Vertebral Artery Dissection Found During Chiropractic Examination
Acknowledging the subsequent information below,�approximately more than 2 million people are injured in automobile accidents each year and among those incidents, the majority of the people involved are diagnosed with whiplash and/or neck injury by a healthcare professional. When the complex structure of the neck is subjected to trauma, tissue damage and other medical complications may occur. Vertebral artery dissection, or VAD, is characterized by a flap-like tear on the inner lining of the vertebral artery in charge of supplying blood to the brain. After the tear, blood can then enter the arterial wall and form a blood clot, thickening the artery wall and often impeding blood flow.
Through years of experience practicing chiropractic care,�VAD may often follow after trauma to the neck, such as that which occurs in an automobile accident, or whiplash injury. The symptoms of vertebral artery dissection include head and neck pain as well as intermittent or permanent stroke symptoms, such as difficulty speaking, impaired coordination and loss of vision. VAD, or vertebral artery dissection, is generally diagnosed with a contrast-enhanced CT or MRI scan.
Abstract
A 30-year-old woman presented to an emergency department with sudden onset of transient loss of left peripheral vision. Owing to a history of migraine headaches, she was released with a diagnosis of ocular migraine. Two days later, she sought chiropractic care for the chief symptom of severe neck pain. The chiropractor suspected the possibility of vertebral artery dissection (VAD). No manipulation was performed; instead, MR angiography (MRA) of the neck was obtained, which revealed an acute left VAD with early thrombus formation. The patient was placed on aspirin therapy. Repeat MRA of the neck 3?months later revealed resolution of the thrombus, without progression to stroke. This case illustrates the importance for all healthcare providers who see patients with neck pain and headache to be attentive to the symptomatic presentation of possible VAD in progress.
Background
Vertebral artery dissection (VAD) leading to stroke is an uncommon but potentially serious disorder. The incidence of stroke related to the vertebrobasilar system varies from 0.75 to 1.12/100?000 person-years. The pathological process in VAD typically involves dissection of the wall of the artery followed sometime later by thrombus formation, which may cause arterial occlusion or may lead to embolisation, causing occlusion of one or more of the distal branches off the vertebral artery, including the basilar artery, which can be catastrophic. VAD typically occurs in patients who have an inherent, transitory weakness in the arterial wall. In at least 80% of cases, the initial symptoms include neck pain with or without headache.
Many patients with VAD may in the early stages present to chiropractors seeking relief from neck pain and headache, without realising they are experiencing VAD. In many of these cases, the patient later develops a stroke. Until recently, it was assumed that the dissection (and subsequent stroke) was caused by cervical manipulative therapy (CMT). However, while early studies found an association between visits to a chiropractor and subsequent stroke related to VAD, recent data suggest that this relationship is not causal.
This case report is illustrative of the scenario in which a patient with an undiagnosed VAD in evolution consulted a chiropractor for neck pain and headache. After thorough history and examination, the chiropractor suspected VAD and did not perform CMT. Instead, the patient was referred for further evaluation, which detected a VAD in progress. Prompt diagnosis and anticoagulant treatment were thought to have averted progression to a stroke.
Case Presentation
A 30-year-old otherwise healthy woman consulted a chiropractor (DBF), reporting of right-sided neck pain in the suboccipital region. The patient reported that, 3?days previously, she had gone to the local hospital emergency department (ED) because of the sudden onset of loss of left peripheral vision. The visual symptoms interfered with her ability to see through her left eye; this was accompanied by �numbness� in her left eyelid. About 2?weeks prior to this ED visit, she had experienced an episode of acute left-sided neck pain with severe left-sided headache. She also related a history of migraine headache without prodrome. She was released from the ED with a tentative diagnosis of ocular migraine. She had never been previously diagnosed with ocular migraine, nor had she ever experienced any visual disturbances with her previous migraines.
Shortly after the left-sided ocular symptoms resolved, she suddenly developed right-sided neck pain without provocation, for which she sought chiropractic treatment. She also reported a transient episode of right-sided visual disturbance occurring that same day as well. This was described as sudden blurriness that was of short duration and resolved spontaneously earlier in the day of her presentation for chiropractic examination. When she presented for the initial chiropractic examination, she denied current visual disturbance. She said that she was not experiencing any numbness, paraesthesia or motor loss in the upper or lower extremities. She denied ataxia or difficulty with balance. Medical history was remarkable for childbirth 2� months prior to initial presentation. She stated that her migraine headaches were associated with her menstrual cycle. Family history was remarkable for a spontaneous ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm in her older sister, who was about 30?years of age when her aneurysm had occurred.
