
Sports Hernia: Core Muscle Injury
A sports hernia is a soft tissue injury that happens in and around the groin area. It is a strain or tear of any soft-tissue muscles, tendons, or ligaments in the lower abdomen or groin area. It usually happens during physical sports activities that require fast, quick, sudden changes of direction and/or intense twisting movements. Despite its name, a sports hernia is not a hernia in the classic sense. The condition’s proper term is athletic pubalgia. However, a sports hernia can lead to an abdominal hernia. The condition can happen to both men and women.
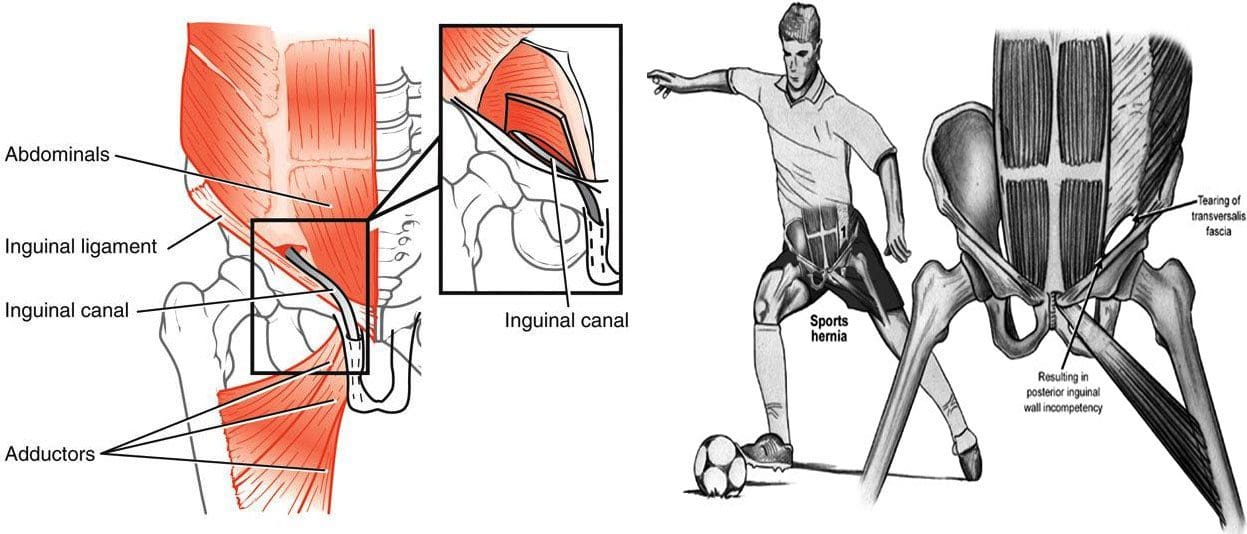
Anatomy
The soft tissues most affected by sports hernias are the oblique muscles in the lower abdomen, along with the tendons that attach the oblique muscles to the pubic bone, are the most at risk. In many cases, the tendons that attach the thigh muscles to the pubic bone or adductors are also stretched or torn.
Core Muscle Injury
A core muscle injury is when the deep layers of the abdominal wall weaken or tear. This can cause nerve irritation and contribute to uncomfortable symptoms of numbness or tingling. The most common causes include:
- Planting the feet and turning or twisting with maximum force.
- Constant repetitive hip and pelvic twisting motions.
- Imbalances between the hip and abdominal muscles can also, over time, cause overuse injuries.
- Weakness in the abdominals and improper or no conditioning can also contribute to injuries.
- Aggressive abdominal exercises can cause and/or aggravate a core muscle injury.
Symptoms
- Chronic groin pain is the primary symptom of a core muscle injury.
- Sharp groin pain with exertion.
- Basic movements like sitting down or getting out of bed can also present with pain or discomfort.
- Pain on one side of the groin.
- Pain or numbness that radiates into the inner thigh.
- Pain when coughing or sneezing.
- Tenderness or pressure on the lower abdominal area.
- Pain decreases with rest.
Diagnosis
A doctor will discuss symptoms and how the injury occurred. They will run a series of strength tests like a sit-up or trunk flex against resistance. If it is a sports hernia, there will be tenderness in the groin or above the pubis, along with discomfort and pain. Further tests will include MRI, ultrasound, or X-rays to rule out hip, low back, or pelvis injuries to confirm a core muscle injury.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Rest
- In the first 7 to 10 days after the injury resting and icing the area is recommended.
- If there is a bulge in the groin, compression or a wrap can help relieve symptoms.
Chiropractic and Physical therapy
- Two weeks after the injury, chiropractic adjustments and physical therapy exercises are recommended to improve strength and flexibility in the abdominal and inner thigh muscles.
- For most cases, 4 to 6 weeks of chiropractic and physical therapy will resolve any pain and allow the individual to return to their exercise or sports activity.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
- A doctor could recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain.
- If the symptoms persist over a prolonged period, a doctor may suggest a cortisone injection.
If the pain comes back when resuming the physical activities, surgery could be needed to repair the torn tissues.
Surgical Treatment
Repairing the torn tissues can be done with a traditional open procedure that involves one long incision or a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure. In an endoscopy, the surgeon makes smaller incisions and uses a small camera, called an endoscope, to see inside the abdomen. The results of traditional and endoscopic procedures are the same. Most individuals can return to sports and physical activities 6 to 12 weeks after surgery.
Body Composition
Muscle Gain
Individuals can’t lose fat forever. At some point, they need to work on developing muscle or work to preserve the muscle that is already present. This requires a different diet and exercise plan than one designed for fat loss. Instead of getting the body into a catabolic state, the body needs to be in an anabolic state where the body builds tissue instead of breaking it down. To build muscle, the body needs resources meaning proper nutrition and sufficient protein intake to increase muscle mass. Maintaining an energy surplus of around 15% is appropriate for developing musculature, meaning a moderately active individual with a BMR of 1,600 calories would want to their intake to about 2,852 calories a day.
References
Hoffman, Jay R et al. “Effect of protein intake on strength, body composition and endocrine changes in strength/power athletes.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition vol. 3,2 12-8. 13 Dec. 2006, doi:10.1186/1550-2783-3-2-12
Larson, Christopher M. “Sports hernia/athletic pubalgia: evaluation and management.” Sports health vol. 6,2 (2014): 139-44. doi:10.1177/1941738114523557
Poor, Alexander E et al. “Core Muscle Injuries in Athletes.” Current sports medicine reports vol. 17,2 (2018): 54-58. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000453
Thorborg, Kristian et al. “Clinical Examination, Diagnostic Imaging, and Testing of Athletes With Groin Pain: An Evidence-Based Approach to Effective Management.” The Journal of orthopedic and sports physical therapy vol. 48,4 (2018): 239-249. doi:10.2519/jospt.2018.7850
Tyler, Timothy F et al. “Groin injuries in sports medicine.” Sports health vol. 2,3 (2010): 231-6. doi:10.1177/1941738110366820





