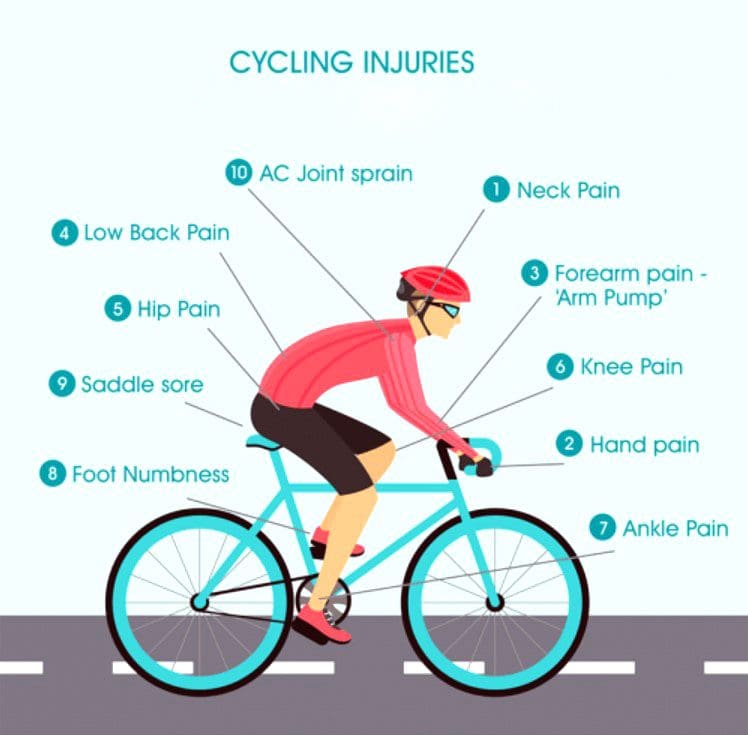
Bicycle riding is a form of transportation and a popular leisure and exercise activity. It helps with brain, heart, and whole body health. Whether recreational or pro cyclist, road or mountain biking, injuries are most often caused by overuse, repetitive strain, or a traumatic fall. If not treated properly by a medical professional, bicycle riding injuries can develop into long-term problems. Chiropractic care, sports massage, and decompression therapy combined with functional medicine can alleviate symptoms, rehabilitate the muscles, release compressed nerves, and restore mobility and function.
Contents
Bicycle Riding Injuries
Long-term cycling can cause muscle fatigue, leading to various injuries.
- Overuse injuries occur when performing the same motion over and over again.
- Musculoskeletal injuries range from sprains, torn ligaments, and tendons to fractures from crashes and falls.
Bicycle Setup
- Not having the correct bike setup for the individual affects posture.
- A seat that is too high causes the hips to rotate, leading to hip, back, and knee pain.
- A seat that is too low causes over-flexion of the knees and pain.
- Improper footwear not set in the right position can lead to pain in the calves and feet.
- Handlebars that are too far forward can cause neck, shoulder, and back problems.
If any discomfort symptoms result from cycling, it’s recommended to get checked by a medical professional as soon as possible. After a correct diagnosis, resolving the issue/s could involve altering the bike setup to reduce the strain on certain body parts. Conversely, a condition could be developing that needs a personalized treatment program consisting of chiropractic care, physical therapy, steroid injections, or, if necessary, surgery.
Injuries
Hips
- Tightness develops at the front of the hip/hip flexors from prolonged sitting and can lead to decreased flexibility and cause irritation of the bursa (fluid-filled sacs between the muscle and bone to reduce friction) at the front of the hip.
- Known as Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome.
- Symptoms at the front and outer side of the hip can travel down the thigh toward the knees.
Checking that the saddle height is correct can help.