Investigations
Based on the history of sudden onset of severe upper cervical pain and headache with visual disturbance and ocular numbness, the DC was concerned about the possibility of early VAD. Urgent MR angiography (MRA) of the neck and head, along with MRI of the head, was ordered. No cervical spine examination or manipulation was performed because of the suspicion that the neck pain was related to VAD rather than to a �mechanical� cervical disorder.
MRA of the neck demonstrated that the left vertebral artery was small and irregular in calibre, extending from the C7 level cephalad to C2, consistent with dissection. There was a patent true lumen with a surrounding cuff of T1 hyper-intensity, consistent with dissection with subintimal thrombus within the false lumen (Figures 1 and ?2). MRI of the head with and without contrast, and MRA of the head without contrast, were both unremarkable. Specifically, there was no intracranial extension of dissection or evidence of infarction. MR perfusion of the brain revealed no focal perfusion abnormalities.
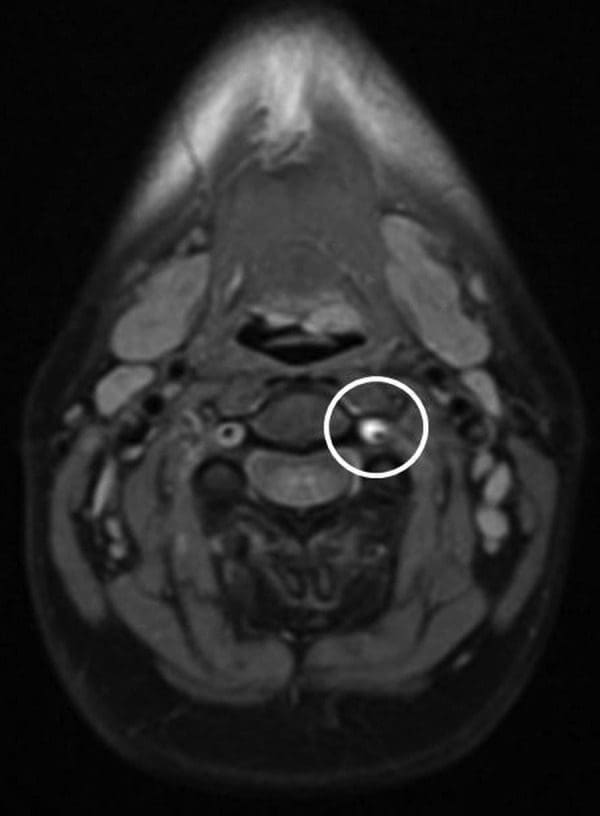
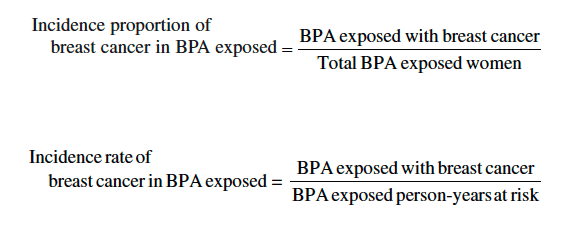
Figure 1: Axial proton density image demonstrates circumferential hyper-intensity surrounding the left cervical vertebral artery (representing the false lumen). Note decreased calibre of true lumen (black flow void) with respect to the right vertebral artery.
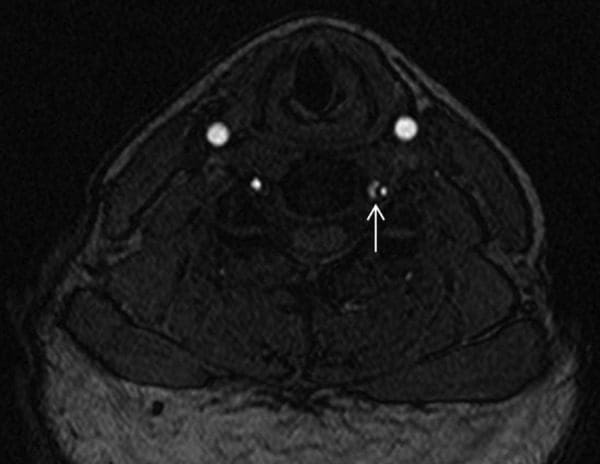
Figure 2: Axial image from three-dimensional time-of-flight MRA demonstrates T1 hypointense dissection flap separating the true lumen (lateral) from the false lumen (medial). MRA, MR angiography.
Differential Diagnosis
The ED released the patient with a tentative diagnosis of ocular migraine, due to her history of migraine headaches. However, the patient stated that the left-sided headache was atypical��like nothing I’ve ever experienced before.� Her previous migraines were associated with her menstrual cycle, but not with any vision changes. She had never been previously diagnosed with ocular migraine. MRA of the cervical region revealed that the patient actually had an acute dissection with thrombus formation in the left vertebral artery.
