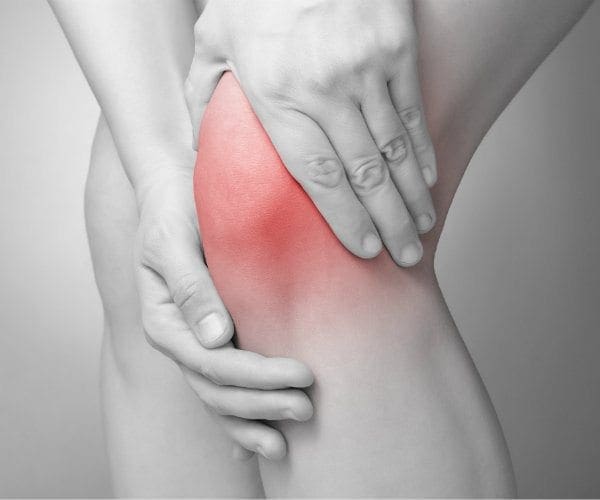
“Keyhole” arthroscopic surgery should rarely be used to repair arthritic knee joints, a panel of international experts says in new clinical guidelines.
Clinical trials have shown that keyhole surgery doesn’t help people suffering from arthritis of the knees any more than mild painkillers, physical therapy or weight loss, said lead author Dr. Reed Siemieniuk. He is a health researcher with McMaster University in Toronto, Canada.
“You can make a pretty strong statement saying that from a long-term perspective, it really doesn’t help at all,” Siemieniuk said. “If they knew all the evidence, almost nobody would choose to have this surgery.”
Keyhole surgery is one of the most common surgical procedures in the world, with more than 2 million performed each year, Siemieniuk said. The United States alone spends about $3 billion a year on the procedure.
The new guidelines — published online May 10 in the BMJ — were issued as part of the journal’s initiative to provide up-to-date recommendations based on the latest evidence. The guidelines make a strong recommendation against arthroscopy for nearly all cases of degenerative knee disease.
This includes osteoarthritis as well as tears of the meniscus, the padding between the two leg bones in the knee, Siemieniuk said.
“With age and with use, the grinding of the two bones together can break down that padding,” he said. “It’s very common to see little rips and tears in that padding in patients with arthritis.”
Siemieniuk and his colleagues noted that a trial published in 2016 showed that surgery was no better than exercise therapy in patients with a meniscus tear.
Despite this and other medical evidence, most guidelines still recommend keyhole surgery for people with meniscus tears, sudden onset of symptoms like pain or swelling, or mild to moderate difficulties with knee movement.
Arthroscopic surgery relies on small incisions through which a tiny camera and miniature instruments are inserted. Doctors can remove or repair damaged tissue without having to cut the knee open.
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons currently advises against performing arthroscopic surgery in patients with full-fledged knee osteoarthritis, said Dr. Kevin Shea, an academy spokesman.
“Most orthopedic surgeons have dramatically reduced arthroscopic surgery in patients with degenerative arthritis,” Shea said. “Most I know have abandoned it over the last 10 to 15 years.”
However, arthroscopic surgery still can help people with joint movement problems caused by meniscus tears who have not developed moderate or severe knee osteoarthritis, said Shea.
Those patients should be treated first with mild painkillers and exercise therapy, but keyhole surgery should remain an option for them, he added. Shea is a professor of orthopedic surgery at the University of Connecticut.
“Not that long ago, I operated on a 67-year-old retired schoolteacher who’s an avid skier,” Shea said. “She had no arthritis in her knee but a huge meniscus tear that kept locking, catching and popping. Not offering treatment to her would not have been fair.”
Under the BMJ guidelines, patients with meniscus tears should be treated with painkillers and physical therapy, as well as weight loss if they are overweight, Siemieniuk said. Knee replacement surgery is the last treatment option, done once degeneration has progressed to the point where all other therapies don’t work.
There is a financial incentive for doctors and hospitals to perform unnecessary keyhole surgeries, but Siemieniuk said these surgeries also might be prompted by the desire to treat a painful medical condition.
“It’s hard to take away one of the options from people when chronic knee pain and arthritis can be very debilitating,” he said. “And there’s an expectation from patients that by the time they see a surgeon, the surgeon is going to have something to be able to offer them.”
Inertia might also play a role. “It’s a lot easier to introduce a new treatment into clinical care than to de-implement one that we later find out doesn’t work,” Siemieniuk said. “That’s what we’re seeing here.”
Keyhole surgery has its downsides. Recovery can last anywhere from 3 days to 6 weeks, Siemieniuk said, and there is a risk of blood clots or infection in the knee.
Patients should go through a shared decision-making process with their surgeon, questioning whether this surgery would truly help them, he said.
The surgery still can be useful to fix torn ligaments or repair damage caused by severe trauma, Siemieniuk said. But in most cases, he said, given the evidence, insurers “may choose not to fund it, which I think would be appropriate.”