Knees
The knee is the most common site for overuse injuries. Common knee overuse injuries include:
- Patellofemoral syndrome
- Patella and quadriceps tendinitis
- Medial plica syndrome
- Iliotibial band friction syndrome
The first four involve discomfort and pain around the kneecap. The last condition results in outer knee pain. Shoe insoles, wedges, and positioning can help prevent some of these injuries.
Feet
- Foot tingling, numbness, burning sensations, or pain on the underside of the foot are common.
- This occurs from pressure on the nerves that travel through the ball of the foot and toward the toes.
- Shoes that are poorly fitted, too tight, or narrow are often the cause.
- Foot numbness can be due to exertional compartment syndrome.
- This comes from increased pressure in the lower leg and results in compressed nerves.
Neck and Back
- Discomfort and pain in the neck result from staying in one riding position for too long.
- Usually, if the handlebars are too low, the rider has to round their back, adding strain to the neck and back.
- Tight hamstrings and/or hip flexor muscles can also cause riders to round/arch the back, causing the neck to be hyperextended.
Doing shoulder shrugs and neck stretches will help relieve neck tension. Regular stretching will create flexibility and make it easier to maintain proper form.
Shoulders
- Shoulder overuse injuries cause muscle weakness, stiffness, swelling, tingling or numbness in the fingers, and pain. Treatments depend on the severity of the condition.
- Shoulder impingement/pinching
- Swelling of soft tissues
- Rotator cuff tears
- Injuries to the ball-and-socket joint tend to be labral tears of the socket lining cartilage or damage to other structures. Damage to the cartilage can lead to arthritis if not treated effectively.
- Falls can cause:
- Minor fractures or dislocation.
- Fractured collarbone/clavicle – must be immobilized for four to six weeks before rehabilitation exercises are started.
- Damage to the joint on the top of the shoulder/acromioclavicular joint or ACJ.
Many of these impact-related injuries can be treated with chiropractic and targeted physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve mobility. However, some cases, like severely displaced fractures, require surgical reconstruction or repair.
Wrists and Forearms
Common wrist overuse injuries include:
- Cyclist’s Palsy
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Intense aching in the forearm can make gripping and ungripping the hands difficult and painful.
- These can be prevented by changing hand positions and alternating the pressure from the inside to the outsides of the palms ensuring the wrists don’t drop below the handlebars.
- Cyclists are recommended to ride with their elbows slightly bent, not with their arms locked or straight. Bent elbows act as shock absorbers when riding over bumps or rough terrain.
Using padded gloves and stretching the hands and wrists before riding can help. Changing the grip on the handlebars takes the stress off of over-used muscles and redistributes pressure to different nerves.
Head Injuries
- Head injuries can range from scrapes, contusions, concussions, or traumatic brain injury.
- Wearing a helmet can reduce the risk of head injury by 85 percent.
Chiropractic Treatment
Chiropractic for cyclists can relieve symptoms, rehabilitate and strengthen muscles, improve posture, and prevent future injuries. Cyclists have also reported enhanced:
- Respiration
- Range of motion
- Heart rate variability
- Muscle strength
- Athletic ability
- Neurocognitive functions such as reaction time and information processing.
Common Bicycle Riding Injuries
References
Mellion, M B. “Common cycling injuries. Management and prevention.” Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 11,1 (1991): 52-70. doi:10.2165/00007256-199111010-00004
Olivier, Jake, and Prudence Creighton. “Bicycle injuries and helmet use: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” International journal of epidemiology vol. 46,1 (2017): 278-292. doi:10.1093/ije/dyw153
Silberman, Marc R. “Bicycling injuries.” Current sports medicine reports vol. 12,5 (2013): 337-45. doi:10.1249/JSR.0b013e3182a4bab7
Virtanen, Kaisa. “Cyclist injuries.” Duodecim; laaketieteellinen aikakauskirja vol. 132,15 (2016): 1352-6.
General Disclaimer, Licenses and Board Certifications *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Bicycle Riding Injuries: El Paso Back Clinic" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those on this site and on our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on naturally restoring health for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card