Treatment
Owing to the potential of impending stroke associated with an acute VAD with thrombus formation, the patient was admitted to the neurology stroke service for close neurological monitoring. During her admission, the patient did not experience any recurrence of neurological deficits and her headaches improved. She was discharged the following day with a diagnosis of left VAD and transient ischaemic attack. She was instructed to avoid vigorous exercise and trauma to the neck. Daily aspirin (325?mg) was prescribed, to be continued for 3�6?months after discharge.
Outcome and Follow-Up
After discharge from the stroke service, the patient had no recurrence of headache or visual disturbances, and her posterior neck pain symptoms resolved. Repeat imaging was performed 3?months after presentation, which demonstrated improved calibre of the cervical left vertebral artery with resolution of the thrombus within the false lumen (Figure 3). Imaging of the intracranial compartment remained normal, without evidence of interval infarction or perfusion asymmetry.
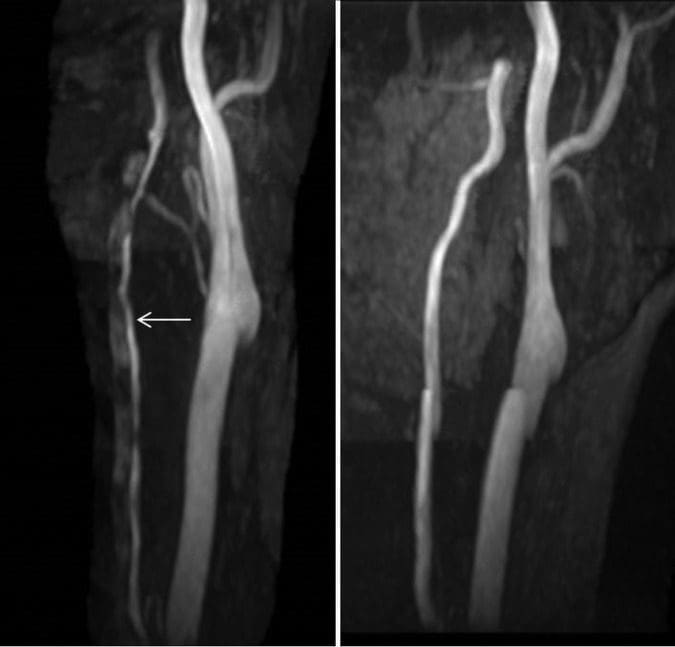
Figure 3: Maximum intensity projection (MIP) images from three-dimensional time-of-flight MRA (left image is at time of presentation and right image is at 3-month follow-up). The initial imaging demonstrates markedly diminutive calibre of the left vertebral artery
Discussion
The pathophysiological process of VAD is thought to start with degeneration of the tissues at the medial-adventitial border of the vertebral artery, leading to the development of microhaematomata within the wall of the artery and, eventually, arterial tear. This can lead to leakage of blood into the arterial wall, causing occlusion of the lumen with subsequent thrombus formation and embolisation, resulting in stroke related to one of the branches of the vertebral artery. This pathological process is similar to that of spontaneous carotid artery dissection, spontaneous thoracic aortic dissection and spontaneous coronary artery dissection. All these conditions tend to occur in younger adults and some have speculated that they may be part of a common inherited pathophysiological process. Notable in this case is the fact that the patient’s older sister had experienced a spontaneous thoracic aortic aneurysm (probably a dissection) at around the same age (30?years) as this patient was when she experienced her VAD.
While the dissection is often sudden, the luminal compromise and complications of VAD can develop gradually leading to variable symptoms and presentation, depending on the stage of the disease. The dissection itself, which develops some time before the onset of neural ischaemia, can cause stimulation of nociceptive receptors within the artery, producing pain that is most commonly felt in the upper cervical spine or head. Only after the pathophysiological process progresses to the point of complete arterial occlusion or thrombus formation with distal embolisation does the full manifestation of infarction occur. However, as illustrated in this case, neurological symptoms can develop early in the process, particularly in cases in which the true lumen demonstrates significant calibre decrease secondary to compression.
There are several interesting aspects to this case. First, it highlights the importance of spine clinicians being alert to the possibility that what may appear to be typical �mechanical� neck pain could be something potentially more sinister, such as VAD. The sudden onset of severe suboccipital pain, with or without headache, and accompanying brainstem related neurological symptoms, should alert the clinician to the possibility of VAD. As in the case reported here, patients with a history of migraine will typically describe the headache as different from their usual migraine. A careful neurological examination should be performed, looking for possible subtle neurological deficits, although the neurological examination will often be negative in the early stages of VAD.
Second, a triad of symptoms raised concern that the patient might be experiencing a VAD in progress. The symptom triad included: (1) spontaneous onset of severe upper cervical pain; (2) severe headache that was distinctly different from the patient’s usual migraine headaches; and (3) brainstem-related neurological symptoms (in the form of transient visual disturbance). Notably, careful neurological examination was negative. Nonetheless, the history was of sufficient concern to prompt immediate investigation.
When VAD is suspected but no frank signs of stroke are present, immediate vascular imaging is indicated. While the optimal imaging evaluation of VAD remains controversial, MRA or CTA are the diagnostic studies of choice given their excellent anatomic delineation and ability to evaluate for complications (including infarction and changes in brain perfusion). Some advocate the use of Doppler ultrasound; however, it has limited utility given the course of the vertebral artery in the neck and limited evaluation of the vertebral arteries cephalad to the origin. Additionally, ultrasound imaging is unlikely to allow visualisation of the dissection itself and thus can be negative in the absence of significant arterial occlusion.
Third, this case is interesting in light of the controversy about cervical manipulation as a potential �cause� of VAD. While case reports have presented patients who have experienced stroke related to VAD after cervical manipulation, and case�control studies have found a statistical association between visits to chiropractors and stroke related to VAD, further investigation has indicated that the association is not causal. Cassidy et al found that a patient who experiences stroke related to VAD is just as likely to have visited a primary care practitioner as to have visited a chiropractor prior to having the stroke. The authors suggested that the most likely explanation for the statistical association between visits to chiropractors and subsequent VAD is that a patient who experiences the initial symptoms of VAD (neck pain with or without headache) seeks medical attention for these symptoms (from a chiropractor, primary care practitioner, or another type of practitioner), then subsequently experiences the stroke, independent of any action taken by the practitioner.
It is important to note that, while there have been reported cases of carotid artery dissection after cervical manipulation, case�control studies have not found this association. The initial symptoms of carotid dissection (neurological symptoms, with neck and head pain less common than VAD), aortic dissection (sudden onset of severe, �tearing� pain) and coronary artery dissection (acute severe chest pain, ventricular fibrillation) are likely to cause the individual to immediately seek ED care, rather than seek chiropractic care. However, VAD has seemingly benign initial symptoms�neck pain and headache�which are symptoms that commonly cause patients to seek out chiropractic care. This may explain why only VAD is associated with visits to chiropractors, while these other types of dissections are not; patients with these other conditions, which have much more alarming symptoms, simply do not present to chiropractors.
This case is a good example of a patient with VAD in progress presenting to a chiropractor for the purpose of seeking relief from neck pain. Fortunately, the chiropractor was astute enough to ascertain that the patient’s symptoms were not suggestive of a �mechanical� cervical spine disorder, and appropriate diagnostic investigation was performed. However, if manipulation had been performed, the VAD that was already in progress from natural history may have been blamed on manipulation, after being detected on MRA imaging. Fortunately, in this case, the chiropractor was able to assist with early detection and treatment, and subsequently a stroke was likely averted.
Learning Points
- A case is presented in which a patient saw a chiropractor, while seeking treatment for neck pain, and the history raised concern for possible vertebral artery dissection (VAD).
- Rather than providing manipulative treatment, the chiropractor referred the patient for advanced imaging, which confirmed the diagnosis of VAD.
- The case illustrates the importance of paying attention to subtle historical factors in patients with VAD.
- It also serves as an example of a patient with a VAD in progress seeking the services of a chiropractor for the initial symptoms of the disorder.
- In this case, early detection of the dissection occurred and the patient had a full recovery without any subsequent stroke.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance of Pierre Cote, DC, PhD, for his assistance with reviewing this manuscript.
Footnotes
Contributors: All the authors acknowledge that they have contributed the following to the submission of this manuscript: conception and design, drafting of the manuscript, critical revisions of the manuscript, literature review and references, and proof reading of the final manuscript.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Information referenced from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic as well as to spinal injuries and conditions. To discuss the subject matter, please feel free to ask Dr. Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Cited by Dr. Alex Jimenez

Additional Topics: Wellness
Overall health and wellness are essential towards maintaining the proper mental and physical balance in the body. From eating a balanced nutrition as well as exercising and participating in physical activities, to sleeping a healthy amount of time on a regular basis, following the best health and wellness tips can ultimately help maintain overall well-being. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables can go a long way towards helping people become healthy.

IMPORTANT TOPIC: EXTRA EXTRA: Treating Sciatica Pain